|
August 5
Events Pre-1600 * AD 25 – Guangwu claims the throne as Emperor of China, restoring the Han dynasty after the collapse of the short-lived Xin dynasty. * 70 – Fires resulting from the destruction of the Second Temple in Jerusalem are extinguished. * 642 – Battle of Maserfield: Penda of Mercia defeats and kills Oswald of Northumbria. * 910 – The last major Danish army to raid England for nearly a century is defeated at the Battle of Tettenhall by the allied forces of Mercia and Wessex, led by King Edward the Elder and Æthelred, Lord of the Mercians. * 939 – The Battle of Alhandic is fought between Ramiro II of León and Abd-ar-Rahman III at Zamora in the context of the Spanish Reconquista. The battle resulted in a victory for the Emirate of Córdoba. * 1068 – Byzantine–Norman wars: Italo-Normans begin a nearly-three-year siege of Bari. * 1100 – Henry I is crowned King of England in Westminster Abbey. * 1278 – Spanish R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AD 25
__NOTOC__ AD 25 ( XXV) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Lentulus and Agrippa (or, less frequently, year 778 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination AD 25 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Emperor Tiberius settles a dispute between Messenia and Sparta over the Ager Dentheliales on Mount Taygetus, awarding the land to Messenia. * Lucius Aelius Sejanus unsuccessfully attempts to marry Livilla. China * August 5 – The Han dynasty is restored in China as Liu Xiu proclaims himself Emperor Guangwu of Han, starting the ''Jianwu'' era (until AD 56). * November 27 – Luoyang becomes the capital of the Houhan or Eastern Han dynasty. Births * Gaius Julius Civilis, Batavian military leader * Quintus Volusius Saturninus, Roman consul De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramiro II Of León
Ramiro II ( 900 – 1 January 951), son of Ordoño II of León, Ordoño II and Elvira Menendez, was a Kingdom of León, King of León from 931 until his death. Initially titular king only of a lesser part of the kingdom, he gained the crown of León (and with it, Kingdom of Galicia, Galicia) after supplanting his brother Alfonso IV of León, Alfonso IV and cousin Alfonso Fróilaz in 931. The scant ''Anales castellanos primeros'' are a primary source for his reign. He actively campaigned against the Moors, who referred to him as the Devil due to his ferocity and fervor in battle. He defeated the hosts of the Umayyad caliph, Abd al-Rahman III, at the Battle of Simancas (939). Succession When, shortly before his death in 910, Alfonso III of Asturias was forced by his sons to abdicate, the Kingdom of Asturias descended into a period of successional crises among the royal family and their supporters from the regional March (territory), marcher aristocracies. The kingdom was initially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1278
Year 1278 (Roman numerals, MCCLXXVIII) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. Events By place Europe * May 1 – William of Villehardouin, prince of Principality of Achaea, Achaea, dies. By the terms of the Treaty of Viterbo, his lands passed under the direct control of Charles I of Anjou, Charles I, king of Kingdom of Sicily, Sicily. Charles appoints a bailiff to rule the Latin principality. In response, Charles swears fealty to the new pope, Pope Nicholas III, Nicholas III, on May 24. He promises not to attack or invade the Byzantine Empire because Nicholas has hopes to unify the Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Church with the Catholic Church. * August 5 – ''Reconquista'': Siege of Algeciras (1278–1279), Siege of Algeciras – Castilian forces (some 30,000 men) led by King Alfonso X of Castile, Alfonso X ("the Wise") besiege Algeciras (at this time under control of the Marinid Sultanate, Marinids). A fleet of 24 ships and so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an Anglican church in the City of Westminster, London, England. Since 1066, it has been the location of the coronations of 40 English and British monarchs and a burial site for 18 English, Scottish, and British monarchs. At least 16 royal weddings have taken place at the abbey since 1100. Although the origins of the church are obscure, an abbey housing Benedictine monks was on the site by the mid-10th century. The church got its first large building from the 1040s, commissioned by King Edward the Confessor, who is buried inside. Construction of the present church began in 1245 on the orders of Henry III. The monastery was dissolved in 1559, and the church was made a royal peculiar – a Church of England church, accountable directly to the sovereign – by Elizabeth I. The abbey, the Palace of Westminster and St Margaret's Church became a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1987 becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of English Monarchs
This list of kings and reigning queens of the Kingdom of England begins with Alfred the Great, who initially ruled Wessex, one of the heptarchy, seven Anglo-Saxon kingdoms which later made up modern England. Alfred styled himself king of the Anglo-Saxons from about 886, and while he was not the first king to claim to rule all of the English people, English, his rule represents the start of the first unbroken line of kings to rule the whole of England, the House of Wessex. Arguments are made for a few different kings thought to have controlled enough Anglo-Saxon kingdoms to be deemed the first king of England. For example, Offa of Mercia and Egbert of Wessex are sometimes described as kings of England by popular writers, but it is no longer the majority view of historians that their wide dominions were part of a process leading to a unified England. The historian Simon Keynes states, for example, "Offa was driven by a lust for power, not a vision of English unity; and what he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry I Of England
Henry I ( – 1 December 1135), also known as Henry Beauclerc, was King of England from 1100 to his death in 1135. He was the fourth son of William the Conqueror and was educated in Latin and the liberal arts. On William's death in 1087, Henry's elder brothers Robert Curthose and William Rufus inherited Duchy of Normandy, Normandy and England, respectively; Henry was left landless. He purchased the County of Cotentin in western Normandy from Robert, but his brothers deposed him in 1091. He gradually rebuilt his power base in the Cotentin and allied himself with William Rufus against Robert. Present in England with his brother William when William died in a hunting accident, Henry seized the English throne, promising at his coronation to correct many of William's less popular policies. He married Matilda of Scotland and they had two surviving children, Empress Matilda and William Adelin; he also had many illegitimate children by his numerous mistresses. Robert, who invaded from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1100
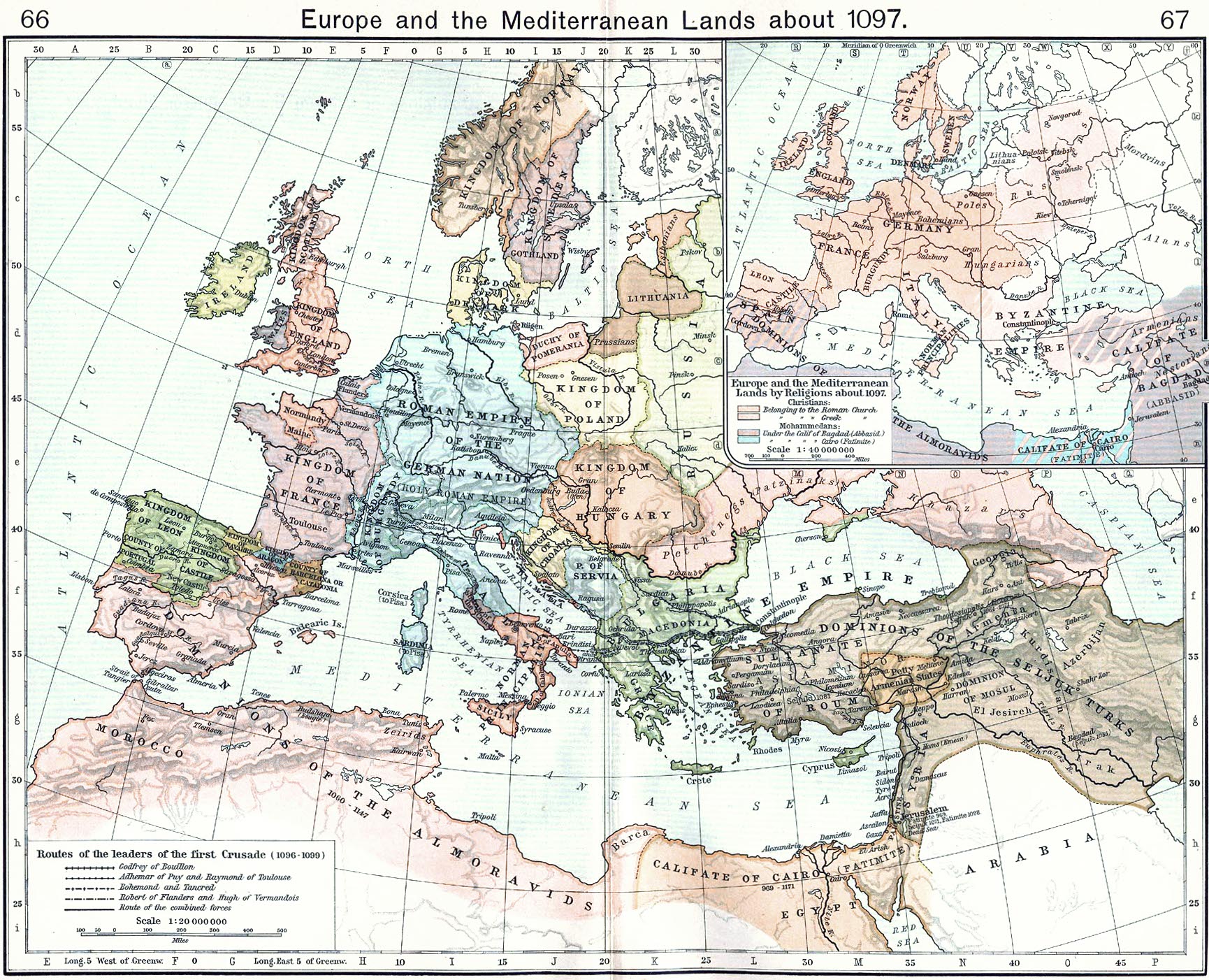
Year 1100 (Roman numerals, MC) was a leap year starting on Sunday in the Julian calendar. It last year of the 11th century and the first year of the 12th century. In the proleptic Gregorian calendar, it was a Common year starting on Monday, non-leap century year starting on Monday (like 1900). Events By place Levant * January – The Seljuk ruler Mahmud I of Great Seljuq, Mahmud I is expelled from Baghdad by his brother Barkiyaruq, but Mahmud manages to retake the city during his spring offensive. * May or June – Raymond IV, Count of Toulouse (Saint-Gilles) sails to Constantinople to obtain the support of Byzantine Emperor Alexios I Komnenos in his attempt to seize Tripoli, Lebanon, Tripoli. * August 1 – A Republic of Genoa, Genoese fleet leaves Italy to support the Crusaders' efforts to conquer the coastal cities; the ships reach Latakia on September 25. * August – Battle of Melitene: Bohemond I of Antioch is captured by the Danishmends, leaving Tancred, Prince ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Bari
The siege of Bari took place 1068–1071, during the Middle Ages, when Norman forces, under the command of Robert Guiscard, laid siege to the city of Bari, a major stronghold of the Byzantines in Italy and the capital of the Catepanate of Italy, starting from 5 August 1068. Bari was captured on 16 April 1071 when Robert Guiscard entered the city, ending not only more than five centuries of Byzantine presence in Southern Italy but also ancient Roman control since the Roman expansion in Italy in the 3rd century BCE. History Background By 1060, only a few coastal cities in Apulia were still in Byzantine hands: during the previous few decades, the Normans had increased their possessions in southern Italy and now aimed to the complete expulsion of the Byzantines from the peninsula before concentrating on the conquest of Sicily, then mostly under Islamic domination. Large military units were thus called from Sicily and under Count Geoffrey of Conversano laid siege to Otranto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italo-Norman
The Italo-Normans (), or Siculo-Normans (''Siculo-Normanni'') when referring to Sicily and Southern Italy, are the Italian-born descendants of the first Norman conquerors to travel to Southern Italy in the first half of the eleventh century. While maintaining much of their distinctly Norman piety and customs of war, they were shaped by the diversity of Southern Italy, by the cultures and customs of the Greeks, Lombards, and Arabs in Sicily. History Normans first arrived in Italy as pilgrims, probably on their way to or returning from either Rome or Jerusalem, or from visiting the shrine at Monte Gargano, during the late tenth and early eleventh centuries. In 1017, the Lombard lords in Apulia recruited their assistance against the dwindling power of the Byzantine Catapanate of Italy. They soon established vassal states of their own and began to expand their conquests until they were encroaching on the Lombard principalities of Benevento and Capua, Saracen-controlled territ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine–Norman Wars
The Byzantine–Norman wars were a series of military conflicts between the Normans and the Byzantine Empire fought from 1040 to 1186 involving the Hauteville family, Norman-led Kingdom of Sicily in the west, and the Principality of Antioch in the Levant. The last of the Norman invasions, though having incurred disaster upon the Byzantine Greeks, Romans by Sack of Thessalonica (1185), sacking Thessalonica in 1185, was eventually driven out and vanquished by 1186. Norman conquest of Southern Italy The Normans' initial military involvement in Southern Italy was on the side of the Lombards against the Byzantines. Eventually, some Normans, including the powerful de Hauteville brothers, served in the army of George Maniakes during the attempted Byzantine reconquest of Sicily, only to turn against their employers when the emirs proved difficult to conquer. By 1030, Rainulf Drengot, Rainulf became count of Aversa, marking the start of permanent Norman settlement in Italy. In 1042, Wil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1068
Year 1068 ( MLXVIII) was a leap year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. Events By place Byzantine Empire * January 1 – Empress Eudokia Makrembolitissa, wife of the late Emperor Constantine X, marries General Romanos Diogenes (a member of a prominent Cappadocian family) – who is proclaimed co-emperor as Romanos IV of the Byzantine Empire. * Autumn – Romanos IV begins a campaign against the Seljuk Turks, leading a Byzantine expeditionary force (which is in poor condition). He is successful in recapturing the fortress city of Hieropolis (modern-day Manbij) near Aleppo in northern Syria. * Winter – Romanos IV leaves a portion of his army as a rearguard at Melitene. The Byzantine garrison fails to check a Seljuk raid that manages to sack Amorium (penetrating deep in Byzantine territory). Romanos winters near Aleppo before returning to Constantinople.George Finlay (1854). ''History of the Byzantine and Greek Empires from 1057–1453'', p. 34. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emirate Of Córdoba
An emirate is a territory ruled by an emir, a title used by monarchs or high officeholders in the Muslim world. From a historical point of view, an emirate is a political-religious unit smaller than a caliphate. It can be considered equivalent to a principality in non-Muslim contexts. Currently in the world, there are two emirates that are independent states (Kuwait and Qatar), one state ruled by an unrecognised emirate (Afghanistan), and a state that consists of a federation of seven emirates (the United Arab Emirates). A great number of previously independent emirates around the world are now part of larger states. Etymology Etymologically, emirate or amirate ( ' plural: ' is the quality, dignity, office, or territorial competence of any emir (prince, commander, governor, etc.). In English, the term is pronounced or in British English and or in American English. Types Monarchies The United Arab Emirates is a federal state that comprises seven federal emirates, each ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |