|
Autoimmunity
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an "autoimmune disease". Prominent examples include celiac disease, diabetes mellitus type 1, Henoch–Schönlein purpura (HSP), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjögren syndrome, eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, Graves' disease, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, Addison's disease, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), ankylosing spondylitis, polymyositis (PM), dermatomyositis (DM), and multiple sclerosis (MS). Autoimmune diseases are very often treated with steroids. Autoimmunity means presence of antibodies or T cells that react with self-protein and is present in all individuals, even in normal health state. It causes autoimmune diseases if self-reactivity can lead to tissue damage. History In the later 19th century it wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunology
Immunology is a branch of medicineImmunology for Medical Students, Roderick Nairn, Matthew Helbert, Mosby, 2007 and biology that covers the medical study of immune systems in humans, animals, plants and sapient species. In such we can see there is a difference of human immunology and comparative immunology in veterinary medicine and animal biosciences. Immunology measures, uses charts and differentiate in context in medicine the studies of immunity on cell and molecular level, and the immune system as part of the physiological level as its functioning is of major importance. In the different states of both health, occurring symptoms and diseases; the functioning of the immune system and immunological responses such as autoimmune diseases, allergic hypersensitivities, or in some cases malfunctioning of immune system as for example in immunological disorders or in immune deficiency, and the specific transplant rejection) Immunology has applications in numerous disciplines of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
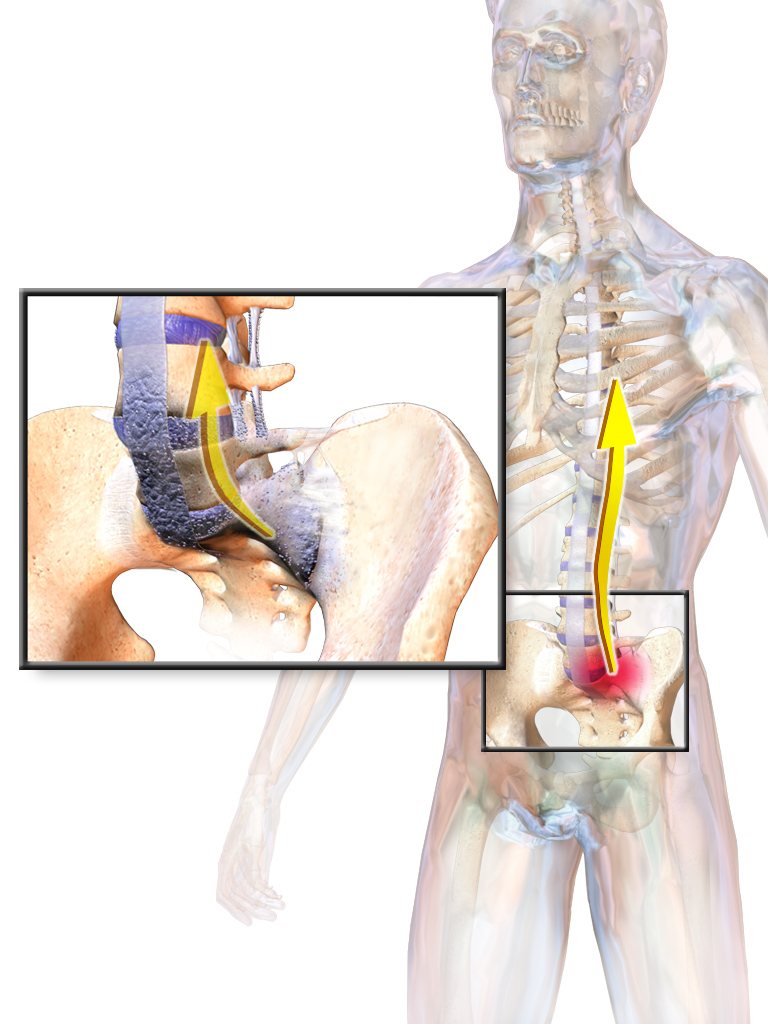
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of arthritis characterized by long-term inflammation of the joints of the spine typically where the spine joins the pelvis. Occasionally areas affected may include other joints such as the shoulders or hips, eye and bowel problems may occur as well as back pain. Joint mobility in the affected areas generally worsens over time. Although the cause of ankylosing spondylitis is unknown, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. More than 85% of those affected in the UK have a specific human leukocyte antigen known as the HLA-B27 antigen. The underlying mechanism is believed to be autoimmune or autoinflammatory. Diagnosis is typically based on the symptoms with support from medical imaging and blood tests. AS is a type of seronegative spondyloarthropathy, meaning that tests show no presence of rheumatoid factor (RF) antibodies. There is no known cure for AS. Treatments may include medication, exerc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogens
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ. The term ''pathogen'' came into use in the 1880s. Typically, the term ''pathogen'' is used to describe an ''infectious'' microorganism or agent, such as a virus, bacterium, protozoan, prion, viroid, or fungus. Small animals, such as helminths and insects, can also cause or transmit disease. However, these animals are usually referred to as parasites rather than pathogens. The scientific study of microscopic organisms, including microscopic pathogenic organisms, is called microbiology, while parasitology refers to the scientific study of parasites and the organisms that host them. There are several pathways through which pathogens can invade a host. The principal pathways have different episodic time frames, but soil has the long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. The term ''antigen'' originally referred to a substance that is an antibody generator. Antigens can be proteins, peptides (amino acid chains), polysaccharides (chains of monosaccharides/simple sugars), lipids, or nucleic acids. Antigens are recognized by antigen receptors, including antibodies and T-cell receptors. Diverse antigen receptors are made by cells of the immune system so that each cell has a specificity for a single antigen. Upon exposure to an antigen, only the lymphocytes that recognize that antigen are activated and expanded, a process known as clonal selection. In most cases, an antibody can only react to and bind one specific antigen; in some instances, however, antibodies may cross-reactivity, cross-react and bind more tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-protein
Self-protein refers to all proteins endogenously produced by DNA-level transcription and translation within an organism of interest. This does not include proteins synthesized due to viral infection, but may include those synthesized by commensal bacteria within the intestines. Proteins that are not created within the body of the organism of interest, but nevertheless enter through the bloodstream, a breach in the skin, or a mucous membrane, may be designated as “non-self” and subsequently targeted and attacked by the immune system. Tolerance to self-protein is crucial for overall wellbeing; when the body erroneously identifies self-proteins as “non-self”, the subsequent immune response against endogenous proteins may lead to the development of an autoimmune disease. Examples Of note, the list provided above is not exhaustive; the list does not mention all possible proteins targeted by the provided autoimmune diseases. Identification by the immune system Auto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alloimmunity
Alloimmunity (sometimes called isoimmunity) is an immune response to nonself antigens from members of the same species, which are called alloantigens or isoantigens. Two major types of alloantigens are blood group antigens and histocompatibility antigens. In alloimmunity, the body creates antibodies (called alloantibodies) against the alloantigens, attacking transfused blood, allotransplanted tissue, and even the fetus in some cases. Alloimmune (isoimmune) response results in graft rejection, which is manifested as deterioration or complete loss of graft function. In contrast, autoimmunity is an immune response to the self's own antigens. (The ''allo-'' prefix means "other", whereas the ''auto-'' prefix means "self".) Alloimmunization (isoimmunization) is the process of becoming alloimmune, that is, developing the relevant antibodies for the first time. Alloimmunity is caused by the difference between products of highly polymorphic genes, primarily genes of the major histocomp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune System
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells and objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy biological tissue, tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use humoral immunity, molecules and cell-mediated immunity, cells to perform their functions. Nearly all organisms have some kind of immune system. Bacteria have a rudimentary immune system in the form of enzymes that protect against bacteriophage, virus infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient eukaryote, plants and animal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Ehrlich
Paul Ehrlich (; 14 March 1854 – 20 August 1915) was a Nobel Prize-winning German physician and scientist who worked in the fields of hematology, immunology, and antimicrobial chemotherapy. Among his foremost achievements were finding a cure for syphilis in 1909 and inventing the precursor technique to Gram staining bacteria. The methods he developed for staining tissue made it possible to distinguish between different types of blood cells, which led to the ability to diagnose numerous blood diseases. His laboratory discovered arsphenamine (Salvarsan), the first effective medicinal treatment for syphilis, thereby initiating and also naming the concept of chemotherapy. Ehrlich popularized the concept of a magic bullet. He also made a decisive contribution to the development of an antiserum to combat diphtheria and conceived a method for standardizing therapeutic serums. In 1908, he received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his contributions to immunology. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-protein
Self-protein refers to all proteins endogenously produced by DNA-level transcription and translation within an organism of interest. This does not include proteins synthesized due to viral infection, but may include those synthesized by commensal bacteria within the intestines. Proteins that are not created within the body of the organism of interest, but nevertheless enter through the bloodstream, a breach in the skin, or a mucous membrane, may be designated as “non-self” and subsequently targeted and attacked by the immune system. Tolerance to self-protein is crucial for overall wellbeing; when the body erroneously identifies self-proteins as “non-self”, the subsequent immune response against endogenous proteins may lead to the development of an autoimmune disease. Examples Of note, the list provided above is not exhaustive; the list does not mention all possible proteins targeted by the provided autoimmune diseases. Identification by the immune system Auto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: CD8+ "killer" and CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presence of the cell surface proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoantibody
An autoantibody is an antibody (a type of protein) produced by the immune system that is directed against one or more of the individual's own proteins. Many autoimmune diseases (notably lupus erythematosus) are associated with such antibodies. Production Antibodies are produced by B cells in two ways: (i) randomly, and (ii) in response to a foreign protein or substance within the body. Initially, one B cell produces one specific kind of antibody. In either case, the B cell is allowed to proliferate or is killed off through a process called clonal deletion. Normally, the immune system is able to recognize and ignore the body's own healthy proteins, cells, and tissues, and to not overreact to non-threatening substances in the environment, such as foods. Sometimes, the immune system ceases to recognize one or more of the body's normal constituents as "self," leading to production of pathological autoantibodies. Autoantibodies may also play a nonpathological role; for instance they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroids
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signaling molecules. Hundreds of steroids are found in plants, animals and fungi. All steroids are manufactured in cells from the sterols lanosterol ( opisthokonts) or cycloartenol (plants). Lanosterol and cycloartenol are derived from the cyclization of the triterpene squalene. The steroid core structure is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in four " fused" rings: three six-member cyclohexane rings (rings A, B and C in the first illustration) and one five-member cyclopentane ring (the D ring). Steroids vary by the functional groups attached to this four-ring core and by the oxidation state of the rings. Sterols are forms of steroids with a hydroxy group at position three and a skeleton derived from cholest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |