|
Autolysin
Autolysins are endogenous lytic enzymes that break down the peptidoglycan components of biological cells which enables the separation of daughter cells following cell division. They are involved in cell growth, cell wall metabolism, cell division and separation, as well as peptidoglycan turnover and have similar functions to lysozymes. Autolysin is formed from the precursor gene, Atl. Amidases (EC 3.5.1.28), gametolysin (EC 3.4.24.38), and glucosaminidase are considered as types of autolysins. Function and mechanisms Autolysins exist in all bacteria containing peptidoglycan and are potentially considered as lethal enzymes when uncontrolled. They target the glycosidic bonds as well as the cross-linked peptides of the peptidoglycan matrix. The peptidoglycan matrix functions for cell wall stability to protect from turgor changes and carries out function for immunological defense. These enzymes break down the peptidoglycan matrix in small sections to allow for peptidoglycan biosynt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corbomycin
Corbomycin is a member of the glycopeptide family of antibiotics that are produced by soil bacteria. Mechanism of action Corbomycin blocks autolysins by attaching to the peptidoglycan cell wall. As a result, the bacterium cannot divide, as division requires the wall to be broken down and remodeled. Ordinary glycopeptides instead block cell wall formation. Applications It can block infections caused by the drug-resistant strain of ''Staphylococcus aureus'' that cause serious infections. As of 2020 it had not been approved by any regulatory body for human use. History The antibiotic was discovered in 2020. Researchers found the substance while studying the biosynthetic genes of glycopeptides that lacked self-resistance mechanisms. Researcher Beth Culp worked with Yves Brun and his team to image the cells to identify the action site. Culp's later team found other antibiotics that employed the same method of action. Complestatin is an existing antibiotic that was shown to use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teichoic Acid
Teichoic acids (''cf.'' Greek τεῖχος, ''teīkhos'', "wall", to be specific a fortification wall, as opposed to τοῖχος, ''toīkhos'', a regular wall) are bacterial copolymers of glycerol phosphate or ribitol phosphate and carbohydrates linked via phosphodiester bonds. Teichoic acids are found within the cell wall of most Gram-positive bacteria such as species in the genera ''Staphylococcus'', ''Streptococcus'', ''Bacillus'', ''Clostridium'', ''Corynebacterium'', and ''Listeria'', and appear to extend to the surface of the peptidoglycan layer. They can be covalently linked to ''N''-acetylmuramic acid or a terminal D-alanine in the tetrapeptide crosslinkage between ''N''-acetylmuramic acid units of the peptidoglycan layer, or they can be anchored in the cytoplasmic membrane with a lipid anchor. Teichoic acid's chemical signal is CH17P4O29NOH. Teichoic acids that are anchored to the lipid membrane are referred to as lipoteichoic acids (LTAs), whereas teichoic acids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii
''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'' is a single-cell green alga about 10 micrometres in diameter that swims with two flagella. It has a cell wall made of hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins, a large cup-shaped chloroplast, a large pyrenoid, and an eyespot apparatus that senses light. '' Chlamydomonas'' species are widely distributed worldwide in soil and fresh water, of which ''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'' is one of the most common and widespread. ''C. reinhardtii'' is an especially well studied biological model organism, partly due to its ease of culturing and the ability to manipulate its genetics. When illuminated, ''C. reinhardtii'' can grow photoautotrophically, but it can also grow in the dark if supplied with organic carbon. Commercially, ''C. reinhardtii'' is of interest for producing biopharmaceuticals and biofuel, as well being a valuable research tool in making hydrogen. History The ''C. reinhardtii'' wild-type laboratory strain c137 (mt+) originates from an isolate c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Subtilis
''Bacillus subtilis'' (), known also as the hay bacillus or grass bacillus, is a gram-positive, catalase-positive bacterium, found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants, humans and marine sponges. As a member of the genus ''Bacillus'', ''B. subtilis'' is rod-shaped, and can form a tough, protective endospore, allowing it to tolerate extreme environmental conditions. ''B. subtilis'' has historically been classified as an obligate aerobe, though evidence exists that it is a facultative anaerobe. ''B. subtilis'' is considered the best studied Gram-positive bacterium and a model organism to study bacterial chromosome replication and cell differentiation. It is one of the bacterial champions in secreted enzyme production and used on an industrial scale by biotechnology companies. Description ''Bacillus subtilis'' is a Gram-positive bacterium, rod-shaped and catalase-positive. It was originally named ''Vibrio subtilis'' by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osmotic Pressure
Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure which needs to be applied to a Solution (chemistry), solution to prevent the inward flow of its pure solvent across a semipermeable membrane. It is also defined as the measure of the tendency of a solution to take in its pure solvent by osmosis. Potential osmotic pressure is the maximum osmotic pressure that could develop in a solution if it was not separated from its pure solvent by a semipermeable membrane. Osmosis occurs when two solutions containing different concentrations of solute are separated by a selectively permeable membrane. Solvent molecules pass preferentially through the membrane from the low-concentration solution to the solution with higher solute concentration. The transfer of solvent molecules will continue until ''osmotic equilibrium'' is attained. Theory and measurement Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff, Jacobus van 't Hoff found a quantitative relationship between osmotic pressure and solute concentration, expre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
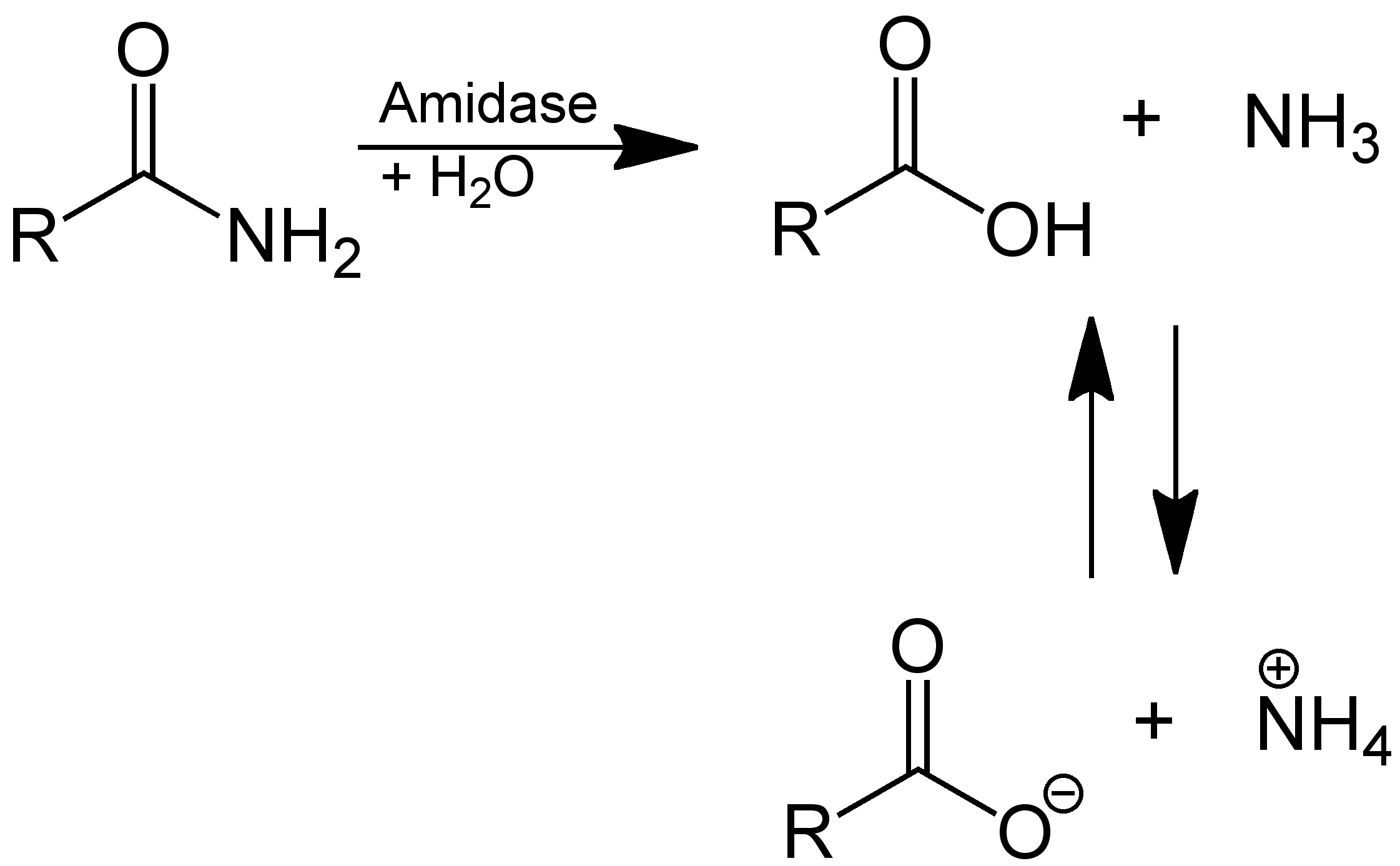
Amidase
In enzymology, an amidase (, ''acylamidase'', ''acylase (misleading)'', ''amidohydrolase (ambiguous)'', ''deaminase (ambiguous)'', ''fatty acylamidase'', ''N-acetylaminohydrolase (ambiguous)'') is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes the hydrolysis of an amide. In this way, the two substrate (biochemistry), substrates of this enzyme are an amide and water, H2O, whereas its two product (chemistry), products are monocarboxylate and ammonia, NH3. This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, those acting on carbon-nitrogen bonds other than peptide bonds, specifically in linear amides. The List of enzymes, systematic name of this enzyme class is acylamide amidohydrolase. Other names in common use include acylamidase, acylase, amidohydrolase, deaminase, fatty acylamidase, and N-acetylaminohydrolase. This enzyme participates in 6 metabolism, metabolic pathways: urea cycle and metabolism of amino groups, phenylalanine metabolism, tryptophan metabolism, cyanoamino acid metabolism, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine Amidase
In enzymology, a N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase () is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes a chemical reaction that cleaves the link between N-acetylmuramoyl residues and L-amino acid residues in certain cell wall, cell-wall glycopeptides. This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, specifically those acting on carbon-nitrogen bonds other than peptide bonds in linear amides. The List of enzymes, systematic name of this enzyme class is peptidoglycan amidohydrolase. Other names in common use include acetylmuramyl-L-alanine amidase, N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanine amidase, N-acylmuramyl-L-alanine amidase, acetylmuramoyl-alanine amidase, N-acetylmuramic acid L-alanine amidase, acetylmuramyl-alanine amidase, N-acetylmuramylalanine amidase, N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase type I, and N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase type II. This enzyme participates in peptidoglycan biosynthesis. Autolysins and some phage lysins are examples of N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidases. See also * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, treatment and antibiotic prophylaxis, prevention of such infections. They may either bactericide, kill or bacteriostatic agent, inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the ones which cause the common cold or influenza. Drugs which inhibit growth of viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals. Antibiotics are also not effective against fungi. Drugs which inhibit growth of fungi are called antifungal drugs. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek language, Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-positive
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall. The Gram stain is used by microbiologists to place bacteria into two main categories, gram-positive (+) and gram-negative bacteria, gram-negative (−). Gram-positive bacteria have a thick layer of peptidoglycan within the cell wall, and gram-negative bacteria have a thin layer of peptidoglycan. Gram-positive bacteria retain the crystal violet stain used in the test, resulting in a purple color when observed through an optical microscope. The thick layer of peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall retains the Stain (biology), stain after it has been fixed in place by iodine. During the decolorization step, the decolorizer removes crystal violet from all other cells. Conversely, gram-negative bacteria cannot retain the violet stain after the decolorization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamete
A gamete ( ) is a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. The name gamete was introduced by the German cytologist Eduard Strasburger in 1878. Gametes of both mating individuals can be the same size and shape, a condition known as isogamy. By contrast, in the majority of species, the gametes are of different sizes, a condition known as anisogamy or heterogamy that applies to humans and other mammals. The human ovum has approximately 100,000 times the volume of a single human sperm cell. The type of gamete an organism produces determines its sex and sets the basis for the sexual roles and sexual selection. In humans and other species that produce two Morphology (biology), morphologically distinct types of gametes, and in which Gonochorism, each individual produces only one type, a femal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |