|
Azaris
Azaris, also known as Azeris, Old Azeris or Adharis, were an Iranian people who spoke Old Azeri. They were the inhabitants of the Azerbaijan region of northwestern Iran, and resided there prior to the Turkification of the region during the Seljuk Empire. Some researchers believe that modern Tats, specifically Harzdani and Karingani speakers, are descendants of ancient Azaris. History Their name derived from their native region. According to the ''Encyclopaedia of Islam'', the name of the region was Āturpātākān in Middle Persian, Ādharbādhagān or Ādharbāyagān (آذربادگان/آذرآبادگان) in older modern Persian, and Āzerbāydjān/Āzarbāydjān in modern Persian. Many believed it derived from Atropat, the founder of Atropatene. The name Atropat in Old Persian became Adharbad in Middle Persian and was influenced by Zoroastrianism. Due to the historic significance of Zoroastrianism in the region, many believed that Zoroaster was Azari, although modern s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Peoples
Iranian peoples, or Iranic peoples, are the collective ethnolinguistic groups who are identified chiefly by their native usage of any of the Iranian languages, which are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages within the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. The Proto-Iranian language, Proto-Iranians are believed to have emerged as a separate branch of the Indo-Iranians in Central Asia around the mid-2nd millennium BC. At their peak of expansion in the mid-1st millennium BC, the territory of the Iranian peoples stretched across the entire Eurasian Steppe; from the Danube, Danubian Plains in the west to the Ordos Plateau in the east and the Iranian Plateau in the south.: "From the first millennium b.c., we have abundant historical, archaeological and linguistic sources for the location of the territory inhabited by the Iranian peoples. In this period the territory of the northern Iranians, they being equestrian nomads, extended over the whole zone of the ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Azeri
Old Azeri (آذری, ''Āzāri''; also spelled Adhari, Azeri or Azari) is the extinct Iranian language that was once spoken in the northwestern Iranian historic region of Azerbaijan (Iranian Azerbaijan) before the Turkification of the region. Some linguists believe the southern Tati varieties of Iranian Azerbaijan around Takestan such as the Harzandi and Karingani dialects to be remnants of Old Azeri. Along with Tat dialects, Old Azeri is known to have strong affinities with Talysh and Zaza language and Zaza and Talysh are considered to be remnants of Old Azeri. Iranologist linguist Henning demonstrated that Harzandi has many common linguistic features with both Talysh and Zaza and positioned Harzandi between the Talysh and Zaza. Old Azeri was the dominant language in Azerbaijan before it was replaced by Azerbaijani, which is a Turkic language. Initial studies Ahmad Kasravi, a preeminent Iranian Azeri scholar and linguist, was the first scholar who examined the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aras (river)
The Aras is a transboundary river in the Caucasus. It rises in eastern Turkey and flows along the borders between Turkey and Armenia, between Turkey and the Nakhchivan exclave of Azerbaijan, between Iran and both Azerbaijan and Armenia, and, finally, through Azerbaijan where it flows into the Kura river as a right tributary. It drains the south side of the Lesser Caucasus Mountains, while the Kura drains the north side of the Lesser Caucasus. The river's total length is and its watershed covers an area of . The Aras is one of the longest rivers in the Caucasus. Names In classical antiquity, the river was known to the Greeks as Araxes (). Its modern Armenian name is ''Arax'' or ''Araks'' (). Historically, it was called (, in modern pronunciation) by Armenians and its Old Georgian name is ''Rakhsi'' (). In Azerbaijani, the river's name is ''Araz''. In Persian, Kurdish and Turkish its name is (''Aras''). Geography The Aras is supported by the Kocagün stream, Dallı s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the List of largest empires#Timeline of largest empires to date, largest empire by that point in history, spanning a total of . The empire spanned from the Balkans and ancient Egypt, Egypt in the west, most of West Asia, the majority of Central Asia to the northeast, and the Indus Basin, Indus Valley of South Asia to the southeast. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Medes, Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognised for its imposition of a succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median Kingdom
Media (Old Persian: ''Māda''; Ancient Greek, Greek: ''Mēdía''; Akkadian language, Akkadian: ''wikt:𐎶𐎠𐎭#Descendants, Mādāya'') was a political entity centered in Ecbatana that existed from the 7th century BCE until the mid-6th century BCE and is believed to have dominated a significant portion of the Iranian plateau, preceding the powerful Achaemenid Empire. The frequent interference of the Assyrians in the Zagros Mountains, Zagros region led to the process of unifying the Median tribes. By 612 BCE, the Medes became strong enough to overthrow the declining Assyrian empire in alliance with the Babylonians. However, contemporary scholarship tends to be skeptical about the existence of a united Median kingdom or state, at least for most of the 7th century BCE. According to classical historiography, Media emerged as one major power of the ancient Near East after the collapse of Assyria. Under Cyaxares (r. 625–585 BCE), the kingdom's borders were expanded to the east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medes
The Medes were an Iron Age Iranian peoples, Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media (region), Media between western Iran, western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, they occupied the mountainous region of northwestern Iran and the northeastern and eastern region of Mesopotamia in the vicinity of Ecbatana (present-day Hamadan). Their consolidation in Iran is believed to have occurred during the 8th century BC. In the 7th century BC, all of western Iran and some other territories were under Median rule, but their precise geographic extent remains unknown. Although widely recognized as playing an important role in the history of the ancient Near East, the Medes left no written records to reconstruct their history. Knowledge of the Medes comes only from foreign sources such as the Assyrians, Babylonians, Armenians and Ancient Greece, Greeks, as well as a few Iranian archaeological sites, which are believed to have been occu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythians
The Scythians ( or ) or Scyths (, but note Scytho- () in composition) and sometimes also referred to as the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranian Eurasian nomads, equestrian nomadic people who had migrated during the 9th to 8th centuries BC from Central Asia to the Pontic Steppe in modern-day Ukraine and Southern Russia, where they remained established from the 7th century BC until the 3rd century BC. Skilled in Horses in warfare, mounted warfare, the Scythians replaced the Agathyrsi and the Cimmerians as the dominant power on the western Eurasian Steppe in the 8th century BC. In the 7th century BC, the Scythians crossed the Caucasus Mountains and frequently raided West Asia along with the Cimmerians. After being expelled from West Asia by the Medes, the Scythians retreated back into the Pontic Steppe in the 6th century BC, and were later conquered by the Sarmatians in the 3rd to 2nd centuries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matiene
Matiene was the name of a kingdom in northwestern Iran on the lands of the earlier kingdom of the Mannae. Ancient historians including Strabo, Ptolemy, Herodotus, Polybius, and Pliny mention names such as Mantiane, Martiane, Matiana, Matiani, Matiene, Martuni to designate a region located to the northwest of Media." Etymology The name Matiene may be related to Mitanni, the name of a state some 800 years earlier, which was founded by an Indo-Aryan ruling class governing the Hurrian population. The name Matiene was applied also to the neighboring Lake Matianus (Lake Urmia) located immediately to the east of the Matieni people. The Iranian root "Mati-" meaning "to tower, to stand out" (from the same Indo-European root that gives us the word "mountain") might explain the name. History The Mannaeans who probably spoke a Hurro-Urartian language, were subdued by the Scytho- Kimmerians during the seventh and eighth centuries BC and assimilated by Matienes. Matiene was ultimate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Plateau
The Iranian plateau or Persian plateau is a geological feature spanning parts of the Caucasus, Central Asia, South Asia, and West Asia. It makes up part of the Eurasian plate, and is wedged between the Arabian plate and the Indian plate. The plateau is situated between the Zagros Mountains to the west, the Caspian Sea and the Köpet Dag to the north, the Armenian Highlands and the Caucasus Mountains to the northwest, the Strait of Hormuz and the Persian Gulf to the south, and the Indian subcontinent to the southeast. As a historical region, it includes Parthia, Media, Persis, and some of the previous territories of Greater Iran."Old Iranian Online" , University of Texas College of Liberal Arts (retrieved 10 February 2007) The Zagros form the plateau's western boundary, and its eastern slopes may also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saqqez
Saqqez (; ; ) is a city in the Central District (Saqqez County), Central District of Saqqez County, Kurdistan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district. Etymology The name Saqqez derives from the Scythian languages, Scythian word "''Eskit''" and then "''Sakez''". Before that, it was Izirtu, the capital of Mannaeans. In some historical sources it has been mentioned that the name of the city is derived from the name of powerful Median ruler Cyaxares (reigned 625–585 BC), who turned the empire into a regional power, but other historians believe that the name of the city is derived from ''Sakez'' and is attributed to the Scythians who settled in the city during the reign of Cyaxares. History Saqqez's history goes back to the seventh millennium BC. Based on historical ruins and Antiques which have been found in Saqqez, like the historical treasures of Ziwiye hoard in the Ziwiyeh Castle, experts like Roman Ghirshman believe that the modern ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
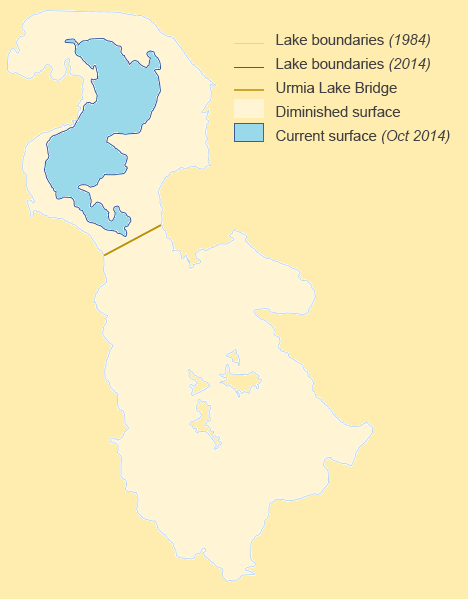
Lake Urmia
Lake Urmia is an endorheic salt lake in Iran. The lake is located between the provinces of East Azerbaijan and West Azerbaijan in Iran, and west of the southern portion of the Caspian Sea. At its greatest extent, it was the largest lake in the Middle East. It is the sixth-largest saltwater lake on Earth, with a surface area of approximately , a length of , a width of , and a maximum depth of . By late 2017, the lake had shrunk to 10% of its former size (and 1/60 of water volume in 1998) due to persistent general drought in Iran, but also the damming of the local rivers that flow into it, and the pumping of groundwater from the surrounding area. This dry spell was broken in 2019 and the lake is now filling up once again, due to both increased rain and water diversion from the Zab River under the Urmia Lake Research Programme. Lake Urmia, along with its approximately 102 (former) islands, is protected as a national park by the Iranian Department of Environment. Names and et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannaeans
Mannaea (, sometimes written as Mannea; Akkadian: ''Mannai'', Biblical Hebrew: ''Minni'', (מנּי)) was an ancient kingdom located in northwestern Iran, south of Lake Urmia, around the 10th to 7th centuries BCE. It neighbored Assyria and Urartu, as well as other small buffer states between the two, such as Musasir and Zikirta. Etymology of name The name of Mannaea and its earliest recorded ruler Udaki were first mentioned in an inscription from the 30th year of the rule of Shalmaneser III (828 BC). The Assyrians usually called Manna the "land of the Mannites", Manash, while the Urartians called it the land of Manna. Describing the march of Salmanasar III in the 16th year (843 BC), it was reported that the king reached the land of Munna, occupying the interior of Zamua. However, the chronicle does not mention any march or taxation on the state of Mannaea. It is possible that the Assyrians either failed to conquer Mannaea, or advanced only to the border of Mannaea, and then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |