|
August Bischler
August Bischler (29 April 1865 – 26 May 1957) was a Russian Empire-born ethnic Crimea German chemist who later emigrated to Switzerland. He discovered the Bischler–Möhlau indole synthesis reaction in 1892 and, together with Bernard Napieralski, discovered the Bischler–Napieralski reaction in 1893. Life He received his Ph.D. at the University of Zurich 1889 worked at the University of Zurich and from 1899 at the University of Basel. After becoming a Swiss citizen in 1925 he worked in the chemical industry in Geneva. Bernard Napieralski Bernard Napieralski was a Ph.D. student of Bischler at the University of Zurich in 1893. Napieralski was born in Ostrowy, Poland Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ..., 1861. References * 1865 births 1957 deaths Chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
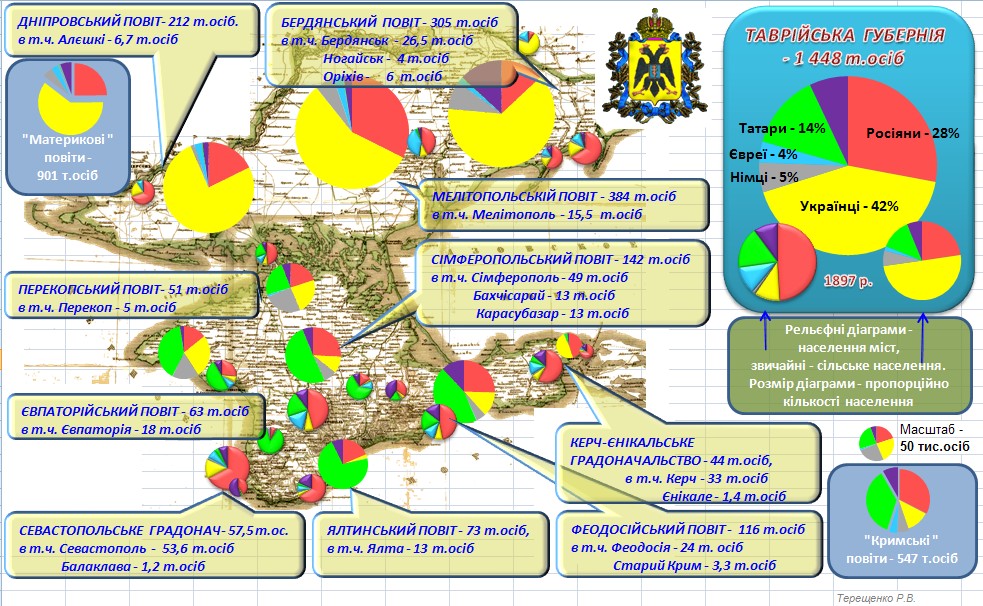
Taurida Governorate
The Taurida Governorate (russian: Тавріическая губернія, modern spelling , ; crh, script=Latn, Tavrida guberniyası, ) or the Government of Taurida, was a historical governorate of the Russian Empire. It included the Crimean Peninsula and the mainland between the lower Dnieper River and the coasts of the Black Sea and Sea of Azov. It was formed after the Taurida Oblast was abolished in 1802 in the course of Paul I's administrative reform of the southwestern territories that had been annexed from the Crimean Khanate. The governorate's centre was the city of Simferopol. The province was named after the ancient Greek name of Crimea - Taurida. Today the territory of the governorate is part of the Crimea, Kherson, and Zaporizhzhia regions of Ukraine. Administrative divisions The governorate comprised three counties ( uyezds) on the mainland: * Berdyansky Uyezd, centred in Berdyansk * Dneprovsky Uyezd, Oleshky * Melitopolsky Uyezd, Melitopol and five ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geneva
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevra ; rm, Genevra is the second-most populous city in Switzerland (after Zürich) and the most populous city of Romandy, the French-speaking part of Switzerland. Situated in the south west of the country, where the Rhône exits Lake Geneva, it is the capital of the Republic and Canton of Geneva. The city of Geneva () had a population 201,818 in 2019 (Jan. estimate) within its small municipal territory of , but the Canton of Geneva (the city and its closest Swiss suburbs and exurbs) had a population of 499,480 (Jan. 2019 estimate) over , and together with the suburbs and exurbs located in the canton of Vaud and in the French departments of Ain and Haute-Savoie the cross-border Geneva metropolitan area as officially defined by Eurostat, which extends over ,As of 2020, the Eurostat-defined Functional Urban Area of Geneva was made up of 93 Swiss communes and 158 French communesFederal Statistical O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Zurich Alumni
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *being a high degree-awarding institute. *using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *having independence from the ecclesiastic schools and issuing secular as well as non-secular degrees (with teaching conducted by both clergy and non-clergy): grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, , p. 55f.de Ridder-Symoens, Hilde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemists From The Russian Empire
A chemist (from Greek ''chēm(ía)'' alchemy; replacing ''chymist'' from Medieval Latin ''alchemist'') is a scientist trained in the study of chemistry. Chemists study the composition of matter and its properties. Chemists carefully describe the properties they study in terms of quantities, with detail on the level of molecules and their component atoms. Chemists carefully measure substance proportions, chemical reaction rates, and other chemical properties. In Commonwealth English, pharmacists are often called chemists. Chemists use their knowledge to learn the composition and properties of unfamiliar substances, as well as to reproduce and synthesize large quantities of useful naturally occurring substances and create new artificial substances and useful processes. Chemists may specialize in any number of subdisciplines of chemistry. Materials scientists and metallurgists share much of the same education and skills with chemists. The work of chemists is often related to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1957 Deaths
1957 ( MCMLVII) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Gregorian calendar, the 1957th year of the Common Era (CE) and ''Anno Domini'' (AD) designations, the 957th year of the 2nd millennium, the 57th year of the 20th century, and the 8th year of the 1950s decade. Events January * January 1 – The Saarland joins West Germany. * January 3 – Hamilton Watch Company introduces the first electric watch. * January 5 – South African player Russell Endean becomes the first batsman to be dismissed for having ''handled the ball'', in Test cricket. * January 9 – British Prime Minister Anthony Eden resigns. * January 10 – Harold Macmillan becomes Prime Minister of the United Kingdom. * January 11 – The African Convention is founded in Dakar. * January 14 – Kripalu Maharaj is named fifth Jagadguru (world teacher), after giving seven days of speeches before 500 Hindu scholars. * January 15 – The film '' Throne of Blood'', Akira Kurosawa's reworking of ''Mac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1865 Births
Events January–March * January 4 – The New York Stock Exchange opens its first permanent headquarters at 10-12 Broad near Wall Street, in New York City. * January 13 – American Civil War : Second Battle of Fort Fisher: United States forces launch a major amphibious assault against the last seaport held by the Confederates, Fort Fisher, North Carolina. * January 15 – American Civil War: United States forces capture Fort Fisher. * January 31 ** The Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution (conditional prohibition of slavery and involuntary servitude) passes narrowly, in the House of Representatives. ** American Civil War: Confederate General Robert E. Lee becomes general-in-chief. * February ** American Civil War: Columbia, South Carolina burns, as Confederate forces flee from advancing Union forces. * February 3 – American Civil War : Hampton Roads Conference: Union and Confederate leaders discuss peace terms. * Febr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 million people, and the List of European countries by area, seventh largest EU country, covering a combined area of . It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordering seven countries. The territory is characterised by a varied landscape, diverse ecosystems, and Temperate climate, temperate transitional climate. The capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city is Warsaw; other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, and Gdańsk. Prehistory and protohistory of Poland, Humans have been present on Polish soil since the Lower Paleolithic, with continuous settlement since the end of the Last Glacial Period over 12,000 years ago. Culturally diverse throughout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostrowy, Wyszków County
Ostrowy is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Somianka, within Wyszków County, Masovian Voivodeship, in east-central Poland. It lies approximately north-east of Somianka, west of Wyszków, and north-east of Warsaw Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia .... References Villages in Wyszków County {{Wyszków-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bischler–Möhlau Indole Synthesis
The Bischler–Möhlau indole synthesis, also often referred to as "The Bischler Indole Synthesis," is a chemical reaction that forms a 2-aryl- indole from an α-bromo- acetophenone and excess aniline; it is named after August Bischler and . Despite its long history, this classical reaction had received relatively little attention in comparison with other methods for indole synthesis, owing to the reactions harsh conditions, poor yields and unpredictable regioselectivity. Recently, milder methods have been developed, including the use of lithium bromide as a catalyst and an improved procedure involving the use of microwave irradiation. History What is now known as the Bischler-Möhlau Indole Synthesis was discovered and formulated through the separate, but complimentary, findings of German Scientist Richard Möhlau in 1882 and Russia-born German chemist August Bischler (with partneH. Brion in 1892. These two researchers did not collaborate with each other, but instead indepe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. The rise of the Russian Empire coincided with the decline of neighbouring rival powers: the Swedish Empire, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Qajar Iran, the Ottoman Empire, and Qing dynasty, Qing China. It also held colonies in North America between 1799 and 1867. Covering an area of approximately , it remains the list of largest empires, third-largest empire in history, surpassed only by the British Empire and the Mongol Empire; it ruled over a population of 125.6 million people per the Russian Empire Census, 1897 Russian census, which was the only census carried out during the entire imperial period. Owing to its geographic extent across three continents at its peak, it featured great ethnic, linguistic, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemist
A chemist (from Greek ''chēm(ía)'' alchemy; replacing ''chymist'' from Medieval Latin ''alchemist'') is a scientist trained in the study of chemistry. Chemists study the composition of matter and its properties. Chemists carefully describe the properties they study in terms of quantities, with detail on the level of molecules and their component atoms. Chemists carefully measure substance proportions, chemical reaction rates, and other chemical properties. In Commonwealth English, pharmacists are often called chemists. Chemists use their knowledge to learn the composition and properties of unfamiliar substances, as well as to reproduce and synthesize large quantities of useful naturally occurring substances and create new artificial substances and useful processes. Chemists may specialize in any number of subdisciplines of chemistry. Materials scientists and metallurgists share much of the same education and skills with chemists. The work of chemists is often related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bischler–Napieralski Reaction
The Bischler–Napieralski reaction is an intramolecular electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction that allows for the cyclization of β-arylethylamides or β-arylethylcarbamates. It was first discovered in 1893 by August Bischler and , in affiliation with Basle Chemical Works and the University of Zurich. The reaction is most notably used in the synthesis of dihydroisoquinolines, which can be subsequently oxidized to isoquinolines. Mechanisms Two types of mechanisms have appeared in the literature for the Bischler–Napieralski reaction. Mechanism I involves a dichlorophosphoryl imine-ester intermediate, while Mechanism II involves a nitrilium ion intermediate (both shown in brackets). This mechanistic variance stems from the ambiguity over the timing for the elimination of the carbonyl oxygen in the starting amide. In Mechanism I, the elimination occurs with imine formation ''after'' cyclization; while in Mechanism II, the elimination yields the nitrilium intermediate ''pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |