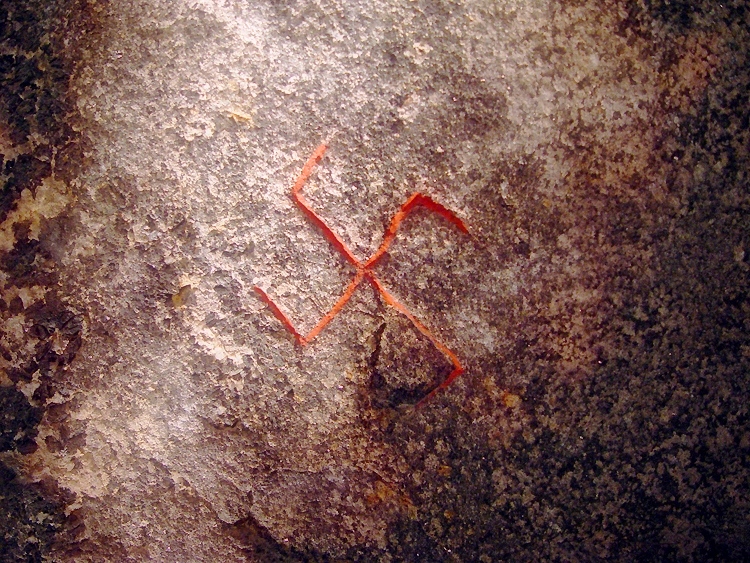|
Ayodhya Inscription Of Dhana
__NOTOC__ Ayodhya Inscription of Dhana is a stone inscription related to a Hindu Deva king named Dhana or Dhana–deva of the 1st-century BCE or 1st century CE. He ruled from the city of Ayodhya, Kosala, in India. His name is found in ancient coins and the inscription. According to P. L. Gupta, he was among the fifteen kings who ruled from Ayodhya between 130 BCE and 158 CE, and whose coins have been found: Muladeva, Vayudeva, Vishakadeva, Dhanadeva, Ajavarman, Sanghamitra, Vijayamitra, Satyamitra, Devamitra and Aryamitra. D.C. Sircar dates the inscription to 1st-century CE based on the epigraphical evidence. The paleography of the inscription is identical to that of the Northern Satraps in Mathura, which gives a 1st century CE date. The damaged inscription is notable for its mention of general Pushyamitra and his descendant ''Dhana–'', his use of Vedic Ashvamedha horse to assert the range of his empire, and the building of a temple shrine. Sunga inscription from Ayodhya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion, diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age#South Asia, Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a lingua franca, link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting effect on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Indo-Aryan languages# ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guru Nanak
Gurū Nānak (15 April 1469 – 22 September 1539; Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਨਾਨਕ; pronunciation: , ), also known as ('Father Nanak'), was an Indian spiritual teacher, mystic and poet, who is regarded as the founder of Sikhism and is the first of the ten Sikh Gurus. Nanak is said to have travelled far and wide across Asia teaching people the message of '' Ik Onkar'' (), who dwells in every one of his creations and constitutes the eternal Truth. With this concept, he would set up a unique spiritual, social, and political platform based on equality, fraternal love, goodness, and virtue. Nanak's words are registered in the form of 974 poetic hymns, or '' shabda'', in the holy religious scripture of Sikhism, the Guru Granth Sahib, with some of the major prayers being the '' Japji Sahib'' (; ''ji'' and ''sahib'' are suffixes signifying respect); the '' Asa di Var'' ('Ballad of Hope'); and the '' Sidh Gosht'' ('Discussion with the Siddhas'). It is part of Sikh religious b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit Inscriptions In India
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting effect on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Old Indo-Aryan language varieties. The most archaic of these is the Vedic Sanskrit found in the Rigveda, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st-century Inscriptions
File:1st century collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Jesus is crucified by Roman authorities in Judaea (17th century painting). Four different men ( Galba, Otho, Vitellius, and Vespasian) claim the title of Emperor within the span of a year; The Great Fire of Rome (18th-century painting) sees the destruction of two-thirds of the city, precipitating the empire's first persecution against Christians, who are blamed for the disaster; The Roman Colosseum is built and holds its inaugural games; Roman forces besiege Jerusalem during the First Jewish–Roman War (19th-century painting); The Trưng sisters lead a rebellion against the Chinese Han dynasty (anachronistic depiction); Boudica, queen of the British Iceni leads a rebellion against Rome (19th-century statue); Knife-shaped coin of the Xin dynasty., 335px rect 30 30 737 1077 Crucifixion of Jesus rect 767 30 1815 1077 Year of the Four Emperors rect 1846 30 3223 1077 Great Fire of Rome rect 30 1108 1106 2155 Bou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st-century BC Inscriptions
File:1st century collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Jesus is crucified by Roman authorities in Judaea (17th century painting). Four different men (Galba, Otho, Vitellius, and Vespasian) claim the title of Emperor within the span of a year; The Great Fire of Rome (18th-century painting) sees the destruction of two-thirds of the city, precipitating the empire's first persecution against Christians, who are blamed for the disaster; The Roman Colosseum is built and holds its inaugural games; Roman forces besiege Jerusalem during the First Jewish–Roman War (19th-century painting); The Trưng sisters lead a rebellion against the Chinese Han dynasty (anachronistic depiction); Boudica, queen of the British Iceni leads a rebellion against Rome (19th-century statue); Knife-shaped coin of the Xin dynasty., 335px rect 30 30 737 1077 Crucifixion of Jesus rect 767 30 1815 1077 Year of the Four Emperors rect 1846 30 3223 1077 Great Fire of Rome rect 30 1108 1106 2155 Boudican revolt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sects Of Sikhism
Sikh sects, denominations, traditions, movements, sub-traditions, also known as ''Sampradaya, sampardai'' (Gurmukhi: ਸੰਪਰਦਾ; ''saparadā'') in the Punjabi language, are sub-traditions within Sikhism that with different approaches to practicing the religion. ''Sampradas'' believe in one God in Sikhism, God, typically rejecting both idol worship and castes. Different interpretations have emerged over time, some of which have a living teacher as the leader. The major traditions in Sikhism, says Harjot Oberoi, have included Udasi, Nirmala (sect), Nirmala, Nanakpanthi, Khalsa, Sahajdhari, Namdhari Kuka, Nirankari, and Sarvaria. During the persecution of Sikhs by Mughals, several splinter groups emerged, such as the Mina (Sikhism), Minas and Ramraiyas, during the period between the death of Guru Har Krishan and the establishment of Guru Tegh Bahadur as the ninth Sikh Guru. These sects have had considerable differences. Some of these sects were financially and administrative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naneghat
Naneghat, also referred to as Nanaghat or Nana Ghat (IAST: Nānāghaṭ), is a mountain pass in the Western Ghats range between the Konkan coast and the ancient town of Junnar in the Deccan plateau. The pass is about north of Pune and about east from Mumbai, Maharashtra, India. It was a part of an ancient trading route, and is famous for a major cave with Sanskrit inscriptions in Brahmi script and Middle Indo-Aryan dialect. These inscriptions have been dated between the 2nd and the 1st century BCE, and attributed to the Satavahana dynasty era. The inscriptions are notable for linking the Vedic and Hinduism deities, mentioning some Vedic srauta rituals and of names that provide historical information about the ancient Satavahanas. The inscriptions present the world's oldest numeration symbols for "2, 4, 6, 7, and 9" that resemble modern era numerals, more closely those found in modern Nagari and Hindu-Arabic script. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya (Sanskrit: [Help:IPA/Sanskrit, t̪͡ɕɐn̪d̪ɾɐgupt̪ɐ mɐʊɾjɐ]) (reigned 320 BCE – c. 298 BCE) was the founder and the first emperor of the Maurya Empire, based in Magadha (present-day Bihar) in the Indian subcontinent. His rise to power began in the period of unrest and local warfare that arose after Alexander the Great's Indian campaign of Alexander the Great, Indian campaign and early death in 323 BCE, although the exact chronology and sequence of events remains subject to debate among historians. He started a war against the unpopular Nanda dynasty in Magadha on the Ganges, Ganges Valley, defeated them and established his own dynasty. In addition, he raised an army to resist the Greeks, defeated them, and took control of the eastern Indus Valley. His conquest of Magadha is generally dated to ca. 322–319 BCE, and his expansion to Punjab subsequently at ca. 317–312 BCE, but some scholars have speculated that he might have initially con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pushyamitra Shunga
Pushyamitra Shunga ( IAST: ; reigned ), also known as Pushpamitra Shunga ( IAST: ) was the founder and the first ruler of the Shunga Empire which he established to succeed the Maurya Empire. His original name was Puṣpaka or Puṣpamitra and the confusion between Puṣyamitra and Puṣpamitra arose because of the erroneous readings of 'p' and 'y' in the manuscripts. Pushyamitra is recorded to have performed the Ashvamedha ritual to legitimize his right to rule. Inscriptions of the Shungas have been found as far as the Ayodhya (the Dhanadeva–Ayodhya inscription), and the '' Divyavadana'' mentions that his empire stretched as far as Sakala (now Sialkot) in Punjab region, now in Pakistan. Though Buddhist texts claim that Pushyamitra persecuted Buddhists, past and contemporary scholars have rejected these claims. Foundation of the Shunga Empire Pushyamitra Shunga founded the Shunga Empire after assassinating the last Mauryan emperor Brihadratha Maurya. Subsequently, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swastika
The swastika (卐 or 卍, ) is a symbol used in various Eurasian religions and cultures, as well as a few Indigenous peoples of Africa, African and Indigenous peoples of the Americas, American cultures. In the Western world, it is widely recognized as a symbol of the German Nazi Party who Cultural appropriation, appropriated it for their party insignia starting in the early 20th century. The appropriation continues with its use by Neo-Nazism, neo-Nazis around the world. The swastika was and continues to be used as a symbol of divinity and spirituality in Indian religions, including Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism. It generally takes the form of a cross, the arms of which are of equal length and perpendicular to the adjacent arms, each bent midway at a right angle. The word ''swastika'' comes from , meaning 'conducive to well-being'. In Hinduism, the right-facing symbol (clockwise) () is called , symbolizing ('sun'), prosperity and good luck, while the left-facing symbol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pushyamitra Epigraph
Pushyamitra Shunga (IAST: ; reigned ), also known as Pushpamitra Shunga (IAST: ) was the founder and the first ruler of the Shunga Empire which he established to succeed the Maurya Empire. His original name was Puṣpaka or Puṣpamitra and the confusion between Puṣyamitra and Puṣpamitra arose because of the erroneous readings of 'p' and 'y' in the manuscripts. Pushyamitra is recorded to have performed the Ashvamedha ritual to legitimize his right to rule. Inscriptions of the Shungas have been found as far as the Ayodhya (the Dhanadeva–Ayodhya inscription), and the ''Divyavadana'' mentions that his empire stretched as far as Sakala (now Sialkot) in Punjab region, now in Pakistan. Though Buddhist texts claim that Pushyamitra persecuted Buddhists, past and contemporary scholars have rejected these claims. Foundation of the Shunga Empire Pushyamitra Shunga founded the Shunga Empire after assassinating the last Mauryan emperor Brihadratha Maurya. Subsequently, he drove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |