|
Avatsara
Avatsara was a Rishi of the Rig Veda. His name first appears in the Fifth Mandala which is older than the Second Mandala. Background Avatsara is the main poet of Sukta 44 of the Fifth Mandala of the Rig veda which hymn addressed to the Rigvedic deities, the Visvedevas. He is more known for the set of eight hymns of four mantras each appearing in the Rig Veda viz. Suktas IX.53 to IX.60, and also in the Samaveda (SV.757, SV.1717). He was the Hotr of the gods. He had delighted Agni by the six-syllable oblation – ''O Agni, enjoy the oblation'', and was set-free. According to Satyasadha (21.3.13), the Parvaras of Kashyaps consist of three rishi – ancestors: – Kashyap, Avatsara and Naidhruva. There are eight notable rishis belonging to the Kashyap family – ''Kashyap'', ''Avatsara'', ''Nidhurva'', ''Rebha'', ''Devala'', ''Asita'', ''Bhutamsa'' and ''Vivrha''; two unnamed sons of ''Rebha'' were also authors of Rigvedic hymns. As Vedic Rishi Avatsara was the son of Rishi Kashyap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pravaras
In Hindu culture, a ''Pravara'' (Sanskrit for "most excellent") is a system of identity, particularly a family line. Pravaras is a particular Brahmin's descent from a ''rishi'' (sage) who belonged to their ''gotra'' (clan). Importance in Hindu Dharma The Pravara has been extensively used in identifying one's ancestry and thus giving salutations to the listener. In vedic ritual, the importance of the pravara appears to be in its use by the ritualist for extolling his ancestry and proclaiming, "as a descendant of worthy ancestors, I am a fit and proper person to do the act I am performing." Generally, there are three, five or seven pravaras. The sacred thread yajnopavita worn on upanayana has close and essential connection with the concept of pravaras related to Brahmin gotra system. While tying the knots of sacred thread, an oath is taken in the name of each one of these three, five or seven of the most excellent rishis belonging to one's gotra. The full affiliation consists o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rishi
''Rishi'' () is a term for an accomplished and enlightened person. They find mentions in various Vedic texts. Rishis are believed to have composed hymns of the Vedas. The Post-Vedic tradition of Hinduism regards the rishis as "great yogis" or "sages" who after intense meditation ( tapas) realized the supreme truth and eternal knowledge, which they composed into hymns.Hartmut Scharfe (2002), Handbook of Oriental Studies, BRILL Academic, , pp. 13–15. The term appears in Pali literature as Ishi and in Buddhism, they can be either Buddhas, Paccekabuddhas, Arahats or a monk of high rank. Etymology According to Indian tradition, the word may be derived from two different meanings of the root 'rsh' (). Sanskrit grammarians derive this word from the second meaning: "to go, to move". V. S. Apte gives this particular meaning and derivation, and Monier-Williams also gives the same, with some qualification. Another form of this root means "to flow, to move near by flowing". (All th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aitareya Brahmana
The Aitareya Brahmana ( sa, ऐतरेय ब्राह्मण) is the Brahmana of the Shakala Shakha of the Rigveda, an ancient Indian collection of sacred hymns. This work, according to the tradition, is ascribed to Mahidasa Aitareya. Authorship Sayana of Vijayanagara, a 14th century commentator, attributes the entire ''Aitareya Brahmana'' to a single man: Mahidasa Aitareya. In his introduction to the text, Sayana suggests that "Aitareya" is a matronymic name. Mahidasa's mother was "Itaraa" (इतरा), whose name is derived from the Sanskrit word "itara". She was one of the wives of a great rishi (sage). The rishi preferred sons from his other wives over Mahidasa. Once he placed all his other sons on his lap, but ignored Mahidasa. On seeing tears in the eyes of her son, Itara prayed to the earth goddess Bhūmi, her kuladevi (tutelary deity). Bhūmi then appeared and gifted Mahidasa the knowledge contained in the ''Aitareya Brahmana''. Mahidasa is mentioned in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandilya
Shandilya ( IAST: Śāṇḍilya) is a Brahmin gotra, named after the Rishi Shandilya, specifying that individuals of the gotra have Shandilya as one of their patrilineal ancestors. Shandilya Rishi and was the progenitor of the Śāṇḍilya gotra, which is also the highest Brahmin gotras. The name derives from the Sanskrit words Śaṇ, and Dilam, thus meaning Full Moon, therefore implying Śāṇḍilya to be the priest of the Moon God This gotra has three pravar, they are Sandilya, Asit and Deval. The Ved of this gotra is Samveda. This gotra is one of the eight highest gotra in Brahmins. Sandilya gotra is the largest gotra in Maithil Brahmins Maithil Brahmins are a Hindu Brahmin community from the Mithila region of the Indian subcontinent that comprises Tirhut, Darbhanga, Kosi, Purnia, Munger, Bhagalpur; Bokaro in Jharkhand and Santhal Pargana divisions of India and some adj .... There are 44 mool (origin) of Sandilya gotra in Maithil Brahmins. References Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manu (Hinduism)
Manu ( sa, मनु) is a term found as various meanings in Hinduism. In early texts, it refers to the archetypal man, or to the first man ( progenitor of humanity). The Sanskrit term for 'human', मानव ( IAST: mānava) means 'of Manu' or 'children of Manu'. In later texts, Manu is the title or name of fourteen rulers of earth, or alternatively as the head of dynasties that begin with each cyclic '' kalpa'' (aeon) when the universe is born anew. The title of the text ''Manusmriti'' uses this term as a prefix, but refers to the first Manu – Svayambhuva, the spiritual son of Brahma. In the earliest mention of Manu, in the Rigveda, Manu is only the ancestor of the "Five Peoples", or "Páñca Jánāḥ" (the five tribes being the Anu, Druhyus, Yadus, Turvashas, and Purus). The Aryans considered all other peoples to be a-manuṣa. Later, in the Hindu cosmology, each ''kalpa'' consists of fourteen Manvantaras, and each Manvantara is headed by a different Manu. The curre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhruva
Dhruva (Sanskrit: ध्रुव, , lit. "''unshakeable, immovable, or fixed"'') was an ascetic devotee of Vishnu mentioned in the Vishnu Purana and the Bhagavata Purana. The Sanskrit term ''dhruva nakshatra'' (ध्रुव नक्षत्र, "polar star") has been used for Pole Star in the Mahabharata, personified as son of Uttānapāda and grandson of Manu, even though Polaris at the likely period of the recension of the text of the Mahabharata was still several degrees away from the celestial pole. Narrative Dhruva was born as son of the King Uttānapāda (the son of Svayambhuva Manu) and his wife Suniti. The king also had another son Uttama, born to his second queen Suruchi, who was the preferred object of his affection. Once, when Dhruva was a child of five years of age, he saw his younger brother, Uttama sitting on his father's lap at the King's throne. Suruchi, who was jealous of the older son from the first wife (since he - Dhruva - would be heir to throne, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhagavata Purana
The ''Bhagavata Purana'' ( sa, भागवतपुराण; ), also known as the ''Srimad Bhagavatam'', ''Srimad Bhagavata Mahapurana'' or simply ''Bhagavata'', is one of Hinduism's eighteen great Puranas (''Mahapuranas''). Composed in Sanskrit by Veda Vyasa, it promotes '' bhakti'' (devotion) towards Krishna, integrating themes from the Advaita (monism) philosophy of Adi Shankara, the Vishishtadvaita (qualified monism) of Ramanujacharya and the Dvaita (dualism) of Madhvacharya. It is widely available in almost all Indian languages. The ''Bhagavata Purana'', like other puranas, discusses a wide range of topics including cosmology, astronomy, genealogy, geography, legend, music, dance, yoga and culture. As it begins, the forces of evil have won a war between the benevolent ''devas'' (deities) and evil ''asuras'' (demons) and now rule the universe. Truth re-emerges as Krishna, (called " Hari" and " Vāsudeva" in the text) – first makes peace with the demons, understands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
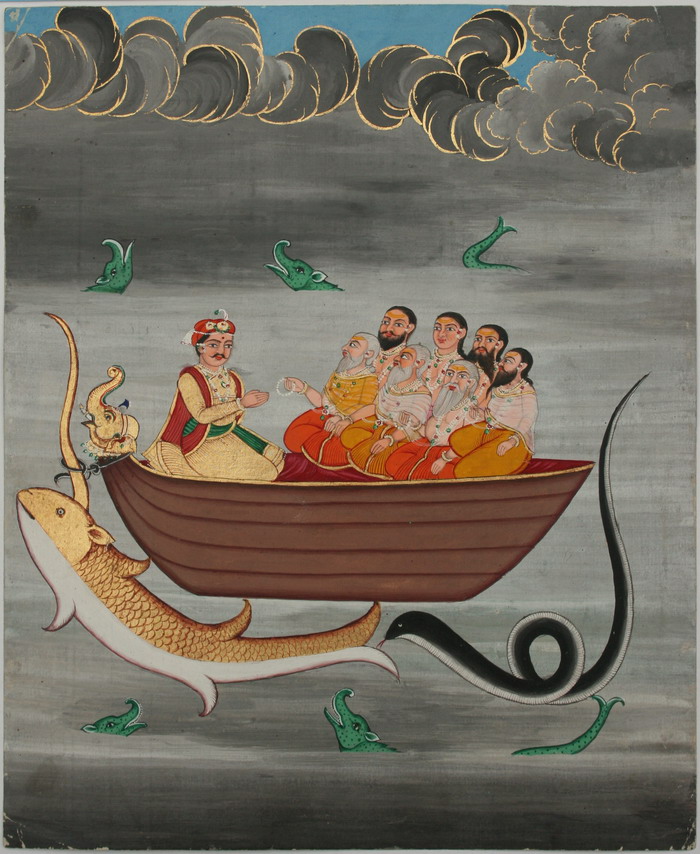
Matsya Purana
The ''Matsya Purana'' ( IAST: Matsya Purāṇa) is one of the eighteen major Puranas (Mahapurana), and among the oldest and better preserved in the Puranic genre of Sanskrit literature in Hinduism. The text is a Vaishnavism text named after the half-human and half-fish avatar of Vishnu. However, the text has been called by the 19th-century Sanskrit scholar Horace Hayman Wilson, "although a Shaivism (Shiva-related) work, it is not exclusively so"; the text has also been referred to one that simultaneously praises various Hindu gods and goddesses. The ''Matsya Purana'' has survived into the modern era in many versions, varying in the details but almost all of the published versions have 291 chapters, except the Tamil language version, written in Grantha script, which has 172 chapters. The text is notable for providing one of earliest known definition of a Purana genre of literature. A history written with five characteristics is called a Purana, states ''Matsya Purana'', otherwise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
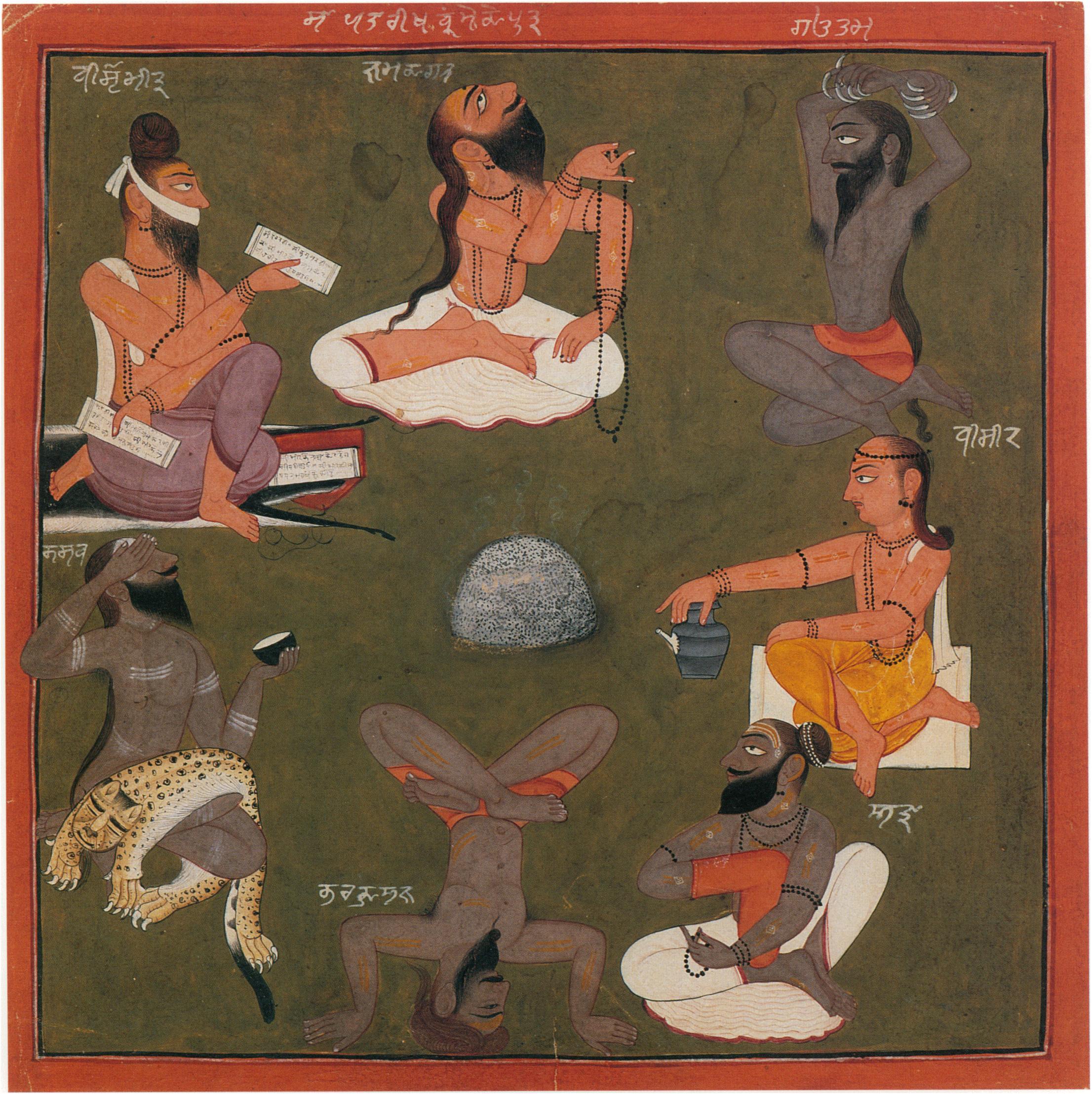
Sapta Rishis
The Saptarishi () are the seven rishis of ancient India who are extolled in the Vedas, and other Hindu literature. The Vedic Samhitas never enumerate these rishis by name, although later Vedic texts such as the Brahmanas and Upanisads do so. Hinduism An early prototype of the "Saptarishi" concept may stem from the six families associated with the six "Family Books" in the Rigveda Samhita (Mandalas 2–7 in ascending order: Gṛtsamāda, Viśvāmitra, Vāmadeva, Atri, Bhardwaja, Vasiṣṭha). While not a "Family Book", Mandala 8 is mostly attributed to Kaṇva, who could be considered the 7th prototypical Saptarishi. The earliest formal list of the seven rishis is given by Jaiminiya Brahmana 2.218–221: Agastya, Atri, Bhardwaja, Gautama, Jamadagni, Vashistha, and Vishvamitra followed by Brihadaranyaka Upanisad 2.2.6 with a slightly different list: Atri, Bharadwaja, Gautama, Jamadagni, Kashyapa, Vashistha, and Vishvamitra. The late Gopatha Brahmana 1.2.8 has Vashistha, Vish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasistha
Vasishtha ( sa, वसिष्ठ, IAST: ') is one of the oldest and most revered Vedic rishis or sages, and one of the Saptarishis (seven great Rishis). Vashistha is credited as the chief author of Mandala 7 of the ''Rigveda''. Vashishtha and his family are mentioned in Rigvedic verse 10.167.4, other Rigvedic mandalas and in many Vedic texts. His ideas have been influential and he was called the first sage of the Vedanta school of Hindu philosophy by Adi Shankara. The '' Yoga Vasishtha'', ''Vasishtha Samhita'', as well as some versions of the ''Agni Purana'' and ''Vishnu Purana'' are attributed to him. He is the subject of many stories, such as him being in possession of the divine cow Kamadhenu and Nandini her child, who could grant anything to their owners. He is famous in Hindu stories for his legendary conflicts with sage Vishvamitra. In the Ramayana, he was the family priest of the Raghu dynasty and teacher of Rama and his brothers. Etymology Vasishtha is also spelled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
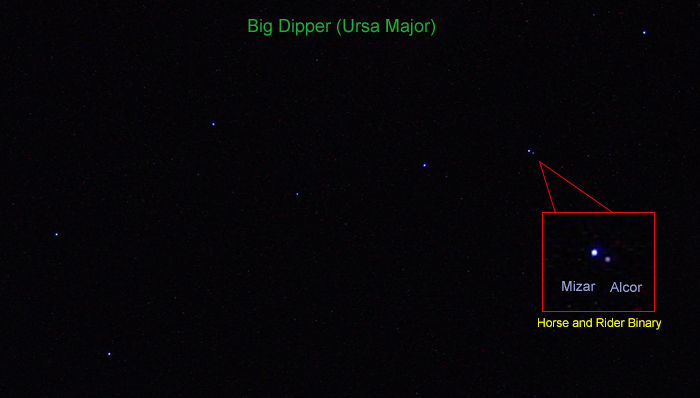
Arundhati (Hinduism)
Arundhati ( sa, अरुन्धती, translit=Arundhatī) is the wife of the sage Vasishtha, one of the seven sages (Saptarshi) of Hinduism. Etymology The name in Sanskrit literally means 'washed from the rays of sun', from 'sun rays', and , 'washed'. Legend Arundhati's birth and life are mentioned in various Hindu scriptures. The birth of Arundhati is found in the Shiva Purana and Bhagavata Purana. The instruction by Brahma to Arundhati is described in the Uttara Kanda of the Ramcharitmanas. The rivalry between Vishvamitra and Vasishtha which leads to the death of her hundred sons is described in the Balakanda of Valmiki's Ramayana. The Mahabharata and several Brahmana works describe her sons, including Shakti, and grandson Parashara. Arundhati's meetings with Sita and Rama are mentioned in the Ramayana, Ramcharitmanas and Vinaya Patrika.Rambhadracharya 1994, pp. ''iii—vi''. Her role in pleading Shiva to marry Parvati is described in the sixth can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narada Muni
Narada ( sa, नारद, ), or Narada Muni, is a sage divinity, famous in Hindu traditions as a travelling musician and storyteller, who carries news and enlightening wisdom. He is one of mind-created children of Brahma, the creator god. He appears in a number of Hindu texts, notably the Mahabharata, regaling Yudhishthira with the story of Prahalada and the Ramayana as well as tales in the Puranas. A common theme in Vaishnavism is the accompaniment of a number of lesser deities such as Narada to offer aid to Vishnu upon his descent to earth to combat the forces of evil, or enjoy a close view of epochal events. He is also referred to as ''Rishiraja'', meaning the king of all sages. He was gifted with the boon of knowledge regarding the past, present, and the future. Hinduism In Indian texts, Narada travels to distant worlds and realms (Sanskrit: '' lokas''). He is depicted carrying a khartal (musical instrument) and the veena, and is generally regarded as one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |