|
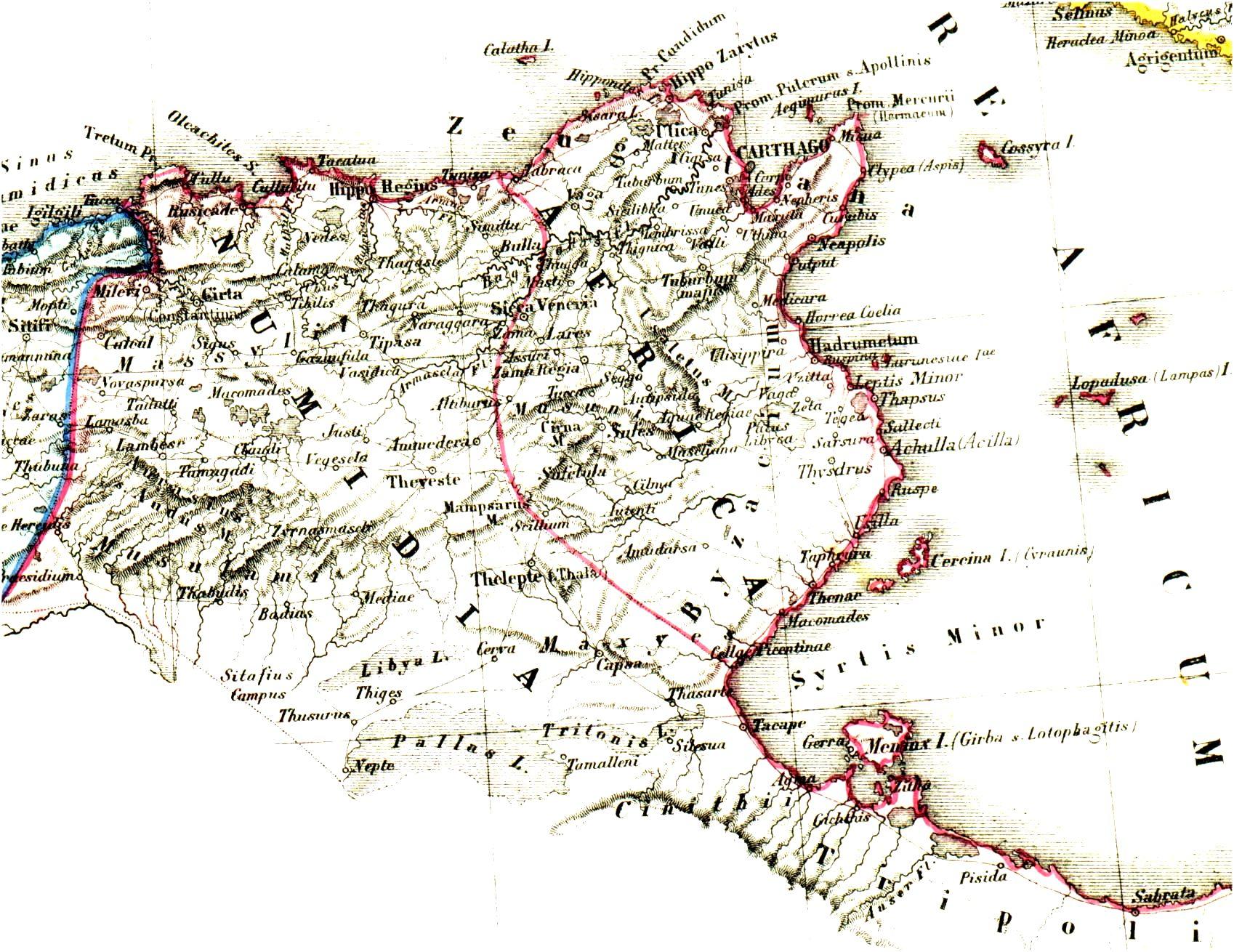
Austuriani
The Austuriani or Austoriani were a Berber people who lived along the frontier of the Roman Empire in Africa. They appear as raiders and enemies in Roman sources between the fourth and sixth centuries. History Austuriani first appear in the historical record in the years 363–365, when they devastated the Roman province of Tripolitania with "more violence than usual", according to Ammianus Marcellinus. These attacks were a response to the execution of the Austurian leader Stachao, who had been arrested by the Romans for spying. The regions around Lepcis and Oea were especially hard hit. The devastation mainly affected the countryside and involved the destruction of fields and orchards. A slightly earlier inscription from Lepcis referring to the "arrogance of the barbarians" may have the Austuriani in mind. Their depredations lasted years. According to Philostorgius, the Auxourianoi lived between the Libyans and the Afri. Later in the century, they raided as far west as Africa Pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laguatan
The Laguatan () was a Berber clan that inhabited the Cyrenaica area during the Roman period. They have been described as primarily raiders and nomadic, but others consider them a settled group who also raided. The Laguatan emerged in the late 3rd century, when the first groups started a westward migration from their original homes in the Libyan Desert. Under the label of Austuriani (probably reflecting a then-dominant sub-tribe) they are recorded as raiding the Cyrenaica and Tripolitania in the 4th century, and in the 520s, under their leader Cabaon, they scored a major victory over the Vandals, gaining effective independence from them. In the 540s, they played a major role in the tribal wars against the Byzantines, until finally defeated by John Troglita. Procopius of Caesarea (''Vandalic War'' II.21.2 & II.28.47) calls them the Leuathae (), while Flavius Cresconius Corippus calls them Ilaguas and Laguantan. According to Corippus, they were still pagan, and worshipped Gurzil, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berbers
Berbers, or the Berber peoples, also known as Amazigh or Imazighen, are a diverse grouping of distinct ethnic groups indigenous to North Africa who predate the arrival of Arab migrations to the Maghreb, Arabs in the Maghreb. Their main connections are identified by their usage of Berber languages, most of them mutually unintelligible, which are part of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. They are indigenous peoples, indigenous to the Maghreb region of North Africa, where they live in scattered communities across parts of Morocco, Algeria, Libya, and to a lesser extent Tunisia, Mauritania, northern Mali and northern Niger. Smaller Berber communities are also found in Burkina Faso and Egypt's Siwa Oasis. Descended from Stone Age tribes of North Africa, accounts of the Imazighen were first mentioned in Egyptian hieroglyphs, Ancient Egyptian writings. From about 2000 BC, Berber languages spread westward from the Nile, Nile Valley across the northern Sahara int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopédie Berbère
''Encyclopédie berbère'' (English: ''Berber Encyclopaedia'') is a French-language encyclopaedia dealing with subjects related to the Berber peoples (''Imazighen'' in Berber language), published both in print editions and in a partial online version. It was launched in 1984 under the aegis of UNESCO and was originally published by Editions Edisud. Its first editor-in-chief was Gabriel Camps. After his death in 2002, he was succeeded by Salem Chaker, Professor of Berber languages at the Aix-Marseille University Aix-Marseille University (AMU; ; formally incorporated as ) is a Public university, public research university located in the Provence region of southern France. It was founded in 1409 when Louis II of Anjou, List of rulers of Provence, Count of .... Up to 2013, volumes 1 to 36 (Oryx - Ozoutae) have been published online through OpenEdition.org. The online site allows part of the encyclopedia to be viewed in full text and in PDF and offers a search function to key ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yves Modéran
Yves Modéran (1955 – 1 July 2010, Paris) was a French historian, a professor of Roman history at the University of Caen Normandy. Agrégé d'histoire in 1978, he was a specialist of North Africa during Antiquity and later, in particular of the Vandals period. He took part to the excavations at Bulla Regia as part of studies organized by the École française de Rome. Works (partial list) *1987: ''"Qui montana Gurubi colunt". Corrippe et le mythe des Maures du cap Bon'', MEFRA, volume 99, n°99-2, (pp. 963-989Read online *1989: ''Gildon, les Maures et l'Afrique romaine'', MEFRA, volume 101, n°101-2, (pp. 821-872Read online *1993: ''La chronologie de la Vie de saint Fulgence de Ruspe et ses incidences sur l'histoire de l'Afrique vandale'', MEFRA, volume 105, n°105-1, (pp. 135-188Read online *2003: ''Les Maures et l'Afrique romaine, IVe–VIIe.'', ed. '' Bibliothèque des Ecoles françaises d'Athènes et de Rome'' *2003: ''L'Empire romain tardif (235-395)'', � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Mattingly (archaeologist)
David John Mattingly, FBA (born 18 May 1958) is an archaeologist and historian of the Roman world. He is currently Professor of Roman Archaeology at the University of Leicester. Biography Mattingly's grandfather, Harold Mattingly, was Keeper of the Department of Coins and Medals at the British Museum, and his father, Harold B. Mattingly, was Professor of Ancient History at Leeds University. He received a Bachelor of Arts (BA) in history at the University of Manchester, and later a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) from the same university, under the supervision of Barri Jones. His doctoral thesis was titled "Tripolitania: A comparative study of a Roman frontier province", and was submitted in 1984. He was then a British Academy Post-doctoral fellow at the Institute of Archaeology, in Oxford until 1989. He was then Assistant Professor at the University of Michigan in the United States. At Leicester University he was first Lecturer, then Reader (1995), and most recently Professor ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marmarides
Marmarica (, ) in Greco-Roman geography, ancient geography was a littoral area in Ancient Libya, located between ''Cyrenaica'' and ''Egypt (Roman province), Aegyptus''. It corresponds to what is now the Libya and Egypt frontier, including the towns of Bomba, Libya, Bomba (ancient ''Phthia''), Timimi (ancient ''Paliurus''), Tobruk (ancient ''Antipyrgus''), Acroma (ancient ''Gonia''), Bardia, Bardiya, Sallum, As-Salum, and Sidi Barrani (ancient ''Zygra''). The territory stretched to the far south, encompassing the Siwa Oasis, which at the time was known for its sanctuary to the deity Amun. The eastern part of Marmarica, by some geographers considered a separate district between Marmarica and Aegyptus, was known as ''Libycus Nomus''. In late antiquity, Marmarica was also known as ''Libya Inferior'', while Cyrenaica was known as ''Libya Superior''. ''Libya'' is found in Africa and is located west of the Nile, more precisely west of the mouth of the Nile at Canopus, Egypt, Canopus. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gurzil
Gurzil was an important ancient Berber deity. He is known from two sources, the Latin poem ''Iohannis'' by the 6th-century Christian Roman poet Corippus and a Neo-Punic inscription from Lepcis Magna.A. F. Elmayer, "The Libyan God Gurzil in a Neo-Punic Inscription from Tripolitania", ''Libyan Studies'' 13 (1982), pp. 49–50. According to Corippus, the Laguatan of Tripolitania carried a representation of Gurzil in the form of a bull into battle against the Romans when they revolted along with the Austurii in AD 546. They regarded Gurzil as the offspring of Amun, presumably the Amun whose temple was at Siwa, and a cow. Corippus also mentions idols of wood and metal, presumably also images of Gurzil. After several battles the Laguatan and their allies were defeated. Ierna, the chief and high priest of the Laguatan, was killed while trying to rescue the image of Gurzil. The image was destroyed. The combination of royal and priestly functions in Ierna is not otherwise attested ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Troglita
John Troglita (, ) was a 6th-century Byzantine Empire, Byzantine general. He participated in the Vandalic War and served in North Africa as a regional military governor during the years 533–538, before being sent east to the wars with the Sassanid Empire, Sassanid Persians. As ''dux Mesopotamiae'', Troglita distinguished himself in several battles, and was noticed by agents of the Byzantine emperor, Justinian I (reign, r. 527–565). In summer 546, Justinian chose John Troglita to assume overall command of Byzantine forces in Africa, where a succession of revolts by the indigenous Berbers, Moorish tribes and within the imperial army itself had seriously reduced the Byzantine position. Troglita quickly secured an initial victory in the winter of 546/547 against the Moors of Byzacena, but was defeated in summer 547 by the tribes of Tripolitania, and Africa was once again laid open to destructive raids. Troglita reorganized his army and secured the assistance of some tribal leaders, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Sidra
The Gulf of Sidra (), also known as the Gulf of Sirte (), is a body of water in the Mediterranean Sea on the northern coast of Libya, named after the oil port of Sidra or the city of Sirte. It was also historically known as the Great Sirte or Greater Syrtis (; ; contrasting with Syrtis Minor on the coast of Tunisia). Geography The Gulf of Sidra or Sirte has been a major center for tuna fishing in the Mediterranean for centuries. It gives its name to the city of Sirte situated on its western coast. The gulf measures from the promontory of Boreum (now Ras Teyonas) on the east side to the promontory of Cephalae (Ras Kasr Hamet) on the west. The greatest extension of the gulf inland is land inward and it occupies an area of 57,000 square kilometres. History Ancient history In ancient literature, the Syrtes (the Greater, or , in the eastern and the Lesser, or , in the western part of the Gulf) were notorious sandbanks, which sailors always took pains to avoid. The local ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corippus
Flavius Cresconius Corippus (floruit 565) was a Roman African epic poet who flourished under East Roman emperors Justinian I and Justin II. His major works are the epic poem '' Iohannis'', a panegyric called "Panegyric of Anastasius", and a poem in praise of the Emperor Justin II, ''In laudem Iustini minoris''. Corippus was probably the last important Latin author of Late Antiquity. Biography Flavius Cresconius Corippus' name is known on a basis of just one document. He was a native of Africa, and in one of the medieval manuscripts is called ''africanus grammaticus''. He has sometimes been identified, but on insufficient grounds, with Cresconius Africanus, a Catholic bishop (7th century), author of a ''Concordia Canonum'', or collection of the laws of the church. Nothing is known of Corippus beyond what is contained in his own poems. He appears to have held the office of tribune or notary ('' scriniarius'') under Anastasius, imperial treasurer and chamberlain of Justinian I, at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iohannis (epic Poem)
{{given name, type=both ...
Iohannis is both a surname and a given name. Notable people with the name include: Given name * Iohannis de Lignano, Italian jurist * Iohannis de Serravalle, Italian Franciscan and humanist * Iohannis Eckii, Latinized name of Johann Maier von Eck Surname * Carmen Iohannis, first lady of Romania * Klaus Iohannis, the fifth president of Romania See also * Johannis (other) * Ioannis * Joannis * Alternate forms for the name John John ( ) is a common male name in the English language ultimately of Hebrew origin. The English form is from Middle English ''Ioon'', ''Ihon'', ''Iohn, Jan'' (mid-12c.), itself from Old French ''Jan'', ''Jean'', ''Jehan'' (Modern French ''Jean ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |