|
Australothyris
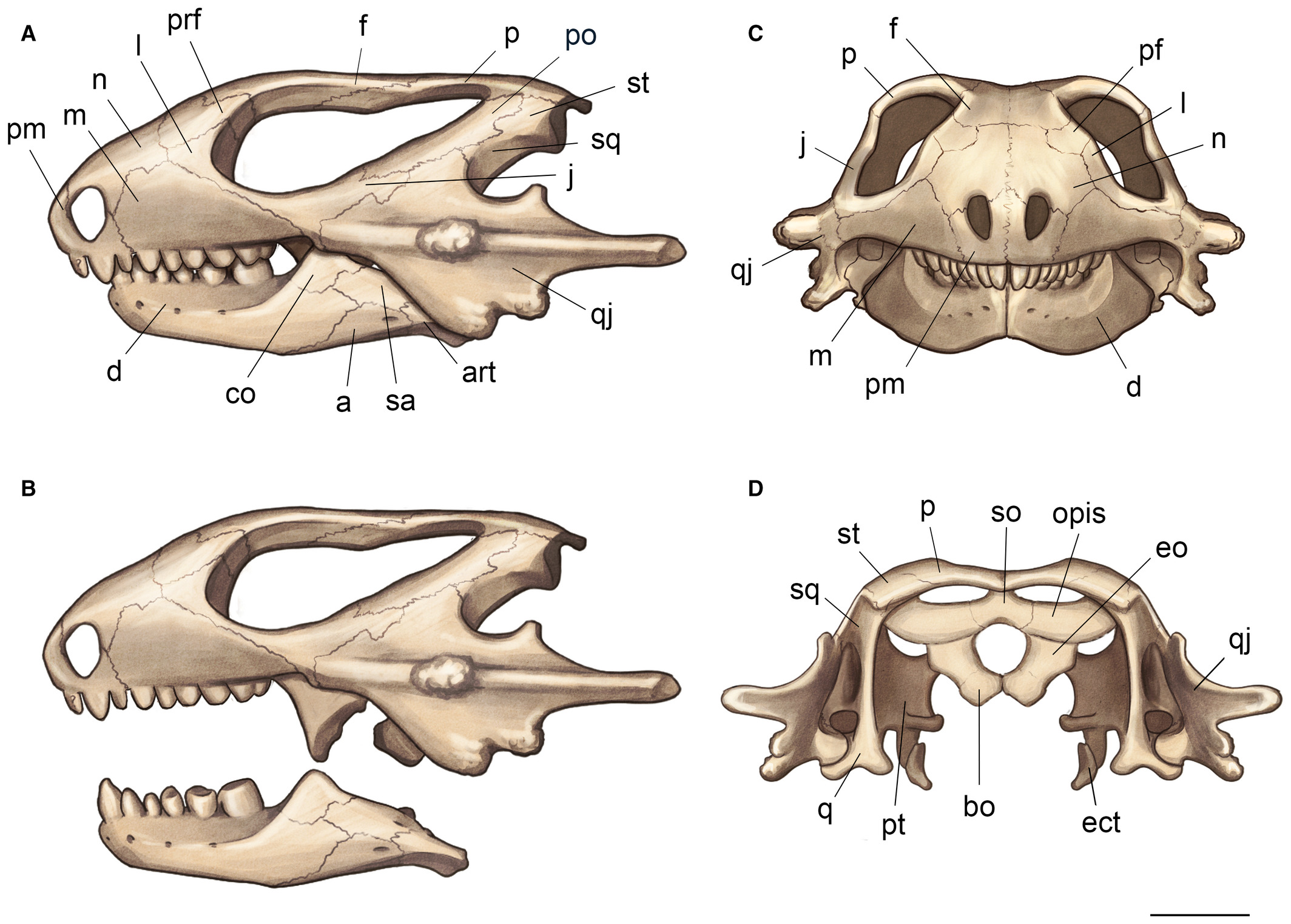
''Australothyris'' is an extinct genus of basal procolophonomorph parareptile known from the Middle Permian (middle Capitanian stage) of ''Tapinocephalus'' Assemblage Zone, South Africa. The type and only known species is ''Australothyris smithi''. As the most basal member of Procolophonomorpha, ''Australothyris'' helped to contextualize the origin of this major parareptile subgroup. It has been used to support the hypotheses that procolophonomorphs originated in Gondwana and ancestrally possess temporal fenestrae, due to its large and fully enclosed temporal fenestra and South African heritage. It also possessed several unique features, including a high tooth number, long postfrontal, small interpterygoid vacuity, and a specialized interaction between the stapes and quadrate. Discovery Australothyris is known from a single specimen discovered at the Beukesplaas farm by Robert Smith in 1995. The fossil site at the Beukesplaas farm contains a diverse parareptile and synapsid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microleter
''Microleter'' is an extinct genus of basal procolophonomorph parareptiles which lived in Oklahoma during the Early Permian period. The type and only known species is ''Microleter mckinzieorum''. ''Microleter'' is one of several parareptile taxa described from the Richards Spur fissure fills, and can be characterized from its high tooth count, lacrimal/ narial contact, short postfrontal, and slit-like temporal emargination edged by the postorbital, jugal, squamosal, and quadratojugal. Contrary to '' Australothyris'', which had a similar phylogenetic position as a basal procolophonomorph, ''Microleter'' suggests that early parareptile evolution occurred in Laurasia and that multiple lineages developed openings or emarginations in the temporal region. Discovery The only known specimen of ''Microleter'' is a well-preserved skull and lower jaw designated as OMNH 71306, the holotype specimen. It was found at the Dolese Brothers limestone quarry near Richards Spur in C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procolophonomorph
Procolophonomorpha is an order or clade containing most parareptiles. Many papers have applied various definitions to the name, though most of these definitions have since been considered synonymous with modern parareptile clades such as Ankyramorpha and Procolophonia. The current definition of Procolophonomorpha, as defined by Modesto, Scott, & Reisz (2009), is that of as a stem-based group containing '' Procolophon'' and all taxa more closely related to it than to '' Milleretta''. It constitutes a diverse assemblage that includes a number of lizard-like forms, as well as more diverse types such as the pareiasaurs. Lee 1995, 1996, 1997 argues that turtles evolved from pareiasaurs, but this view is no longer considered likely. Rieppel and deBraga 1996 and deBraga and Rieppel, 1997 argue that turtles evolved from sauropterygians, and there is both molecular and fossil ('' Pappochelys'') evidence for the origin of turtles among diapsid reptiles. Classification The following cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2009 In Paleontology
Arthropods Cephalopods Three new species of extinct Octopoda discovered in 2009. The species – '' Keuppia hyperbolaris'', ''Keuppia levante'', and ''Styletoctopus annae'' – lived about 95 million years ago, and bear a strong resemblance to modern octopuses, suggesting that the Octopoda order has remained relatively unchanged for tens of millions of years. The fossils included evidence of arms, muscles, rows of suckers, ink, and internal gills. The discovery was made by a team led by Dirk Fuchs of the Freie University, which is located at Berlin, Germany.Rare fossil octopuses found NBC News, March 18, 2009 The fossils were found at Hakel and Hadjoula, . [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Permian
The Guadalupian is the second and middle series/ epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico and Texas, and dates between 272.95 ± 0.5 – 259.1 ± 0.4 Mya. The series saw the rise of the therapsids, a minor extinction event called Olson's Extinction and a significant mass extinction called the end-Capitanian extinction event. The Guadalupian was previously known as the Middle Permian. Name and background The Guadalupian is the second and middle series or epoch of the Permian. Previously called Middle Permian, the name of this epoch is part of a revision of Permian stratigraphy for standard global correlation. The name "Guadalupian" was first proposed in the early 1900s, and approved by the International Subcommission on Permian Stratigraphy in 1996. References to the Middle Permian still exist. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanthanosuchoidea
Lanthanosuchoidea is an extinct superfamily of ankyramorph parareptiles from the middle Pennsylvanian to the middle Guadalupian epoch (Moscovian - Wordian stages) of Europe, North America and Asia. It was named by the Russian paleontologist Ivachnenko in 1980, and it contains two families Acleistorhinidae and Lanthanosuchidae. Phylogeny Lanthanosuchoidea is a node-based taxon defined in 1997 as "the most recent common ancestor of '' Lanthanosuchus'', '' Lanthaniscus'', and '' Acleistorhinus''". The cladogram below follows the topology from a 2011 analysis by Ruta ''et al.'' The cladogram below follows the topology from a 2016 analysis by MacDougall ''et al.'' However, the phylogenetic analysis conducted by Cisneros ''et al.'' (2021) did not recover a clade uniting lanthanosuchids and acleistorhinids to the exclusion of all other parareptiles. Instead, acleistorhinids were recovered as the sister group of the clade Procolophonia The Procolophonia are a subord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontal Bone
The frontal bone is a bone in the human skull. The bone consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, part of the bony orbital cavity holding the eye, and part of the bony part of the nose respectively. The name comes from the Latin word ''frons'' (meaning " forehead"). Structure of the frontal bone The frontal bone is made up of two main parts. These are the squamous part, and the orbital part. The squamous part marks the vertical, flat, and also the biggest part, and the main region of the forehead. The orbital part is the horizontal and second biggest region of the frontal bone. It enters into the formation of the roofs of the orbital and nasal cavities. Sometimes a third part is included as the nasal part of the frontal bone, and sometimes this is included with the squamous part. The nasal part is between the brow ridges, and ends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procolophonidae
Procolophonidae is an extinct family of small, lizard-like parareptiles known from the Late Permian to Late Triassic that were distributed across Pangaea, having been reported from Europe, North America, China, South Africa, South America, Antarctica and Australia. The most primitive procolophonids were likely insectiovous or omnivorous, more derived members of the clade developed bicusped molars, and were likely herbivorous feeding on high fiber vegetation or durophagous omnivores. Many members of the group are noted for spines projecting from the quadratojugal bone of the skull, which likely served a defensive purpose as well as possibly also for display. At least some taxa were likely fossorial A fossorial () animal is one adapted to digging which lives primarily, but not solely, underground. Some examples are badgers, naked mole-rats, clams, meerkats, and mole salamanders, as well as many beetles, wasps, and bees. Prehistoric eviden ... burrowers. While diverse d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbit (anatomy)
In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human, the volume of the orbit is , of which the eye occupies . The orbital contents comprise the eye, the orbital and retrobulbar fascia, extraocular muscles, cranial nerves II, III, IV, V, and VI, blood vessels, fat, the lacrimal gland with its sac and duct, the eyelids, medial and lateral palpebral ligaments, cheek ligaments, the suspensory ligament, septum, ciliary ganglion and short ciliary nerves. Structure The orbits are conical or four-sided pyramidal cavities, which open into the midline of the face and point back into the head. Each consists of a base, an apex and four walls."eye, human."Encyclopædia Britannica from Encyclopædia Britannica 2006 Ultimate Reference Suite DVD 2009 Openings There are two important foramina, or windows, two important f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prefrontal Bone
The prefrontal bone is a bone separating the lacrimal and frontal bones in many tetrapod skulls. It first evolved in the sarcopterygian clade Rhipidistia, which includes lungfish and the Tetrapodomorpha. The prefrontal is found in most modern and extinct lungfish, amphibians and reptiles. The prefrontal is lost in early mammaliaforms and so is not present in modern mammals either. In dinosaurs The prefrontal bone is a very small bone near the top of the skull, which is lost in many groups of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs and is completely absent in their modern descendants, the bird Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...s. Conversely, a well developed prefrontal is considered to be a primitive feature in dinosaurs. The prefrontal makes contact with several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanthanosuchus
''Lanthanosuchus'' is an extinct genus of parareptile from the Late Permian. It was found at Isheevo in Tatarstan The Republic of Tatarstan (russian: Республика Татарстан, Respublika Tatarstan, p=rʲɪsˈpublʲɪkə tətɐrˈstan; tt-Cyrl, Татарстан Республикасы), or simply Tatarstan (russian: Татарстан, tt .... ''Lanthanosuchus'' had a length of 75 cm. References Procolophonomorphs Permian reptiles of Asia Prehistoric reptile genera {{permian-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible (lower jaw), which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw. Structure In humans, the maxilla consists of: * The body of the maxilla * Four processes ** the zygomatic process ** the frontal process of maxilla ** the alveolar process ** the palatine process * three surfaces – anterior, posterior, medial * the Infraorbital foramen * the maxillary sinus * the incisive foramen Articulations Each maxilla articulates with nine bones: * two of the cranium: the frontal and ethmoid * seven of the face: the nasal, zygomatic, lacrimal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Name (zoology)
In zoological nomenclature, the specific name (also specific epithet or species epithet) is the second part (the second name) within the scientific name of a species (a binomen). The first part of the name of a species is the name of the genus or the generic name. The rules and regulations governing the giving of a new species name are explained in the article species description. For example, the scientific name for humans is ''Homo sapiens'', which is the species name, consisting of two names: ''Homo'' is the " generic name" (the name of the genus) and ''sapiens'' is the "specific name". Historically, ''specific name'' referred to the combination of what are now called the generic and specific names. Carl Linnaeus, who formalized binomial nomenclature, made explicit distinctions between specific, generic, and trivial names. The generic name was that of the genus, the first in the binomial, the trivial name was the second name in the binomial, and the specific the proper term fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)