|
August Toepler
August Joseph Ignaz Toepler (7 September 1836 – 6 March 1912) was a German chemist and physicist known for his experiments in electrostatics. Biography August Toepler was born on 7 September 1836. He studied chemistry at the Gewerbe-Institut Berlin (1855–1858) and graduated from the University of Jena in 1860. Later Toepler turned to experimental physics. August Toepler was a lecturer of chemistry and physics at the Academy Poppelsdorf (1859-1864). He received a chair of chemistry and chemical technology at the Polytechnic Institute of Riga and he hold this position between 1864 and 1868. In 1864, he applied Foucault's knife-edge test for telescope mirrors to the analysis of fluid flow and the shock wave. He named this new method schlieren photography, for which he is justifiably famous. He also developed the Toepler machine, an electrostatic influence machine (high voltage generator) in 1865, which would one day find use in early medical x-ray machines. Improved v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Influence Machine
An electrostatic generator, or electrostatic machine, is an electrical generator that produces ''static electricity'', or electricity at high voltage and low continuous current. The knowledge of static electricity dates back to the earliest civilizations, but for millennia it remained merely an interesting and mystifying phenomenon, without a theory to explain its behavior and often confused with magnetism. By the end of the 17th century, researchers had developed practical means of generating electricity by friction, but the development of electrostatic machines did not begin in earnest until the 18th century, when they became fundamental instruments in the studies about the new science of electricity. Electrostatic generators operate by using manual (or other) power to transform mechanical work into electric energy, or using electric currents. Manual electrostatic generators develop electrostatic charges of opposite signs rendered to two conductors, using only electric forces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1912 Deaths
Year 191 ( CXCI) was a common year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Apronianus and Bradua (or, less frequently, year 944 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 191 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Parthia * King Vologases IV of Parthia dies after a 44-year reign, and is succeeded by his son Vologases V. China * A coalition of Chinese warlords from the east of Hangu Pass launches a punitive campaign against the warlord Dong Zhuo, who seized control of the central government in 189, and held the figurehead Emperor Xian hostage. After suffering some defeats against the coalition forces, Dong Zhuo forcefully relocates the imperial capital from Luoyang to Chang'an. Before leaving, Dong Zhuo orders his troops to loot the tombs of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1836 Births
Events January–March * January 1 – Queen Maria II of Portugal marries Prince Ferdinand Augustus Francis Anthony of Saxe-Coburg-Gotha. * January 5 – Davy Crockett arrives in Texas. * January 12 ** , with Charles Darwin on board, reaches Sydney. ** Will County, Illinois, is formed. * February 8 – London and Greenwich Railway opens its first section, the first railway in London, England. * February 16 – A fire at the Lahaman Theatre in Saint Petersburg kills 126 people."Fires, Great", in ''The Insurance Cyclopeadia: Being an Historical Treasury of Events and Circumstances Connected with the Origin and Progress of Insurance'', Cornelius Walford, ed. (C. and E. Layton, 1876) p76 * February 23 – Texas Revolution: The Battle of the Alamo begins, with an American settler army surrounded by the Mexican Army, under Santa Anna. * February 25 – Samuel Colt receives a United States patent for the Colt revolver, the first revolving barrel multishot firearm. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximilien Toepler
Maximilien August Topler (25 June 1870 – 14 March 1960) was a German physicist known for his work on electrostatics, sparks and Schlieren photography. His father was the physicist August Toepler August Joseph Ignaz Toepler (7 September 1836 – 6 March 1912) was a German chemist and physicist known for his experiments in electrostatics. Biography August Toepler was born on 7 September 1836. He studied chemistry at the Gewerbe-Insti .... Toepler's law (1906) states that the resistance of an electric arc at any time is inversely proportional to the charge which has flowed through the arc: :R(t)= where ''I(t)'' is the current in the arc discharge at time ''t'', and ''D'' is the gap between the electrodes. The parameter k_T is a constant whose value is 4 \times 10^ \, V \cdot s \cdot m^. References Toepler's law (PDF)High Voltage Engineering Fundamentals* Toepler, ''Annalen der Physik'', 1906; 4: 191. (original publication) {{DEFAULTSORT:Toepler, Maximilien 1870 birth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Léon Foucault
Jean Bernard Léon Foucault (, ; ; 18 September 1819 – 11 February 1868) was a French physicist best known for his demonstration of the Foucault pendulum, a device demonstrating the effect of Earth's rotation. He also made an early measurement of the speed of light, discovered eddy currents, and is credited with naming the gyroscope. Early years The son of a publisher, Foucault was born in Paris on 18 September 1819. After an education received chiefly at home, he studied medicine, which he abandoned in favour of physics due to a blood phobia. He first directed his attention to the improvement of Louis Daguerre's photographic processes. For three years he was experimental assistant to Alfred Donné (1801–1878) in his course of lectures on microscopic anatomy. With Hippolyte Fizeau he carried out a series of investigations on the intensity of the light of the sun, as compared with that of carbon in the arc lamp, and of lime in the flame of the oxyhydrogen blowpipe; on the inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
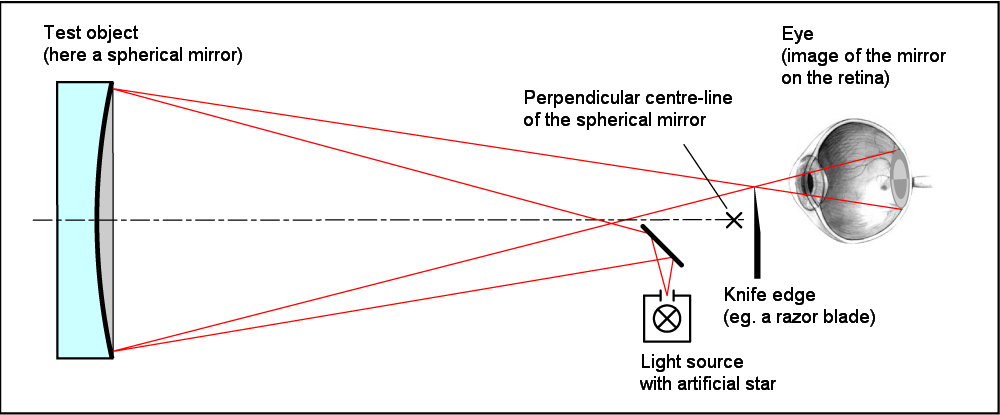
Foucault Knife-edge Test
The Foucault knife-edge test is an optical test to accurately measure the shape of concave curved mirrors. It is commonly used by amateur telescope makers for figuring primary mirrors in reflecting telescopes. It uses a relatively simple, inexpensive apparatus compared to other testing techniques. Overview The Foucault knife-edge test was described in 1858 by French physicist Léon Foucault as a way to measure conic shapes of optical mirrors. It measures mirror surface dimensions by reflecting light into a knife edge at or near the mirror's centre of curvature. In doing so, it only needs a tester which in its most basic 19th century form consists of a light bulb, a piece of tinfoil with a pinhole in it, and a razor blade to create the knife edge. The testing device is adjustable along the X-axis (knife cut direction) across the Y-axis (optical axis), and is usually equipped with measurable adjustment to 0.001 inch (25 µm) or better along lines parallel to the optical ax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schlieren Photography
Schlieren photography is a process for photographing fluid flow. Invented by the German physicist August Toepler in 1864 to study supersonic motion, it is widely used in aeronautical engineering to photograph the flow of air around objects. Classical optical system The classical implementation of an optical schlieren system uses light from a single collimated source shining on, or from behind, a target object. Variations in refractive index caused by density gradients in the fluid distort the collimated light beam. This distortion creates a spatial variation in the intensity of the light, which can be visualised directly with a shadowgraph system. Classical schlieren imaging systems appear in two configurations, using either one or two mirrors. In each case, a transparent object is illuminated with collimated or nearly-collimated light. Rays that are not deflected by the object proceed to their focal point, where they are blocked by a knife edge. Rays that are de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous city and state. A landlocked country, Austria is bordered by Germany to the northwest, the Czech Republic to the north, Slovakia to the northeast, Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west. The country occupies an area of and has a population of 9 million. Austria emerged from the remnants of the Eastern and Hungarian March at the end of the first millennium. Originally a margraviate of Bavaria, it developed into a duchy of the Holy Roman Empire in 1156 and was later made an archduchy in 1453. In the 16th century, Vienna began serving as the empire's administrative capital and Austria thus became the heartland of the Habsburg monarchy. After the dissolution of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Graz
The University of Graz (german: link=no, Karl-Franzens-Universität Graz, ), located in Graz, Austria, is the largest and oldest university in Styria, as well as the second-largest and second-oldest university in Austria. History The university was founded in 1585 by Archduke Charles II of Austria. The bull of 1 January 1586, published on 15 April 1586, was approved by Pope Sixtus V. For most of its existence it was controlled by the Catholic Church, and was closed in 1782 by Emperor Joseph II in an attempt to gain state control over educational institutions. Joseph II transformed it into a ''lyceum'', where civil servants and medical personnel were trained. In 1827 it was re-instituted as a university by Emperor Francis I, thus gaining the name ''Karl-Franzens-Universität'', meaning ''Charles Francis University''. Over 30,000 students are currently enrolled at the university. Academics The university is divided into six faculties, the two largest are the Faculty of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Holtz
Wilhelm Holtz (15 October 1836 – 27 September 1913) was a German physicist who was a native of Saatel bei Barth, Mecklenburg. Between 1857 and 1862, he studied physics and natural sciences in Berlin, Dijon and Edinburgh. Afterwards, he performed experiments with electricity in Berlin, and later became associated with research at the universities of Halle and Greifswald, where in 1884 he became a professor of physics. In 1865 Holtz invented the "Holtz electrostatic influence machine", an electrostatic induction generator that converted mechanical work into electrostatic energy, needing only an initial charge to begin operation. In the following years, Holtz made modifications, and in the process, manufactured several more of the devices. Electrostatic generators from this era were sometimes referred to as "Toepler-Holtz machines", being named in conjunction with German physicist August Toepler August Joseph Ignaz Toepler (7 September 1836 – 6 March 1912) was a German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |