|
Autofluorescence
Autofluorescence is the natural fluorescence of biological structures such as mitochondria and lysosomes, in contrast to fluorescence originating from artificially added fluorescent markers (fluorophores). The most commonly observed autofluorescencing molecules are NADPH and flavin group, flavins; the extracellular matrix can also contribute to autofluorescence because of the intrinsic properties of collagen and elastin. Generally, proteins containing an increased amount of the amino acids tryptophan, tyrosine, and phenylalanine show some degree of autofluorescence. Autofluorescence also occurs in non-biological materials found in many papers and textiles. Autofluorescence from U.S. paper money has been demonstrated as a means for discerning counterfeit currency from authentic currency. Microscopy Autofluorescence can be problematic in fluorescence microscopy. Light-emitting staining, stains (such as fluorescently labelled antibody, antibodies) are applied to Sample (material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescence
Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. When exposed to ultraviolet radiation, many substances will glow (fluoresce) with colored visible light. The color of the light emitted depends on the chemical composition of the substance. Fluorescent materials generally cease to glow nearly immediately when the radiation source stops. This distinguishes them from the other type of light emission, phosphorescence. Phosphorescent materials continue to emit light for some time after the radiation stops. This difference in duration is a result of quantum spin effects. Fluorescence occurs when a photon from incoming radiation is absorbed by a molecule, exciting it to a higher energy level, followed by the emission of light as the molecule returns to a lower energy state. The emitted light may have a longer wavelength and, therefore, a lower photon energy than the absorbed radi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescence Microscopy
A fluorescence microscope is an optical microscope that uses fluorescence instead of, or in addition to, scattering, reflection, and attenuation or absorption, to study the properties of organic or inorganic substances. A fluorescence microscope is any microscope that uses fluorescence to generate an image, whether it is a simple setup like an epifluorescence microscope or a more complicated design such as a confocal microscope, which uses optical sectioning to get better resolution of the fluorescence image. Principle The specimen is illuminated with light of a specific wavelength (or wavelengths) which is absorbed by the fluorophores, causing them to emit light of longer wavelengths (i.e., of a different color than the absorbed light). The illumination light is separated from the much weaker emitted fluorescence through the use of a spectral emission filter. Typical components of a fluorescence microscope are a light source (xenon arc lamp or mercury-vapor lamp are com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
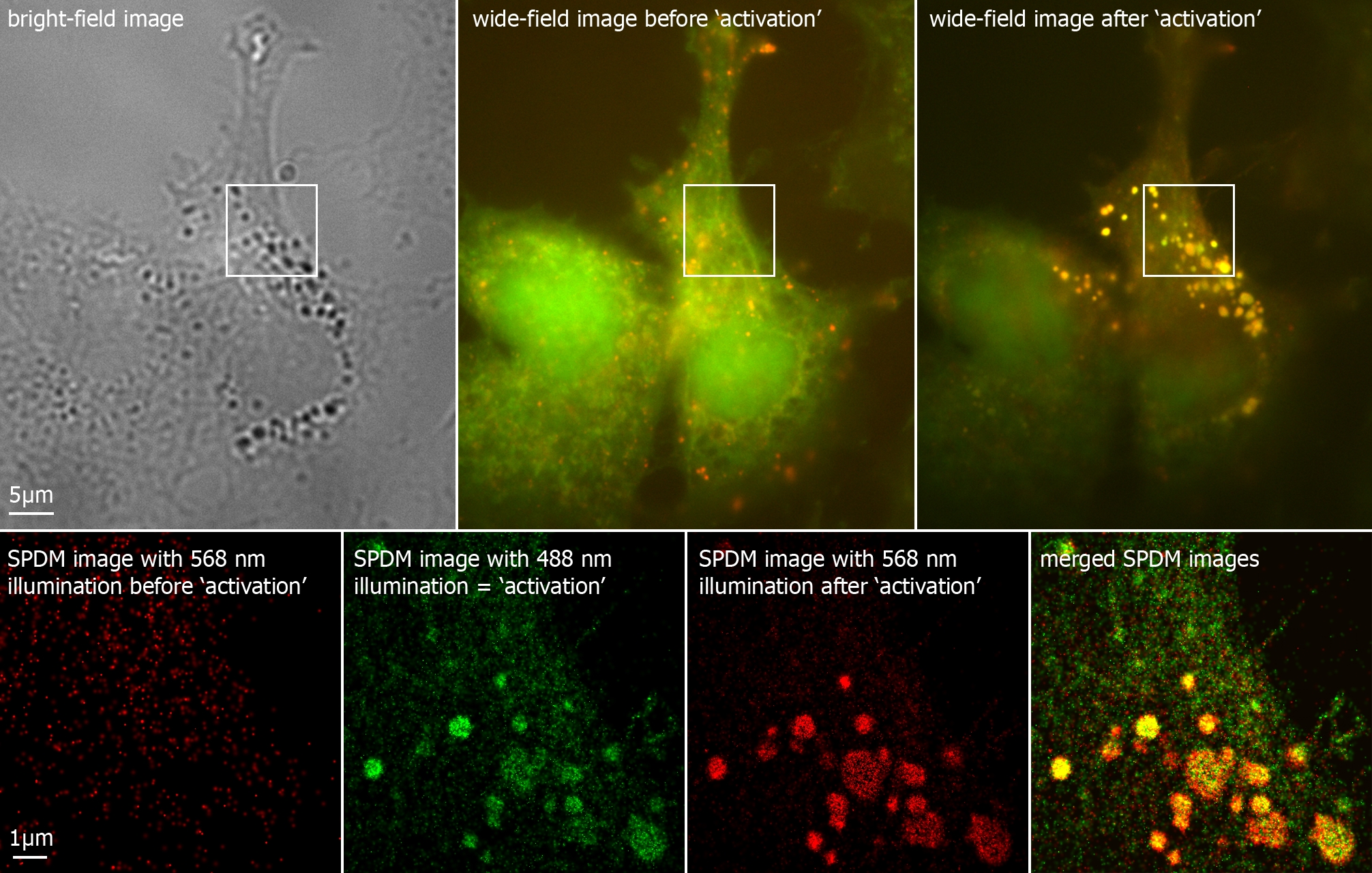
Super Resolution Microscopy
Super-resolution microscopy is a series of techniques in optical microscopy that allow such images to have resolutions higher than those imposed by the diffraction limit, which is due to the diffraction of light. Super-resolution imaging techniques rely on the near-field (photon-tunneling microscopy as well as those that use the Pendry Superlens and near field scanning optical microscopy) or on the far-field. Among techniques that rely on the latter are those that improve the resolution only modestly (up to about a factor of two) beyond the diffraction-limit, such as confocal microscopy with closed pinhole or aided by computational methods such as deconvolution or detector-based pixel reassignment (e.g. re-scan microscopy, pixel reassignment), the 4Pi microscope, and structured-illumination microscopy technologies such as SIM and SMI. There are two major groups of methods for super-resolution microscopy in the far-field that can improve the resolution by a much larger fact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiplexing
In telecommunications and computer networking, multiplexing (sometimes contracted to muxing) is a method by which multiple analog or digital signals are combined into one signal over a shared medium. The aim is to share a scarce resource—a physical transmission medium. For example, in telecommunications, several telephone calls may be carried using one wire. Multiplexing originated in telegraphy in the 1870s, and is now widely applied in communications. In telephony, George Owen Squier is credited with the development of telephone carrier multiplexing in 1910. The multiplexed signal is transmitted over a communication channel such as a cable. The multiplexing divides the capacity of the communication channel into several logical channels, one for each message signal or data stream to be transferred. A reverse process, known as demultiplexing, extracts the original channels on the receiver end. A device that performs the multiplexing is called a multiplexer (MUX), and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multispectral
Multispectral imaging captures image data within specific wavelength ranges across the electromagnetic spectrum. The wavelengths may be separated by filters or detected with the use of instruments that are sensitive to particular wavelengths, including light from frequencies beyond the visible light range (i.e. infrared and ultraviolet). It can allow extraction of additional information the human eye fails to capture with its visible receptors for red, green and blue. It was originally developed for military target identification and reconnaissance. Early space-based imaging platforms incorporated multispectral imaging technology to map details of the Earth related to coastal boundaries, vegetation, and landforms. Multispectral imaging has also found use in document and painting analysis. Multispectral imaging measures light in a small number (typically 3 to 15) of spectral bands. ''Hyperspectral imaging'' is a special case of spectral imaging where often hundreds of contig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Imaging
Medical optical imaging is the use of light as an investigational imaging technique for medical applications, pioneered by American Physical Chemist Britton Chance. Examples include optical microscopy, spectroscopy, endoscopy, scanning laser ophthalmoscopy, laser Doppler imaging, optical coherence tomography, and transdermal optical imaging. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, similar phenomena occur in X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves. Optical imaging systems may be divided into diffusive and ballistic imaging systems. A model for photon migration in turbid biological media has been developed by Bonner et al. Such a model can be applied for interpretation data obtained from laser Doppler blood-flow monitors and for designing protocols for therapeutic excitation of tissue chromophores. Diffusive optical imaging Diffuse optical imaging (DOI) is a method of imaging using near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) or fluorescence-based methods. When used to create 3D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function (biology), function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are associated with specific signs and symptoms. A disease may be caused by external factors such as pathogens or by internal dysfunctions. For example, internal dysfunctions of the immune system can produce a variety of different diseases, including various forms of immunodeficiency, hypersensitivity, allergy, allergies, and autoimmune disorders. In humans, ''disease'' is often used more broadly to refer to any condition that causes pain, Abnormality (behavior), dysfunction, distress (medicine), distress, social problems, or death to the person affected, or similar problems for those in contact with the person. In this broader sense, it sometimes includes injury in humans, injuries, disability, disabilities, Disorder (medicine) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Glycation End-product
Advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) are proteins or lipids that become Glycation, glycated as a result of exposure to sugars. They are a bio-marker implicated in aging and the development, or worsening, of many degenerative diseases, such as diabetes, atherosclerosis, chronic kidney disease, and Alzheimer's disease. Dietary sources Animal-derived foods that are high in fat and protein are generally AGE-rich and are prone to further AGE formation during cooking. However, only low molecular weight AGEs are absorbed through diet, and vegetarians have been found to have higher concentrations of overall AGEs compared to non-vegetarians. Therefore, it is unclear whether dietary AGEs contribute to disease and aging, or whether only endogenous AGEs (those produced in the body) matter. This does not free diet from potentially negatively influencing AGE, but potentially implies that dietary AGE may deserve less attention than other aspects of diet that lead to elevated Blood sugar level, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation. Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different developmental origin, structure and chemical composition. The adjective cutaneous means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'' 'skin'). In mammals, the skin is an organ of the integumentary system made up of multiple layers of ectodermal tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments, and internal organs. Skin of a different nature exists in amphibians, reptiles, and birds. Skin (including cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues) plays crucial roles in formation, structure, and function of extraskeletal apparatus such as horns of bovids (e.g., cattle) and rhinos, cervids' antlers, giraffids' ossicones, armadillos' osteoderm, and os penis/ os clitoris. All mammals have some hair on their skin, even marine mammals like whales, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytotoxicity
Cytotoxicity is the quality of being toxic to cells. Examples of toxic agents are toxic metals, toxic chemicals, microbe neurotoxins, radiation particles and even specific neurotransmitters when the system is out of balance. Also some types of drugs, e.g alcohol, and some venom, e.g. from the puff adder (''Bitis arietans'') or brown recluse spider (''Loxosceles reclusa'') are toxic to cells. Cell physiology Treating cells with the cytotoxic compound can result in a variety of prognoses. The cells may undergo necrosis, in which they lose membrane integrity and die rapidly as a result of cell lysis. The cells can stop actively growing and dividing (a decrease in cell viability), or the cells can activate a genetic program of controlled cell death (apoptosis). Cells undergoing necrosis typically exhibit rapid swelling, lose membrane integrity, shut down metabolism, and release their contents into the environment. Cells that undergo rapid necrosis in vitro do not have sufficient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagnosis
Diagnosis (: diagnoses) is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in a lot of different academic discipline, disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine "causality, cause and effect". In systems engineering and computer science, it is typically used to determine the causes of symptoms, mitigations, and solutions. Computer science and networking * Bayesian network * Complex event processing * Diagnosis (artificial intelligence) * Event correlation * Fault management * Fault tree analysis * Grey problem * RPR problem diagnosis * Remote diagnostics * Root cause analysis * Troubleshooting * Unified Diagnostic Services Mathematics and logic * Bayesian probability * Hickam's dictum, Block Hackam's dictum * Occam's razor * Regression analysis#Regression diagnostics, Regression diagnostics * Sutton's law Medicine * Medical diagnosis * Molecular diagnostics Methods * CDR computerized assessment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |