|
Austro-Marxism
Austromarxism (also stylised as Austro-Marxism) was a Marxist theoretical current, led by Victor Adler, Otto Bauer, Karl Renner, Max Adler and Rudolf Hilferding, members of the Social Democratic Workers' Party of Austria in Austria-Hungary and the First Austrian Republic, and later supported by Austrian-born revolutionary and assassin of the Imperial Minister-President Count von Stürgkh, Friedrich Adler. It is known for its theory of nationality and nationalism, and its attempt to conciliate it with socialism in the imperial context. More generally, the Austromarxists strove to achieve a synthesis between social democracy and revolutionary socialism. Uniquely, Austromarxists posited that class consciousness in the working class could be achieved more organically through the maintenance of national autonomy, in contrast to the internationalist perspective and the notion of the party vanguard popular in orthodox Marxist circles elsewhere in Europe. Overview Beginning in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SDAPÖ
The Social Democratic Party of Austria (german: Sozialdemokratische Partei Österreichs , SPÖ), founded and known as the Social Democratic Workers' Party of Austria (german: link=no, Sozialdemokratische Arbeiterpartei Österreichs, SDAPÖ) until 1945 and later the Socialist Party of Austria (german: link=no, Sozialistische Partei Österreichs) until 1991, is a social-democratic political party in Austria. Founded in 1889, it is the oldest extant political party in Austria. Along with the Austrian People's Party (ÖVP), it is one of the country's two traditional major parties. It is positioned on the centre-left on the political spectrum. Since November 2018, the party has been led by Pamela Rendi-Wagner. It is currently the second largest of five parties in the National Council, with 40 of the 183 seats, and won 21.2% of votes cast in the 2019 legislative election. It holds seats in the legislatures of all nine states; of these, it is the largest party in three ( Burgenlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marxist
Marxism is a left-wing to far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand class relations and social conflict and a dialectical perspective to view social transformation. It originates from the works of 19th-century German philosophers Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. As Marxism has developed over time into various branches and schools of thought, no single, definitive Marxist theory exists. In addition to the schools of thought which emphasize or modify elements of classical Marxism, various Marxian concepts have been incorporated and adapted into a diverse array of social theories leading to widely varying conclusions. Alongside Marx's critique of political economy, the defining characteristics of Marxism have often been described using the terms dialectical materialism and historical materialism, though these terms were coined after Marx's death and their tenets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Renner
Karl Renner (14 December 1870 – 31 December 1950) was an Austrian politician and jurist of the Social Democratic Workers' Party of Austria. He is often referred to as the "Father of the Republic" because he led the first government of German-Austria and the First Austrian Republic in 1919 and 1920, and was once again decisive in establishing the present Second Republic after the fall of Nazi Germany in 1945, becoming its first President after World War II (and fourth overall). Early life Renner was born the 18th child of an ethnic German family of poor wine-growers in Unter-Tannowitz (present-day Dolní Dunajovice in the Czech Republic), then part of the Margraviate of Moravia, a crown land of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Because of his intelligence, he was allowed to attend a selective '' gymnasium'' in nearby Nikolsburg (Mikulov), where one of his teachers was Wilhelm Jerusalem. From 1890 to 1896 he studied law at the University of Vienna. In 1895 he was one of the foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labour And Socialist International
The Labour and Socialist International (LSI; german: Sozialistische Arbeiter-Internationale, label= German, SAI) was an international organization of socialist and labour parties, active between 1923 and 1940. The group was established through a merger of the rival Vienna International and the former Second International, based in London, and was the forerunner of the present-day Socialist International. The LSI had a history of rivalry with the Communist International (Comintern), with which it competed over the leadership of the international socialist and labour movement. However, unlike the Comintern, the LSI maintained no direct control over the actions of its sections, being constituted as a federation of autonomous national parties. History Founding Despite the hostility expressed by the Communist International, the left wing of the social democratic movement sought an international "union of the whole proletariat" through 1922.Julius Braunthal, ''History of the Intern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis B
Louis may refer to: * Louis (coin) * Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name * Louis (surname) * Louis (singer), Serbian singer * HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy See also Derived or associated terms * Lewis (other) * Louie (other) * Luis (other) * Louise (other) * Louisville (other) * Louis Cruise Lines * Louis dressing, for salad * Louis Quinze, design style Associated names * * Chlodwig, the origin of the name Ludwig, which is translated to English as "Louis" * Ladislav and László - names sometimes erroneously associated with "Louis" * Ludovic, Ludwig Ludwig may refer to: People and fictional characters * Ludwig (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters * Ludwig (surname), including a list of people * Ludwig Ahgren, or simply Ludwig, American YouTube live streamer and co ..., Ludwick, Ludwik, names sometimes translated to English as "Louis" {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Working Union Of Socialist Parties
The International Working Union of Socialist Parties (IWUSP; also known as the 2½ International or the Vienna International; german: Internationale Arbeitsgemeinschaft Sozialistischer Parteien, IASP) was a political international for the co-operation of socialist parties. History The IWUSP was founded on February 27, 1921, at a conference in Vienna, Austria, by ten parties, including the Independent Social Democratic Party of Germany (USPD), the French Section of the Workers' International (SFIO), the Independent Labour Party (ILP), the Social Democratic Party of Switzerland (SPS), the Social Democratic Party of Austria (SPÖ), and the Federation of Romanian Socialist Parties (FPSR, created by splinter groups of the Socialist Party of Romania). In April 1921, it was joined by the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party. The Maximalist faction of the Italian Socialist Party (PSI) also joined. Members The secretary of the IWUSP was the Austrian Friedrich Adler of the SPÖ; ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second International
The Second International (1889–1916) was an organisation of Labour movement, socialist and labour parties, formed on 14 July 1889 at two simultaneous Paris meetings in which delegations from twenty countries participated. The Second International continued the work of the dissolved International Workingmen's Association, First International, though excluding the powerful Anarcho-syndicalism, anarcho-syndicalist movement. While the international had initially declared its opposition to all War, warfare between European powers, most of the major European parties ultimately chose to support their respective states in World War I. After splitting into pro-Allies of World War I, Allied, pro-Central Powers, and Antimilitarism, antimilitarist factions, the international ceased to function. After the war, the remaining factions of the international went on to found the Labour and Socialist International, the International Working Union of Socialist Parties, and the Communist Internation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comintern
The Communist International (Comintern), also known as the Third International, was a Soviet Union, Soviet-controlled international organization founded in 1919 that advocated world communism. The Comintern resolved at its Second Congress to "struggle by all available means, including armed force, for the overthrow of the international bourgeoisie and the creation of an international Soviet republic (system of government), Soviet republic as a transition stage to the complete abolition of the state". The Comintern was preceded by the 1916 dissolution of the Second International. The Comintern held seven World Congresses in Moscow between 1919 and 1935. During that period, it also conducted thirteen Enlarged Plenums of its governing Executive Committee of the Communist International, Executive Committee, which had much the same function as the somewhat larger and more grandiose Congresses. Joseph Stalin, leader of the Soviet Union, dissolved the Comintern in 1943 to avoid antag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586, it is the second oldest university press after Cambridge University Press. It is a department of the University of Oxford and is governed by a group of 15 academics known as the Delegates of the Press, who are appointed by the vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho. For the last 500 years, OUP has primarily focused on the publication of pedagogical texts a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
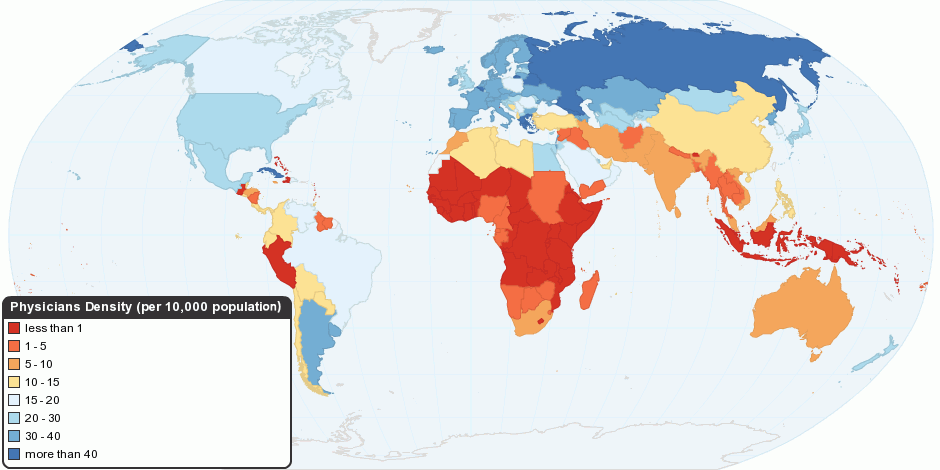
Healthcare
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health professionals and allied health fields. Medicine, dentistry, pharmacy, midwifery, nursing, optometry, audiology, psychology, occupational therapy, physical therapy, athletic training, and other health professions all constitute health care. It includes work done in providing primary care, secondary care, and tertiary care, as well as in public health. Access to health care may vary across countries, communities, and individuals, influenced by social and economic conditions as well as health policies. Providing health care services means "the timely use of personal health services to achieve the best possible health outcomes". Factors to consider in terms of health care access include financial limitations (such as insurance cover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neokantian
In late modern continental philosophy, neo-Kantianism (german: Neukantianismus) was a revival of the 18th-century philosophy of Immanuel Kant. The Neo-Kantians sought to develop and clarify Kant's theories, particularly his concept of the "thing-in-itself" and his moral philosophy. It was influenced by Arthur Schopenhauer's critique of the Kantian philosophy in his work '' The World as Will and Representation'' (1818), as well as by other post-Kantian philosophers such as Jakob Friedrich Fries and Johann Friedrich Herbart. Origins The "back to Kant" movement began in the 1860s, as a reaction to the German materialist controversy in the 1850s. In addition to the work of Hermann von Helmholtz and Eduard Zeller, early fruits of the movement were Kuno Fischer's works on Kant and Friedrich Albert Lange's ''History of Materialism'' ('' Geschichte des Materialismus'', 1873–75), the latter of which argued that transcendental idealism superseded the historic struggle between ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)