|
Avioccala
Avioccala was a Roman and Byzantine era town in the Roman province of Africa Proconsularis in northern Tunisia. The town lasted from 30BC to about 640AD, and has been tentatively identified with the stone ruins at Sidi-Amara, Tunisia. The city was endowed by a woman of senatorial rank, Osica Modesta Cornelia Patruina Publiana, and a statue of her has been found in the ruins. The town was also the seat of a Catholic bishopric in the ecclesiastical province of Carthage. Although the diocese ceased to function in the end of the 7th century, the diocese remains a titular see in the Roman Catholic Church. at GCatholic.org. Known bishops include: *Donatus ( [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aggar (city)
Aggar was a town and bishopric (now titular) in the Roman province of Byzacena. One of two cities in the area, it left vast ruins that are now called (Henchir) Sidi Amara. These edifices are situated in the plain of Siliana Governorate, Siliana, around 60 kilometres east of Maktar. A distinct Sidi Amara further north in Tunisia holds the ruins of the Ancient town of Avioccala, located in the Roman province of Africa Proconsularis. Ruins The ruins of Aggar, whose identity is confirmed by inscriptions found there, include those of a triumphal arch opening onto a large porticoed area, with a temple behind it, which must have been the forum and the capitol. A Byzantine Empire, Byzantine fortress, 30 m square with square, slightly projecting corner towers was built on an arcaded structure identified as a temple of Juno. Another temple of unidentified dedication adjoins this citadel. Outside the city proper stands a two-storey mausoleum of a certain C. Maria gens, Marius Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert James Carlson
Robert James Carlson (born June 30, 1944) is an American prelate of the Catholic Church. He served as the ninth archbishop of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of St. Louis in Missouri from 2009 to 2020. Carlson previously served as an auxiliary bishop of the Archdiocese of St. Paul and Minneapolis in Minnesota (1983–1994), as bishop of the Diocese of Sioux Falls in South Dakota (1995–2004), and as bishop of the Diocese of Saginaw in Michigan (2004–2009). Biography Early life Robert Carlson was born June 30, 1944, in Minneapolis, to Robert and Jeanne Carlson. His father was serving in the U.S. Navy on a destroyer in Guam during World War II when his son was born. Robert senior worked as a Prudential insurance salesman for 43 years. The eldest of five children, Robert Carlson has four younger sisters, two of whom died in childhood. During high school, he studied under the Christian Brothers and played football. He then attended Nazareth Hall Preparatory Seminary in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
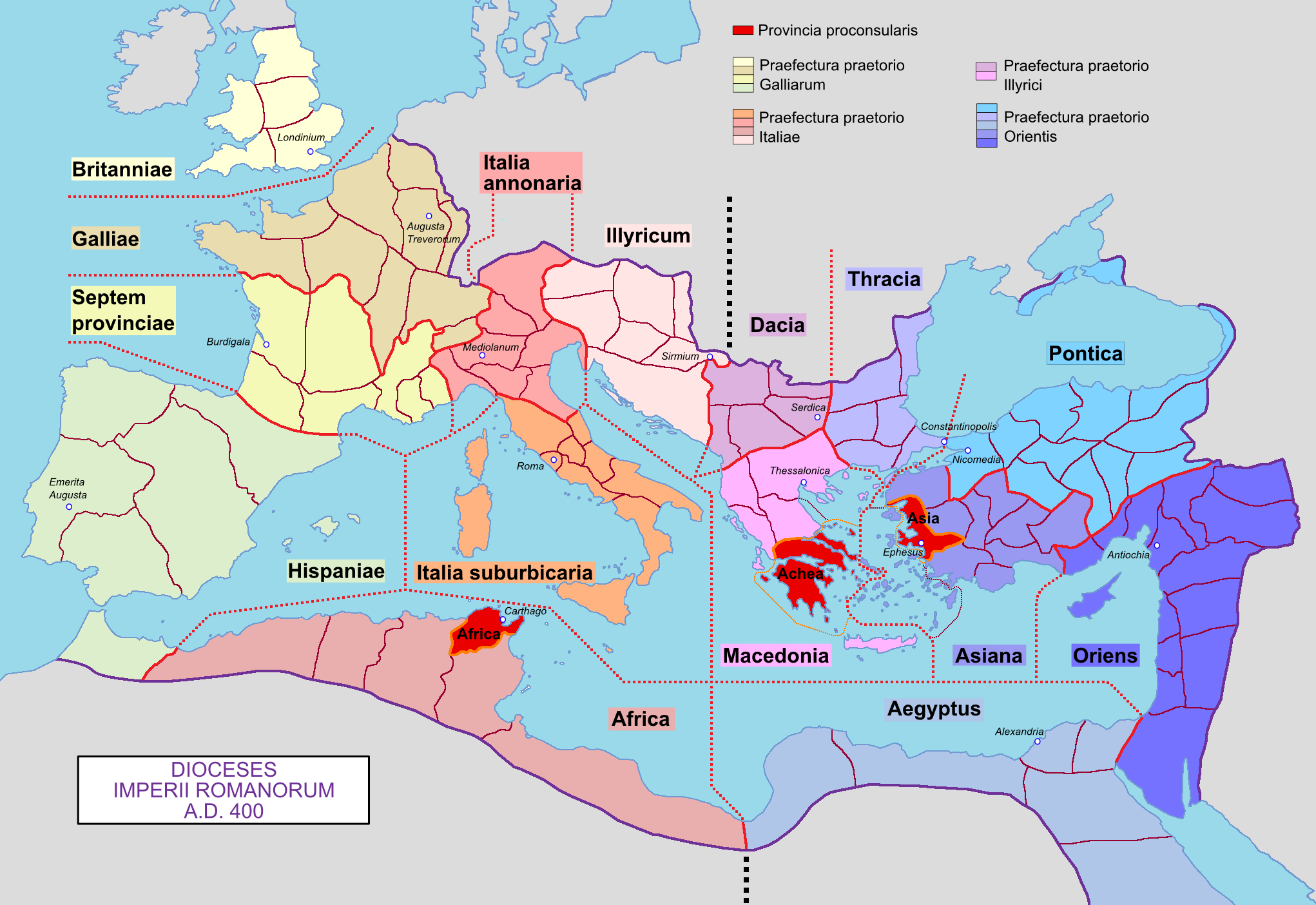
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese
In Ecclesiastical polity, church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop. History In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided Roman province, provinces were administratively associated in a larger unit, the Roman diocese, diocese (Latin ''dioecesis'', from the Greek language, Greek term διοίκησις, meaning "administration"). Christianity was given legal status in 313 with the Edict of Milan. Churches began to organize themselves into Roman diocese, dioceses based on the Roman diocese, civil dioceses, not on the larger regional imperial districts. These dioceses were often smaller than the Roman province, provinces. Christianity was declared the Empire's State church of the Roman Empire, official religion by Theodosius I in 380. Constantine the Great, Constantine I in 318 gave litigants the right to have court cases transferred from the civil courts to the bishops. This situa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzacena
Byzacena (or Byzacium) (, ''Byzakion'') was a Late Roman province in the central part of Roman North Africa, which is now roughly Tunisia, split off from Africa Proconsularis. History At the end of the 3rd century AD, the Roman emperor Diocletian divided the great Roman province of Africa Proconsularis into three smaller provinces: Zeugitana in the north, still governed by a proconsul and referred to as Proconsularis; Byzacena to its adjacent south, and Tripolitania to its adjacent south, roughly corresponding to southeast Tunisia and northwest Libya. Byzacena corresponded roughly to eastern Tunisia or the modern Tunisian region of Sahel, Tunisia, Sahel. Hadrumetum (modern Sousse) became the capital of the newly made province, whose governor had the rank of ''consularis''. At this period the Metropolitan Archbishopric of Byzacena was, after the great metropolis Carthage, the most important city in Roman (North) Africa west of Egypt and its Patriarch of Alexandria. Episcopal s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floruit
''Floruit'' ( ; usually abbreviated fl. or occasionally flor.; from Latin for 'flourished') denotes a date or period during which a person was known to have been alive or active. In English, the unabbreviated word may also be used as a noun indicating the time when someone flourished. Etymology and use is the third-person singular perfect active indicative of the Latin verb ', ' "to bloom, flower, or flourish", from the noun ', ', "flower". Broadly, the term is employed in reference to the peak of activity for a person or movement. More specifically, it often is used in genealogy and historical writing when a person's birth or death dates are unknown, but some other evidence exists that indicates when they were alive. For example, if there are Will (law), wills Attestation clause, attested by John Jones in 1204 and 1229, as well as a record of his marriage in 1197, a record concerning him might be written as "John Jones (fl. 1197–1229)", even though Jones was born before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donatist
Donatism was a schism from the Catholic Church in the Archdiocese of Carthage from the fourth to the sixth centuries. Donatists argued that Christian clergy must be faultless for their ministry to be effective and their prayers and sacraments to be valid. Donatism had its roots in the long-established Christian community of the Roman province Africa Proconsularis (present-day Tunisia, the northeast of Algeria, and the western coast of Libya) and Mauretania Tingitana (roughly with the northern part of present-day Morocco), in the persecutions of Christians under Diocletian. Named after the Berber Christian bishop Donatus Magnus, Donatism flourished during the fourth and fifth centuries. Donatism mainly spread among the indigenous Berber population, and Donatists were able to blend Christianity with many of the Berber local customs. Origin and controversy The Roman governor of North Africa, lenient to the large Christian minority under his rule throughout the Diocletianic Persecu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.Gerald O'Collins, O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical rites#Churches, ''sui iuris'' (autonomous) churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and Eparchy, eparchies List of Catholic dioceses (structured view), around the world, each overseen by one or more Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishops. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the Papal supremacy, chief pastor of the church. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classical world. It became the capital city of the civilization of Ancient Carthage and later Roman Carthage. The city developed from a Phoenician colony into the capital of a Punic people, Punic empire which dominated large parts of the Southwest Mediterranean during the first millennium BC. The legendary Queen Elissa, Alyssa or Dido, originally from Tyre, Lebanon, Tyre, is regarded as the founder of the city, though her historicity has been questioned. In the myth, Dido asked for land from a local tribe, which told her that she could get as much land as an oxhide could cover. She cut the oxhide into strips and laid out the perimeter of the new city. As Carthage prospered at home, the polity sent colonists abroad as well as magistrates to rule t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, experienced recurring cycles of decline and recovery. It reached its greatest extent un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecclesiastical Province
An ecclesiastical province is one of the basic forms of jurisdiction in Christian churches, including those of both Western Christianity and Eastern Christianity, that have traditional hierarchical structures. An ecclesiastical province consists of several dioceses (or eparchies), one of them being the archdiocese (or archeparchy), headed by a metropolitan bishop or archbishop who has ecclesiastical jurisdiction over all other bishops of the province. In the Greco-Roman world, ''ecclesia'' (; ) was used to refer to a lawful assembly, or a called legislative body. As early as Pythagoras, the word took on the additional meaning of a community with shared beliefs. This is the meaning taken in the Greek translation of the Hebrew Scriptures (the Septuagint), and later adopted by the Christian community to refer to the assembly of believers. In the history of Western world (sometimes more precisely as Greco-Roman world) adopted by the Roman Empire and the Byzantine Empire, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishopric
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop. History In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associated in a larger unit, the diocese (Latin ''dioecesis'', from the Greek term διοίκησις, meaning "administration"). Christianity was given legal status in 313 with the Edict of Milan. Churches began to organize themselves into dioceses based on the civil dioceses, not on the larger regional imperial districts. These dioceses were often smaller than the provinces. Christianity was declared the Empire's official religion by Theodosius I in 380. Constantine I in 318 gave litigants the right to have court cases transferred from the civil courts to the bishops. This situation must have hardly survived Julian, 361–363. Episcopal courts are not heard of again in the East until 398 and in the West in 408. The quality of these court ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |