|
Axial Turbine
In turbomachinery, an axial turbine is a turbine in which the flow of the working fluid is parallel to the shaft, as opposed to radial turbines, where the fluid runs around a shaft, as in a watermill. An axial turbine has a similar construction as an axial compressor, but it operates in the reverse, converting flow of the fluid into rotating mechanical energy. A set of static guide vanes or nozzle vanes accelerates and adds swirl to the fluid and directs it to the next row of turbine blades mounted on a turbine rotor. Stage velocity triangle The angles in the absolute system are noted by alpha () and the angles in the relative system are noted by beta (). Axial and tangential components of both absolute and relative velocities are shown in the figure. Static and stagnation values of pressure and enthalpy in the absolute and relative systems are also shown. It is often assumed that the axial velocity component remains constant through the stage. From this condition we get: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbomachinery
Turbomachinery, in mechanical engineering, describes machines that transfer energy between a Rotor (electric), rotor and a fluid, including both turbines and gas compressor, compressors. While a turbine transfers energy from a fluid to a rotor, a compressor transfers energy from a rotor to a fluid.Logan, Earl. "Handbook of turbomachinery". 1995. Marcel Deckker.Vandad Talimi (Original author unknown). "Mechanical Equipment and Systems". 2013. Memorial University of Newfoundland. http://www.engr.mun.ca/~yuri/Courses/MechanicalSystems/Turbomachinery.pdf It is an important application of fluid mechanics. These two types of machines are governed by the same basic relationships including Newton's laws of motion, Newton's second law of motion and Euler's pump and turbine equation for compressible fluids. Centrifugal pumps are also turbomachines that transfer energy from a rotor to a fluid, usually a liquid, while turbines and compressors usually work with a gas. History The first tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
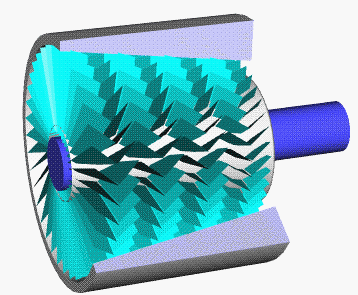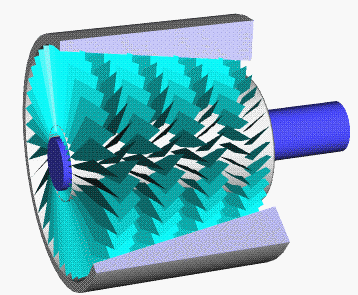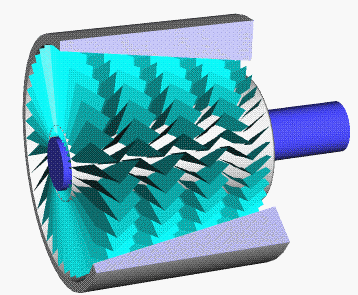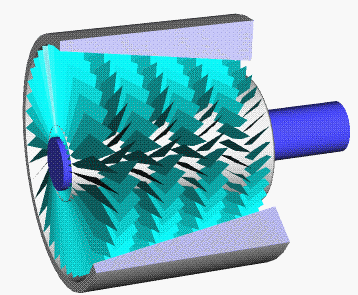
Single Stage Impulse Turbine
Single may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media * Single (music), a song release Songs * "Single" (Natasha Bedingfield song), 2004 * "Single" (New Kids on the Block and Ne-Yo song), 2008 * "Single" (William Wei song), 2016 * "Single", by Meghan Trainor from the album '' Only 17'' * "Single", from the musical ''The Wedding Singer'' Film * ''#Single'' (film), an Indian Telugu-language romantic comedy film Sports * Single (baseball), the most common type of base hit * Single (cricket), point in cricket * Single (football), Canadian football point * Single-speed bicycle Transportation * Single-cylinder engine, an internal combustion engine design with one cylinder, or a motorcycle using such engine * Single (locomotive), a steam locomotive with a single pair of driving wheels * As a verb: to convert a double-track railway to a single-track railway Other uses * Single (mathematics) (1-tuple), a list or sequence with only one element * Single person, a person who is not in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrifugal Compressor
Centrifugal compressors, sometimes called impeller compressors or radial compressors, are a sub-class of dynamic axisymmetric work-absorbing turbomachinery. They achieve pressure rise by adding energy to the continuous flow of fluid through the rotor/impeller. The equation in the next section shows this specific energy input. A substantial portion of this energy is kinetic which is converted to increased potential energy/static pressure by slowing the flow through a diffuser. The static pressure rise in the impeller may roughly equal the rise in the diffuser. Components of a simple centrifugal compressor A simple centrifugal compressor stage has four components (listed in order of throughflow): inlet, impeller/rotor, diffuser, and collector. Figure 1.1 shows each of the components of the flow path, with the flow (working gas) entering the centrifugal impeller axially from left to right. This turboshaft (or turboprop) impeller is rotating counter-clockwise when looking downs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axial Compressor
An axial compressor is a gas compressor that can continuously pressurize gases. It is a rotating, airfoil-based compressor in which the gas or working fluid principally flows parallel to the axis of rotation, or axially. This differs from other rotating compressors such as centrifugal compressor, axi-centrifugal compressors and mixed-flow compressors where the fluid flow will include a "radial component" through the compressor. The energy level of the fluid increases as it flows through the compressor due to the action of the rotor blades which exert a torque on the fluid. The stationary blades slow the fluid, converting the circumferential component of flow into pressure. Compressors are typically driven by an electric motor or a steam or a gas turbine. Axial flow compressors produce a continuous flow of compressed gas, and have the benefits of high efficiency and large mass flow rate, particularly in relation to their size and cross-section. They do, however, require several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Flow Diagram For The Impulse Stage Of An Axial Turbine
Energy () is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J). Forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a Classical field theory, field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system, and rest energy associated with an object's rest mass. These are not mutually exclusive. All life, living organisms constantly take in and release energy. The Earth's climate and ecosystems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variation Of Utilization Factor And Stage Efficiency With Blade-to-gas Speed Ratio
Variation or Variations may refer to: Science and mathematics * Variation (astronomy), any perturbation of the mean motion or orbit of a planet or satellite, particularly of the moon * Genetic variation, the difference in DNA among individuals or the differences between populations ** Human genetic variation, genetic differences in and among populations of humans * Magnetic variation, difference between magnetic north and true north, measured as an angle * ''p''-variation in mathematical analysis, a family of seminorms of functions * Coefficient of variation in probability theory and statistics, a standardized measure of dispersion of a probability distribution or frequency distribution * Total variation in mathematical analysis, a way of quantifying the change in a function over a subset of \mathbb^n or a measure space * Calculus of variations in mathematical analysis, a method of finding maxima and minima of functionals Arts * Variation (ballet) or pas seul, solo dance or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two Stage Reaction Turbine
2 (two) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 1 and preceding 3. It is the smallest and the only even prime number. Because it forms the basis of a duality, it has religious and spiritual significance in many cultures. Mathematics The number 2 is the second natural number after 1. Each natural number, including 2, is constructed by succession, that is, by adding 1 to the previous natural number. 2 is the smallest and the only even prime number, and the first Ramanujan prime. It is also the first superior highly composite number, and the first colossally abundant number. An integer is determined to be even if it is divisible by two. When written in base 10, all multiples of 2 will end in 0, 2, 4, 6, or 8; more generally, in any even base, even numbers will end with an even digit. A digon is a polygon with two sides (or edges) and two vertices. Two distinct points in a plane are always sufficient to define a unique line in a nontrivial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velocity Triangle For An Axial Turbine Stage
Velocity is a measurement of speed in a certain direction of motion. It is a fundamental concept in kinematics, the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of physical objects. Velocity is a vector quantity, meaning that both magnitude and direction are needed to define it. The scalar absolute value (magnitude) of velocity is called , being a coherent derived unit whose quantity is measured in the SI (metric system) as metres per second (m/s or m⋅s−1). For example, "5 metres per second" is a scalar, whereas "5 metres per second east" is a vector. If there is a change in speed, direction or both, then the object is said to be undergoing an ''acceleration''. Definition Average velocity The average velocity of an object over a period of time is its change in position, \Delta s, divided by the duration of the period, \Delta t, given mathematically as\bar=\frac. Instantaneous velocity The instantaneous velocity of an object is the limit average velocity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbine
A turbine ( or ) (from the Greek , ''tyrbē'', or Latin ''turbo'', meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced can be used for generating electrical power when combined with a generator.Munson, Bruce Roy, T. H. Okiishi, and Wade W. Huebsch. "Turbomachines." Fundamentals of Fluid Mechanics. 6th ed. Hoboken, NJ: J. Wiley & Sons, 2009. Print. A turbine is a turbomachine with at least one moving part called a rotor assembly, which is a shaft or drum with blades attached. Moving fluid acts on the blades so that they move and impart rotational energy to the rotor. Gas, steam, and water turbines have a casing around the blades that contains and controls the working fluid. Modern steam turbines frequently employ both reaction and impulse in the same unit, typically varying the degree of reaction and impulse from the blade root to its periphery. History Hero of Alexandria demonstrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enthalpy
Enthalpy () is the sum of a thermodynamic system's internal energy and the product of its pressure and volume. It is a state function in thermodynamics used in many measurements in chemical, biological, and physical systems at a constant external pressure, which is conveniently provided by the large ambient atmosphere. The pressure–volume term expresses the work (physics), work W that was done against constant external pressure P_\text to establish the system's physical dimensions from V_\text=0 to some final volume V_\text (as W=P_\text\Delta V), i.e. to make room for it by displacing its surroundings. The pressure-volume term is very small for solids and liquids at common conditions, and fairly small for gases. Therefore, enthalpy is a stand-in for energy in chemical systems; Bond energy, bond, Lattice energy, lattice, solvation, and other chemical "energies" are actually enthalpy differences. As a state function, enthalpy depends only on the final configuration of internal e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |