|
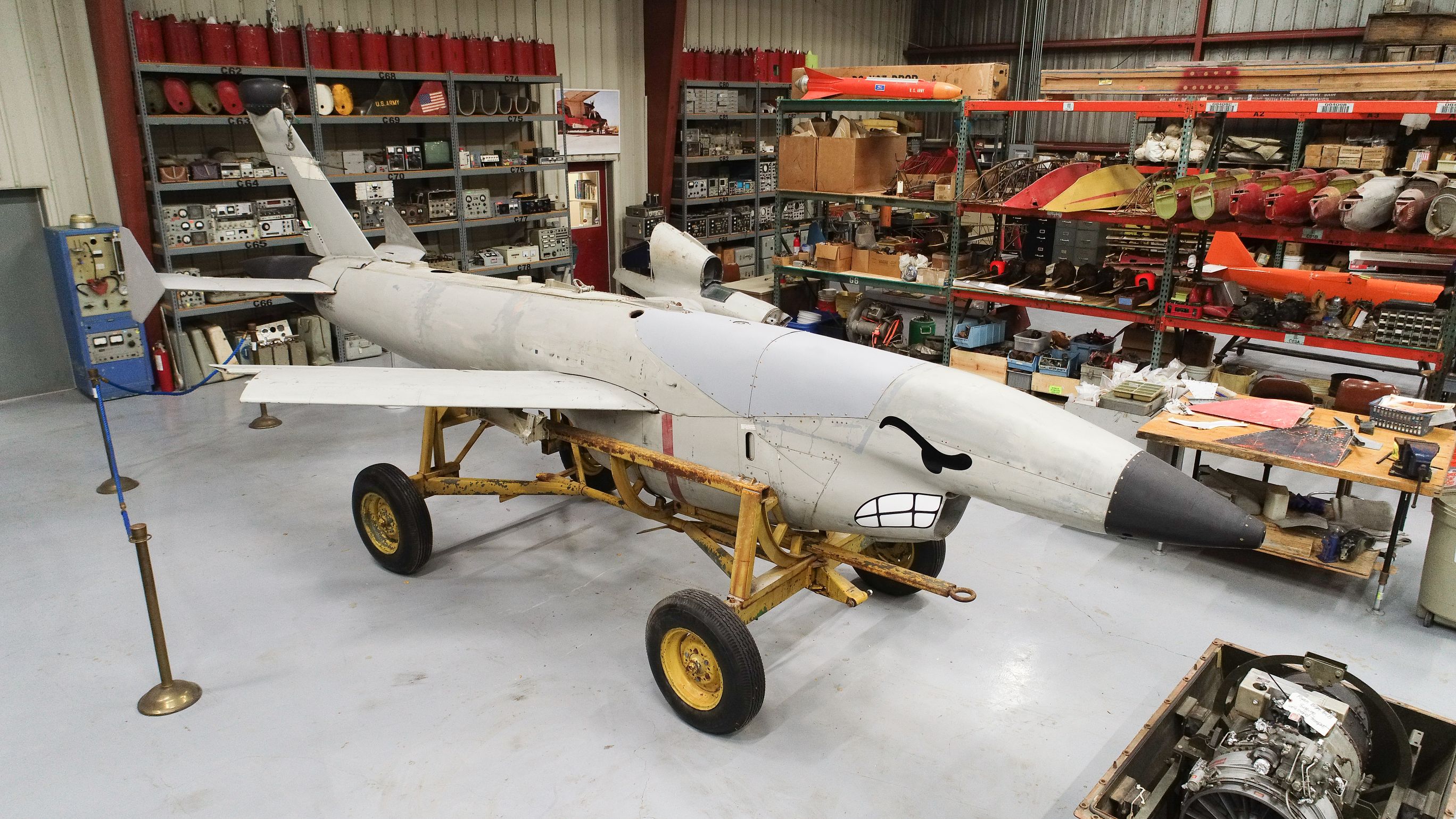
Aviation Unmanned Vehicle Museum
The Aviation Unmanned Vehicle Museum is an aviation museum located at the Caddo Mills Municipal Airport in Caddo Mills, Texas focused on the history of unmanned aerial vehicles An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) or unmanned aircraft system (UAS), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft with no human pilot, crew, or passengers onboard, but rather is controlled remotely or is autonomous.De Gruyter Handbook of Dron .... History A few years after retiring from the United States Air Force, Lt. Col. Harold F. "Red" Smith began a drone manufacturing business. Over the years, he gathered a collection of various drones in a building at the Caddo Mills Municipal Airport. By 2014, he began raising funds to establish a museum. However, Smith was killed in a car accident in 2017. His family continued the project and the museum opened to the public on 16 May 2021. Collection * Beechcraft AQM-37 Jayhawk * Beechcraft MQM-61 Cardinal * Culver PQ-14 Cadet * General Atomics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caddo Mills, Texas
Caddo Mills ( ) is a rural city in Hunt County, Texas located at the western edge of Northeast Texas. The population was 1,495 at the 2020 census, up from 1,338 at the 2010 census. History Before settlers arrived, the area was the site of a Caddo campground. Pioneers arrived in the late 1850s. About twenty years later, I.T. Johnson and Henry King built a gristmill, and residents started referring to the community as Caddo Mills after the facility. On June 16, 1879, a post office opened. Around this time, the community had about 100 residents, 3 churches, and a school. In 1886, the Missouri, Kansas and Texas Railway (MK&T) built a line through the town, and the population increased to 500. In the 1890s and early 1900s, the town became home to a newspaper and a bank. The population swelled to 790 but began declining in the 1920s. Caddo Mills had 390 residents and 20 businesses when it was finally incorporated in the early 1940s. Geography Caddo Mills is located in Northeast Tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed X-7
The Lockheed X-7 (dubbed the "Flying Stove Pipe") is an American unmanned test bed of the 1950s for ramjet engines and missile guidance technology. It was the basis for the later Lockheed AQM-60 Kingfisher, a system used to test American air defenses against nuclear missile attack. Early development Development of the Kingfisher was first initiated in December 1946. The X-7 was called into production by the United States Air Force requirement for the development of an unmanned ramjet test plane with a top speed of at least . The X-7 project was developed under the AMC designator MX-883 and was given in the Lockheed in-house designation L-171. The L-171 was initially designated the PTV-A-1 by the USAF but was later designated the X-7 in 1951. Despite its first launch being a failure, after re-development of the original ramjet, following test flights were successful. A total of 130 X-7 flights were conducted from April 1951 to July 1960. Purpose The X-7 laid the foundation for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerospace Museums In Texas
Aerospace is a term used to collectively refer to the atmosphere and outer space. Aerospace activity is very diverse, with a multitude of commercial, industrial, and military applications. Aerospace engineering consists of aeronautics and astronautics. Aerospace organizations research, design, manufacture, operate, maintain, and repair both aircraft and spacecraft. The border between space and the atmosphere has been proposed as above the ground according to the physical explanation that the air density is too low for a lifting body to generate meaningful lift force without exceeding orbital velocity. This border has been called the Kármán line. Overview In most industrial countries, the aerospace industry is a co-operation of the public and private sectors. For example, several states have a civilian space program funded by the government, such as National Aeronautics and Space Administration in the United States, European Space Agency in Europe, the Canadian Space Agency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Aviation Museums
This is a list of aviation museums and museums that contain significant aerospace-related exhibits throughout the world. The aviation museums are listed alphabetically by country and their article name. Afghanistan * OMAR Mine Museum, Kabul - includes a large collection of Soviet aircraft Argentina * , Bahía Blanca * Museo Nacional de Aeronáutica de Argentina, Morón, Buenos Aires, Morón Armenia * Civil Aviation Museum (Armenia), Civil Aviation Museum, Zvartnots, Armenia, Zvartnots Australia Australian Capital Territory * Australian War Memorial, Canberra New South Wales * Australian Aviation Museum, Bankstown – closed * Camden Museum of Aviation, Camden, New South Wales, Camden * Luskintyre Aviation Flying Museum, Luskintyre * Temora Aviation Museum, Temora, New South Wales, Temora * Fighter World Museum, RAAF Williamtown * Narromine Aviation Museum, Narromine * Historical Aircraft Restoration Society, Shellharbour Airport, Albion Park Rail * Fleet Air Arm Museum (Austra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryan Firebee
The Ryan Firebee is a series of target drones developed by the Ryan Aeronautical, Ryan Aeronautical Company beginning in 1951. It was one of the first Jet engine, jet-propelled drones, and remains one of the most widely used target drones ever built. Development Ryan Firebee I Q-2/KDA-1 Firebee The Firebee I was the result of a 1948 United States Air Force, U.S. Air Force request and contract to Ryan for a jet-powered gunnery target. The first flight of the XQ-2 Firebee prototype took place in early 1951. The drone featured swept flight surfaces and a circular nose inlet. The initial models had distinctive "arrowhead" shaped endplates on the tailplane. The Firebee could be Air launch, air-launched from a specially modified launch aircraft (Douglas A-26 Invader was first to be used for this purpose), or ground-launched with a single JATO, RATO Solid-propellant rocket, booster. Following successful evaluation the target was ordered into production for the USAF as the Q-2A, powe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioplane OQ-2
The Radioplane OQ-2 was the first mass-produced UAV or drone in the United States, manufactured by the Radioplane Company. A follow-on version, the OQ-3, became the most widely used target drone in US service, with over 9,400 being built during World War II. History The OQ-2 was originally a radio-controlled aircraft model designed by Walter Righter. The design, along with its engine design, was purchased by actor Reginald Denny, who had demonstrated another model to the US Army in 1940. Calling the new design the RP-2, he demonstrated several updated versions to the Army as the RP-2, RP-3 and RP-4 in 1939. In 1940, the Army placed an order for 53 RP-4s (some sources refer to the RP-4 as OQ-1. but that designation was never assigned). This small order led to a much bigger 1941 order for the similar RP-5, which became the US Army OQ-2, the ''OQ'' meaning a "subscale target". The US Navy also bought the drone, designating it TDD-1, for ''Target Drone, Denny, 1''. Thousands were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioplane BTT
The Radioplane BTT, known as RP-71 by the company, as WS-426/2 by the United States Navy, and as WS-462/2 by the US Air Force, is a family of target drones produced by the Radioplane Company (later a division of Northrop). History In the post-World War II period, Radioplane followed up the success of the OQ-2 target drone with another very successful series of piston-powered target drones, what would become known as the Basic Training Target (BTT) family (the BTT designation wasn't created until the 1980s, but is used here as a convenient way to resolve the tangle of designations). The BTTs remained in service for the rest of the 20th century. Variants OQ-19 / KD2R The BTT family began life in the late 1940s, evolving through a series of refinements with the US Army designations of OQ-19A through OQ-19D, and the US Navy name of Quail with designated KD2R. Early models had a metal fuselage and wooden wings, but production standardized on an all-metal aircraft. Radioplane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop BQM-74 Chukar
The BQM-74 Chukar is a series of aerial target drones produced by Northrop. The Chukar has gone through three major revisions, including the initial MQM-74A Chukar I, the MQM-74C Chukar II, and the BQM-74C Chukar III. They are recoverable, remote controlled, subsonic aerial target, capable of speeds up to Mach 0.86 and altitudes from . Description The BQM-74E is propelled during flight by a single Williams J400 (J400-WR-404) turbojet engine, which produces a maximum thrust of at sea level. The BQM-74 is launched from a zero length ground launcher using dual Jet Assisted Takeoff (JATO) bottles. When equipped with an air launch kit, the BQM-74 can be air launched from a TA-4J, F-16, Grumman Gulfstream I or DC-130 aircraft. The BQM-74 is used primarily as a realistic aerial target, capable of simulating enemy threats for gunnery and missile training exercises. Drones are capable of being recovered following a training exercise. A parachute is deployed by remote control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
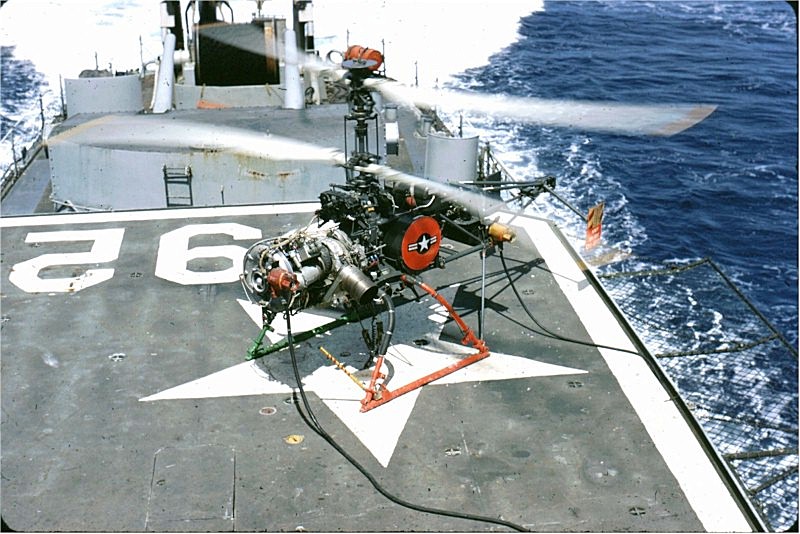
Gyrodyne QH-50 DASH
The Gyrodyne QH-50 DASH (''Drone Anti-Submarine Helicopter'') is a small drone helicopter built by Gyrodyne Company of America for use as a long-range anti-submarine weapon on ships that would otherwise be too small to operate a full-sized helicopter. It remained in production until 1969. Several are still used today for various land-based roles. Design and development DASH was a major part of the United States Navy's Fleet Rehabilitation and Modernization (FRAM) program of the late 1950s. FRAM was started because the Soviet Union was building submarines faster than the US could build anti-submarine frigates. Instead of building frigates, the FRAM upgrade series allowed the US to rapidly update by converting older ships that were less useful in modern naval combat. The navy could upgrade the sonar on World War II-era destroyers but needed a stand-off weapon to attack at the perimeter of the sonar's range. The old destroyers had little room for add-ons such as a full flight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aviation Museum
An aviation museum, air museum, or air and space museum is a museum exhibiting the history and cultural artifacts, artifacts of aviation. In addition to actual, replica or accurate reproduction aircraft, exhibits can include photographs, maps, Physical model, models, dioramas, clothing and equipment used by aviators. Aviation museums vary in size from housing just one or two aircraft to hundreds. They may be owned by national, regional or local governments or be privately owned. Some museums address the history and artifacts of space exploration as well, illustrating the close association between aeronautics and astronautics. Many aviation museums concentrate on military or civil aviation, or on aviation history of a particular era, such as Aviation in the pioneer era, pioneer aviation or Aviation between the World Wars, the succeeding "golden age" between the World Wars, aircraft of World War II or a specific type of aviation, such as gliding. Aviation museums may display their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Atomics MQ-1 Predator
The General Atomics MQ-1 Predator (often referred to as the Predator drone) is an American remotely piloted aircraft (RPA) built by General Atomics that was used primarily by the United States Air Force (USAF) and Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). Conceived in the early 1990s for aerial reconnaissance and forward observation roles, the Predator carries cameras and other sensors. It was modified and upgraded to carry and fire two AGM-114 Hellfire missiles or other munitions. The aircraft entered service in 1995, and saw combat in the war in Afghanistan, Pakistan, the NATO intervention in Bosnia, the NATO bombing of Yugoslavia, the Iraq War, Yemen, the 2011 Libyan civil war, the 2014 intervention in Syria, and Somalia. The USAF describes the Predator as a "Tier II" MALE UAS (medium-altitude, long-endurance unmanned aircraft system). The UAS consists of four aircraft or "air vehicles" with sensors, a ground control station (GCS), and a primary satellite link communication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culver PQ-14 Cadet
The Culver PQ-14 Cadet is a modified version of the Culver LFA Cadet used as a target drone. In 1940, the U.S. Army Air Corps drew up a requirement for a radio-controlled target drone for training anti-aircraft artillery gunners. The first aircraft in a series of target drones was a modification of the Culver LFA Cadet which eventually led to the PQ-14 series used throughout World War II and beyond. Design and development Culver proposed a modification of its civilian Model LFA Cadet which the Army purchased as the Culver Cadet, PQ-8. The success of the PQ-8 led to the development of the "NRD"; a single PQ-8 was converted to the new configuration and tested by the USAAF as the XPQ-14. Larger and faster than the PQ-8, the PQ-14 also had retractable landing gear and fuselage, wings and tail components made of wood with stressed plywood skin. This prototype was followed by YPQ-14A service test aircraft and 1,348 PQ-14A production models. Of the latter, 1,198 were transferred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |