|
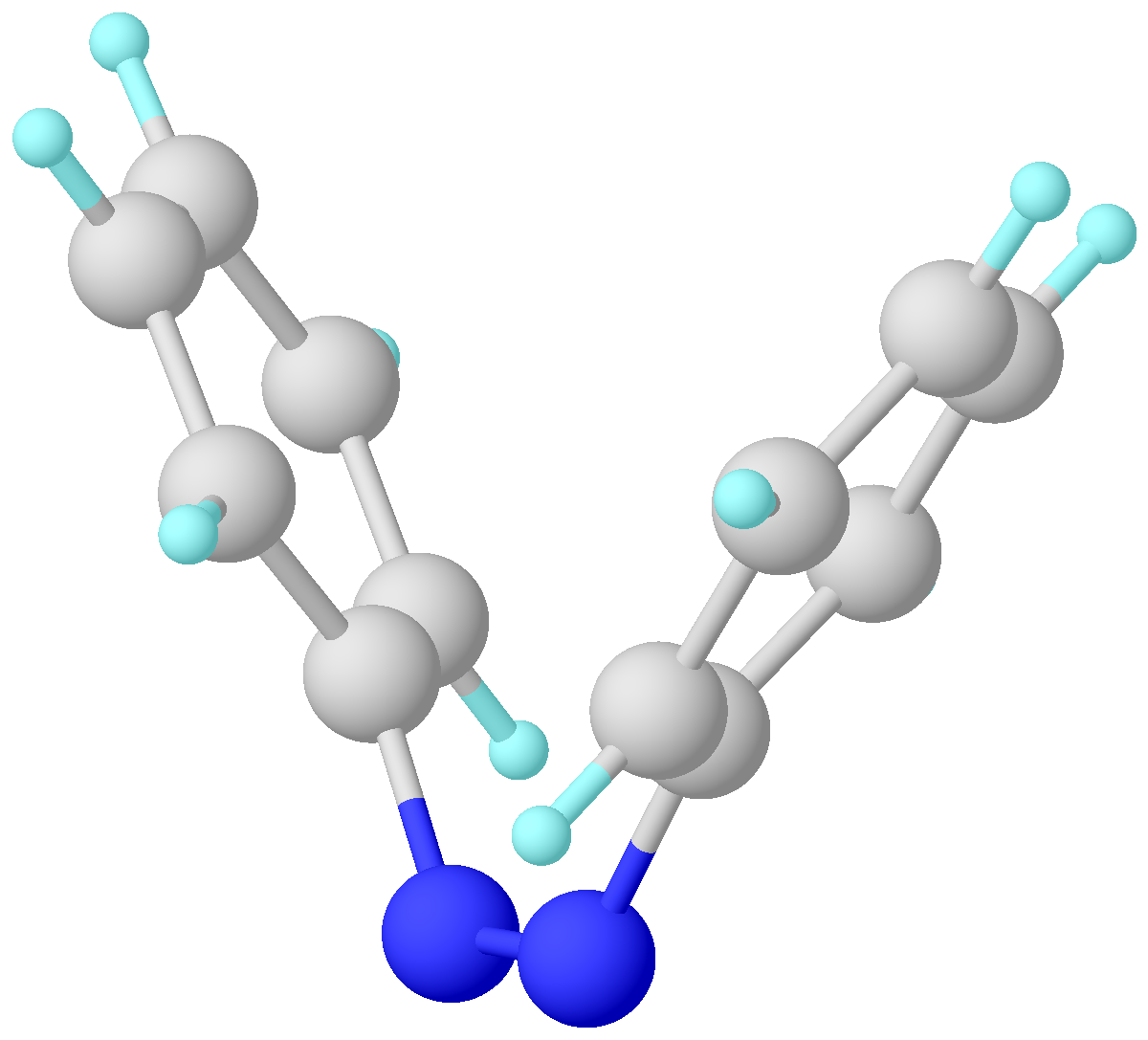
Azobenzene Isomerization
Azobenzene is a photoswitchable chemical compound composed of two phenyl rings linked by a N=N double bond. It is the simplest example of an aryl azo compound. The term 'azobenzene' or simply 'azo' is often used to refer to a wide class of similar compounds. These azo compounds are considered as derivatives of diazene (diimide), and are sometimes referred to as 'diazenes'. The diazenes absorb light strongly and are common dyes. Structure and synthesis ''trans''-Azobenzene is planar. The N-N distance is 1.189 Å. ''cis''-Azobenzene is nonplanar with a C-N=N-C dihedral angle of 173.5°. The N-N distance is 1.251 Å. Azobenzene was first described by Eilhard Mitscherlich in 1834. Yellowish-red crystalline flakes of azobenzene were obtained in 1856. Its original preparation is similar to the modern one. According to the 1856 method, nitrobenzene is reduced by iron filings in the presence of acetic acid. In the modern synthesis, zinc is the reductant in the presence of a base. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debye
The debye (symbol: D) (; ) is a CGS unit (a non- SI metric unit) of electric dipole momentTwo equal and opposite charges separated by some distance constitute an electric dipole. This dipole possesses an electric dipole moment whose value is given as charge times length of separation, it is a vector whose direction is in the direction of the unit vector of the position vector of the positive charge w.r.t negative charge: :p = ''q''r. named in honour of the physicist Peter J. W. Debye. It is defined as statcoulomb- centimeters.The statcoulomb is also known as the franklin or electrostatic unit of charge. :1 statC = 1 Fr = 1 esu = 1 cm3/2⋅g1/2⋅s−1. Historically the debye was defined as the dipole moment resulting from two charges of opposite sign but an equal magnitude of 10−10 statcoulomb10−10 statcoulomb corresponds to approximately 0.2083 units of elementary charge. (generally called e.s.u. (electrostatic unit) in older scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Process Research & Development
''Organic Process Research & Development'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published since 1997 by the American Chemical Society. Its publication frequency switched from bimonthly to monthly in 2012. It is indexed in Chemical Abstracts Service, Scopus, EBSCOhost, British Library, and Web of Science. The current editor-in-chief is Kai Rossen. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2017 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 3.584. References External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:Organic Process Research and Development American Chemical Society academic journals Monthly journals Publications established in 1997 English-language journals Pharmaceutical sciences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromatic Para Position
Arene substitution patterns are part of organic chemistry IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry, IUPAC nomenclature and pinpoint the position of substituents other than hydrogen in relation to each other on an aromatic hydrocarbon. ''Ortho'', ''meta'', and ''para'' substitution * In ''ortho''-substitution, two substituents occupy positions next to each other, which may be numbered 1 and 2. In the diagram, these positions are marked R and ''ortho''. * In ''meta''-substitution the substituents occupy positions 1 and 3 (corresponding to R and ''meta'' in the diagram). * In ''para''-substitution, the substituents occupy the opposite ends (positions 1 and 4, corresponding to R and ''para'' in the diagram). The toluidines serve as an example for these three types of substitution. Synthesis Electron donating groups, for example amino, hydroxyl, alkyl group, alkyl, and phenyl group, phenyl groups tend to be ''ortho''/''para''-directors, and electron withdrawing groups such as nitro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arene Substitution Patterns
Arene substitution patterns are part of organic chemistry IUPAC nomenclature and pinpoint the position of substituents other than hydrogen in relation to each other on an aromatic hydrocarbon. ''Ortho'', ''meta'', and ''para'' substitution * In ''ortho''-substitution, two substituents occupy positions next to each other, which may be numbered 1 and 2. In the diagram, these positions are marked R and ''ortho''. * In ''meta''-substitution the substituents occupy positions 1 and 3 (corresponding to R and ''meta'' in the diagram). * In ''para''-substitution, the substituents occupy the opposite ends (positions 1 and 4, corresponding to R and ''para'' in the diagram). The toluidines serve as an example for these three types of substitution. Synthesis Electron donating groups, for example amino, hydroxyl, alkyl, and phenyl groups tend to be ''ortho''/''para''-directors, and electron withdrawing groups such as nitro, nitrile, and ketone groups, tend to be ''meta''-directors. Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack the energy to ionize atoms, it can cause chemical reactions and causes many substances to glow or fluoresce. Consequently, the chemical and biological effects of UV are greater than simple heating effects, and many practical applications of UV radiation derive from its interactions with organic molecules. Short-wave ultraviolet light damages DNA and sterilizes surfaces with which it comes into contac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
(E)-Stilbene
(''E'')-Stilbene, commonly known as ''trans''-stilbene, is an organic compound represented by the condensed structural formula CHCH=CHCH. Classified as a diarylethene, it features a central ethylene moiety with one phenyl group substituent on each end of the carbon–carbon double bond. It has an (''E'') stereochemistry, meaning that the phenyl groups are located on opposite sides of the double bond, the opposite of its geometric isomer, ''cis''-stilbene. ''Trans''-stilbene occurs as a white crystalline solid at room temperature and is highly soluble in organic solvents. It can be converted to ''cis''-stilbene photochemically, and further reacted to produce phenanthrene. Stilbene was discovered in 1843 by the French chemist Auguste Laurent. The name "stilbene" is derived from the Greek word ''στίλβω'' (''stilbo''), which means "I shine", on account of the lustrous appearance of the compound. Isomers Stilbene exists as two possible stereoisomers. One is ''trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoswitch
A photoswitch is a type of molecule that can change its structural geometry and chemical properties upon irradiation with electromagnetic radiation. Although often used interchangeably with the term molecular machine, a switch does not perform work upon a change in its shape whereas a machine does. However, photochromic compounds are the necessary building blocks for light driven molecular motors and machines. Upon irradiation with light, photoisomerization about double bonds in the molecule can lead to changes in the cis- or trans- configuration. These photochromic molecules are being considered for a range of applications. Chemical structures and properties A photochromic compound can change its configuration or structure upon irradiation with light. Several examples of photochromic compounds include: azobenzene, spiropyran, merocyanine, diarylethene, spirooxazine, fulgide, hydrazone, nobormadiene, thioindigo, acrylamide-azobenzene-quaternary ammonia, donor-acceptor Stenhous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans Isomer
Trans- is a Latin prefix meaning "across", "beyond", or "on the other side of". Used alone, trans may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media * Trans (festival), a former festival in Belfast, Northern Ireland, United Kingdom * ''Trans'' (film), a 1998 American film * Trans Corp, an Indonesian business unit of CT Corp in the fields of media, lifestyle, and entertainment ** Trans Media, a media subsidiary of Trans Corp *** Trans TV, an Indonesian television network *** Trans7, an Indonesian television network Literature * '' Trans: Gender and Race in an Age of Unsettled Identities'', a 2016 book by Rogers Brubaker * '' Trans: When Ideology Meets Reality'', a 2021 book by Helen Joyce Music * ''Trans'' (album), by Neil Young * ''Trans'' (Stockhausen), a 1971 orchestral composition Places * Trans, Mayenne, France, a commune * Trans, Switzerland, a village Science and technology * Trans effect in inorganic chemistry, the increased lability of ligands that are trans to certain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoisomerization
In chemistry, photoisomerization is a form of isomerization induced by photoexcitation. Both reversible and irreversible photoisomerizations are known for photoswitchable compounds. The term "photoisomerization" usually, however, refers to a reversible process. Applications Photoisomerization of the compound retinal in the eye allows for vision. Photoisomerizable substrates have been put to practical use, for instance, in pigments for rewritable CDs, DVDs, and 3D optical data storage solutions. In addition, interest in photoisomerizable molecules has been aimed at molecular devices, such as molecular switches, molecular motors, and molecular electronics. Another class of device that uses the photoisomerization process is as an additive in liquid crystals to change their linear and nonlinear properties. Due to the photoisomerization is possible to induce a molecular reorientation in the liquid crystal bulk, which is used in holography, as spatial filter or optical switchi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrazobenzene
Hydrazobenzene (1,2-diphenylhydrazine) is an aromatic organic compound consisting of two aniline groups joined via their nitrogen atoms. It is an important industrial chemical used in the manufacture of dyes, pharmaceuticals, and hydrogen peroxide Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3% .... References {{aromatic-compound-stub Hydrazines Anilines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azoxybenzene
Azoxybenzene is organic compound with the formula C6H5N(O)NC6H5. It is a yellow, low-melting solid. The molecule has a planar C2N2O core. The N-N and N-O bond lengths are nearly the same at 1.23 Å. Preparation It can be prepared by partial reduction of nitrobenzene. This reaction is proposed to proceed via the intermediacy of phenylhydroxylamine and nitrosobenzene: :PhNHOH + PhNO → PhN(O)NPh + H2O Another option is the oxidation of aniline by hydrogen peroxide Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3% ..., in acetonitrile at 50 ºC. In this reaction, the pH should be kept around 8, to activate the hydrogen peroxide and avoid too much oxygen evolution at the same time. First, the acetonitrile is oxidized, forming an imine hydroperoxide. Then, this intermediate o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |