|
Awaroa Inlet
Awaroa Inlet is a remote, alluring body of water within the Abel Tasman National Park, at the northern end of Tasman Bay, in the Tasman Region of the South Island, New Zealand. In 2016, Awaroa Beach became known as the "People's Beach" after New Zealanders bought it through a crowdfunding campaign. Naming Awaroa is a Māori language term (''awa'' meaning river or valley, and ''roa'' meaning long). In other words, it is a long river. It is one of many places named Awaroa in New Zealand, for example, Awaroa /Godley Head in Lyttelton Harbour and Awaroa River in the Northland Region. Access Access is not easy. Some people arrive on foot along the Abel Tasman Track. Other people come to Awaroa Beach by boat, kayak and water taxi, or to the north west upper reaches via a winding road, or on small planes or helicopter to the airstrip near Awaroa Lodge. #buythisbeachNZ campaign Although located within the Abel Tasman National Park, a part of Awaroa Beach remained in private o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tasman Bay
Tasman Bay (; officially Tasman Bay / Te Tai-o-Aorere), originally known in English as Blind Bay, is a large V-shaped bay at the north end of New Zealand's South Island. Located in the centre of the island's northern coast, it stretches along of coastline and is across at its widest point. It is an arm of the Tasman Sea, lying on the western approach to Cook Strait. At the bay's western extremity, the land around the bay is rough and densely forested. Separation Point, the westernmost point of the bay, is located in Abel Tasman National Park and separates Tasman Bay from its smaller neighbour, Golden Bay. To the east, the land is also steep, with the westernmost points of sea-drowned valleys of the Marlborough Sounds. D'Urville Island sits to the northeast of Tasman Bay's easternmost point. Arrow Rock is situated off the coast of Nelson. The land between these two extremes is more gently rolling, and also includes the coastal plains around the mouth of the Waimea R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gareth Morgan (economist)
Gareth Huw Morgan (born 17 February 1953) is a New Zealand businessman, economist, investment manager, philanthropist, public commentator and former political figure. Early life and education Morgan was born in Putāruru, New Zealand, to Welsh migrants Roderic and Mary Morgan. He was the second of five children and the first to be born in New Zealand. From 1958 to 1970, Morgan attended school in Putāruru at Oraka Heights Primary and Putaruru High. He then attended Massey University for four years gaining a BA(Hons) in economics. In 1982, he graduated from Victoria University of Wellington with a PhD in economics. Work Career and business Morgan worked for the Reserve Bank of New Zealand in the early 1980s, before founding economics forecasting company Infometrics Limited in 1983. That company became one of New Zealand's largest independent economics consultancy and forecasting businesses and for 18 years while under Morgan's leadership (until the end of the 1990s) maintain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pateke
The brown teal (''Anas chlorotis''; mi, pāteke) is a species of dabbling duck of the genus ''Anas'' native to New Zealand. For many years it had been considered to be conspecific with the flightless Auckland and Campbell teals in ''Anas aucklandica''; the name "brown teal" has also been largely applied to that entire taxon. Common in the early years of European colonisation, the "brown duck" (as it had been often referred to) was heavily harvested as a food source. Its numbers quickly fell, especially in the South Island, and in 1921 they became fully protected. Captive breeding and releasing into predator-controlled areas has seen good localised populations re-introduced around the country in recent years. Description There are no distinctive differences between a male, female and a juvenile brown teal during non-mating season. They all have a white ring around their eyes as well as a mottled brown color on their heads and throat. During breeding season the male will begin to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Fernbird
The New Zealand fernbird or simply fernbird (''Poodytes punctatus'') is an insectivorous bird endemic to New Zealand. In the Māori language, it is named or . Taxonomy The New Zealand fernbird was described by the French zoologists Jean Quoy and Joseph Gaimard in 1832 from a specimen collected in Tasman Bay / Te Tai-o-Aorere, South Island, New Zealand. They coined the binomial name, ''Synallaxis punctata''. In the past, this species had the binomial name ''Megalurus punctatus.'' There are five subspecies present on different islands. They differ in extent of reddish-brown and intensity of streaking, as well as size: * ''P. p. vealeae'' (Kemp, R, 1912) – North Island (New Zealand) * ''P. p. punctatus'' (Quoy & Gaimard, 1832) – South Island (New Zealand) * ''P. p. stewartianus'' ( Oliver, 1930) – Stewart Island (New Zealand) * ''P. p. wilsoni'' (Stead, 1936) – Codfish Island (=Whenua Hou, west of Stewart Island, New Zealand) * ''P. p. caudatus'' ( Buller, 1894) – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
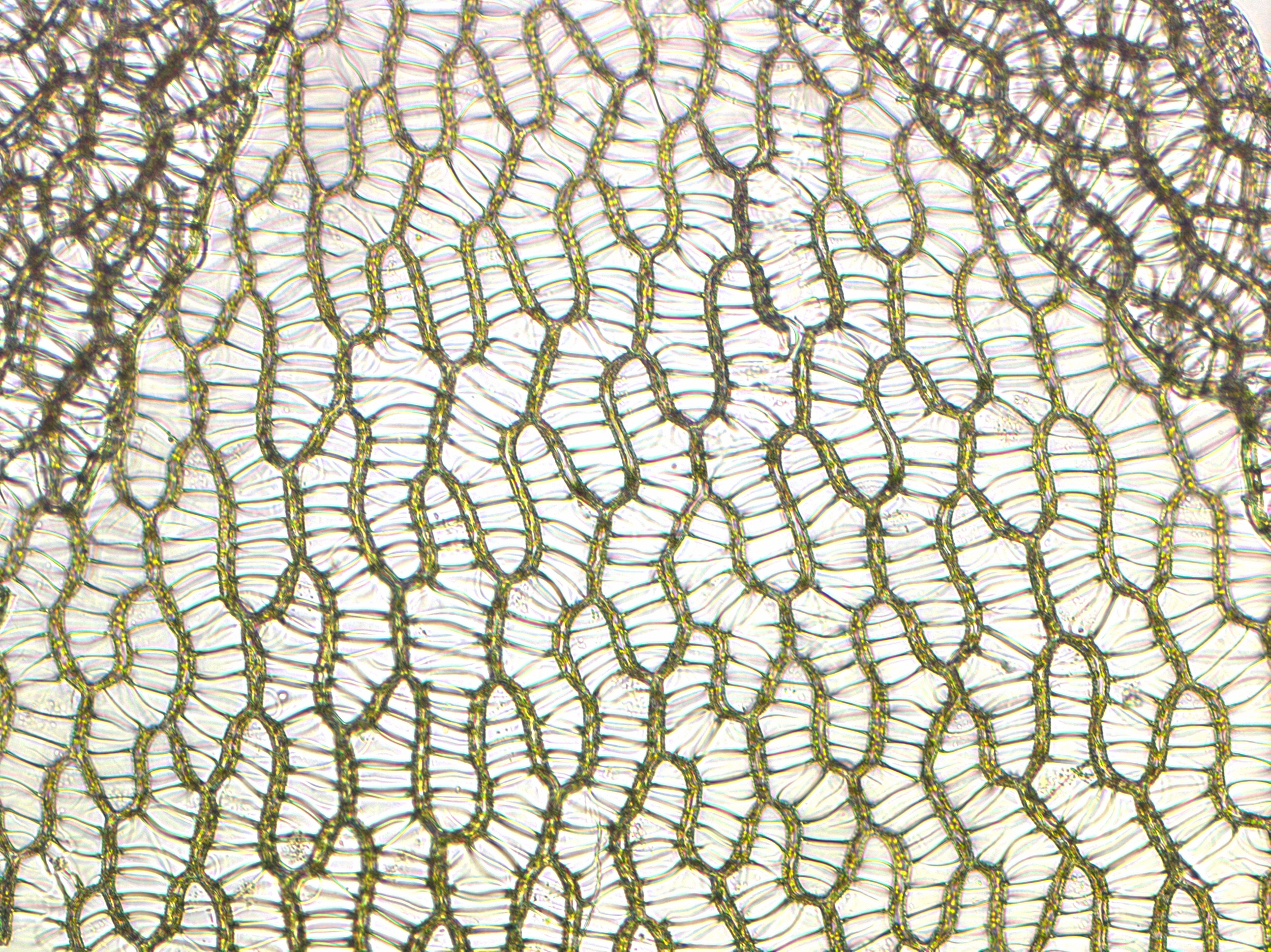
Sphagnum
''Sphagnum'' is a genus of approximately 380 accepted species of mosses, commonly known as sphagnum moss, peat moss, also bog moss and quacker moss (although that term is also sometimes used for peat). Accumulations of ''Sphagnum'' can store water, since both living and dead plants can hold large quantities of water inside their cells; plants may hold 16 to 26 times as much water as their dry weight, depending on the species.Bold, H. C. 1967. Morphology of Plants. second ed. Harper and Row, New York. p. 225-229. The empty cells help retain water in drier conditions. As sphagnum moss grows, it can slowly spread into drier conditions, forming larger mires, both raised bogs and blanket bogs. Thus, sphagnum can influence the composition of such habitats, with some describing sphagnum as 'habitat manipulators'. These peat accumulations then provide habitat for a wide array of peatland plants, including sedges and ericaceous shrubs, as well as orchids and carnivorous plants.Keddy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Janszoon
Abel Tasman National Park is a New Zealand national park located between Golden Bay and Tasman Bay / Te Tai-o-Aorere at the north end of the South Island. It is named after Abel Tasman, who in 1642 became the first European explorer to sight New Zealand and who anchored nearby in Golden Bay. History The park was founded in 1942, largely through the efforts of ornithologist and author Pérrine Moncrieff to have land reserved for the purpose. Moncrieff served on the park board from 1943 to 1974. The park was opened on the 18 December 1942 to mark the 300th anniversary of Abel Tasman's visit.Historic Event, Evening Post, Wellington, volume=CXXXIV, issue=127, 25 November 1942, Page 3 Those in attendance at the opening ceremony at Tarakohe included Charles van der Plas, as personal representative of the Netherlands' Queen, Wilhelmina. The Queen was made Patron of the park. The idea for the park had been under consideration since June 1938. The Crown set aside , comprising of pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Awapoto River
The Awapoto River, also known as Little River as a literal translation from Māori, is a river in the Tasman District of New Zealand. It rises east of Evans Ridge. There are no named peaks near the source, but the Abel Tasman Inland Track follows Evans Ridge near the river's source. The Awapoto River initially flows north-east and then east through the Abel Tasman National Park. It flows through Hadfield Clearing and then passes under Awaroa Road before entering the Awaroa Inlet. What became known as Hadfield Clearing is part of the of land purchased by Frederick Hadfield in 1863; the river flows through this land. Together with William Lightband, he had also leased north of Abel Head, on the south side of Awaroa Inlet, from the previous year. Two of Frederick Hadfield's sons would take up farming in this area: William Hadfield (1844–1920) farmed along the Awapoto River; and Harry Hadfield (1847–1913) farmed along the Awaroa River that flows into the southern reaches of Aw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ghost Towns By Country
The following is a list of ghost towns, listed by continent, then by country. Africa Angola * The settlement of Saint Martin of the Tigers (in Portuguese: ''São Martinho dos Tigres''), situated on a peninsula now known as the Tigres Island (in Portuguese: ''Ilha dos Tigres''), was originally a small but well-established fishing village. It was supplied with water from the nearby town of Foz do Cunene, at the mouth of the Cunene River. In the 1970s, Saint Martin of the Tigers was cut off from the mainland by the rising sea levels, and its water supply line was severed; both Tigres and Foz do Cunene were subsequently abandoned. The island, bound by the South Atlantic Ocean and the Tigres Strait, lies in a zone that is ideally suited for ecological projects. The island was mentioned in the BBC documentary "Unknown Africa: Angola". Central African Republic * Goroumo, Beogombo Deux, and Paoua are among the many deserted villages created by the actions of government forces and kil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picton, New Zealand
Picton ( mi, Waitohi) is a town in the Marlborough Region of New Zealand's South Island. The town is located near the head of the Queen Charlotte Sound / Tōtaranui, north of Blenheim and west of Wellington. Waikawa lies just north-east of Picton and is considered to be a contiguous part of the Picton urban area. Picton is a major hub in New Zealand's transport network, connecting the South Island road and rail network with ferries across Cook Strait to Wellington and the North Island. The Picton urban area has a population of making it the second-largest town in the Marlborough Region behind Blenheim. It is the easternmost town in the South Island with a population of at least 1,000 people. Toponymy The town is named after Sir Thomas Picton, the Welsh military associate of the Duke of Wellington, who was killed at the Battle of Waterloo. Thomas Picton's connection to the slave trade and controversial governorship of Trinidad has resulted in calls for places ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Press
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of water. Small rivers can be referred to using names such as creek, brook, rivulet, and rill. There are no official definitions for the generic term river as applied to geographic features, although in some countries or communities a stream is defined by its size. Many names for small rivers are specific to geographic location; examples are "run" in some parts of the United States, "burn" in Scotland and northeast England, and "beck" in northern England. Sometimes a river is defined as being larger than a creek, but not always: the language is vague. Rivers are part of the water cycle. Water generally collects in a river from precipitation through a drainage basin from surface runoff and other sources such as groundwater recharge, springs, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wellington
Wellington ( mi, Te Whanganui-a-Tara or ) is the capital city of New Zealand. It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the second-largest city in New Zealand by metro area, and is the administrative centre of the Wellington Region. It is the world's southernmost capital of a sovereign state. Wellington features a temperate maritime climate, and is the world's windiest city by average wind speed. Legends recount that Kupe discovered and explored the region in about the 10th century, with initial settlement by Māori iwi such as Rangitāne and Muaūpoko. The disruptions of the Musket Wars led to them being overwhelmed by northern iwi such as Te Āti Awa by the early 19th century. Wellington's current form was originally designed by Captain William Mein Smith, the first Surveyor General for Edward Wakefield's New Zealand Company, in 1840. The Wellington urban area, which only includes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Reserve
A marine reserve is a type of marine protected area (MPA). An MPA is a section of the ocean where a government has placed limits on human activity. A marine reserve is a marine protected area in which removing or destroying natural or cultural resources is prohibited, marine reserves may also be "no-take MPAs,” which strictly forbid all extractive activities, such as fishing and kelp harvesting.. As of 2007 less than 1% of the world's oceans had been set aside in marine reserves. Benefits include increases in the diversity, density, biomass, body size and reproductive potential of fishery and other species within their boundaries. As of 2010, scientists had studied more than 150 marine reserves in at least 61 countries and monitored biological changes inside the reserves. The number of species in each study ranged from 1 to 250 and the reserves ranged in size from 0.006 to 800 square kilometers (0.002 to 310 square miles). In 2014, the World Parks Association adopted a target ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(cropped).jpg)