|
Auditory Processing Disorder
Auditory processing disorder (APD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder affecting the way the brain processes sounds. Individuals with APD usually have normal structure and function of the ear, but cannot process the information they hear in the same way as others do, which leads to difficulties in recognizing and interpreting sounds, especially the sounds composing speech. It is thought that these difficulties arise from dysfunction in the central nervous system. A subtype is known as King-Kopetzky syndrome or auditory disability with normal hearing (ADN), characterised by difficulty in hearing speech in the presence of background noise. This is essentially a failure or impairment of the cocktail party effect ( selective hearing) found in most people. The American Academy of Audiology notes that APD is diagnosed by difficulties in one or more auditory processes known to reflect the function of the central auditory nervous system. It can affect both children and adults, and may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Audiology
Audiology (from Latin 'to hear'; and from Ancient Greek, Greek branch of learning , ''wikt:-logia, -logia'') is a branch of science that studies hearing, balance, and related disorders. Audiologists treat those with hearing loss and proactively prevent related damage. By employing various testing strategies (e.g. behavioral hearing tests, otoacoustic emission measurements, and electrophysiologic tests), audiologists aim to determine whether someone has normal sensitivity to sounds. If hearing loss is identified, audiologists determine which portions of hearing (high, middle, or low frequencies) are affected, to what degree (severity of loss), and where the lesion causing the hearing loss is found (outer ear, middle ear, inner ear, auditory nerve and/or central nervous system). If an audiologist determines that a hearing loss or vestibular abnormality is present, they will provide recommendations for interventions or rehabilitation (e.g. hearing aids, cochlear implants, appropria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Polymicrogyria
Polymicrogyria (PMG) is a condition that affects the development of the human brain by multiple small gyri ( microgyri) creating excessive folding of the brain leading to an abnormally thick cortex. This abnormality can affect either one region of the brain or multiple regions. The time of onset has yet to be identified; however, it has been found to occur before birth in either the earlier or later stages of brain development. Early stages include impaired proliferation and migration of neuroblasts, while later stages show disordered post-migration development. The symptoms experienced differ depending on what part of the brain is affected. There is no specific treatment to get rid of this condition, but there are medications that can control the symptoms such as seizures, delayed development or weakened muscles as some of the noted effects. Syndromes Significant technological advances have been made within the past few decades that have allowed more extensive studies to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Seizure
A seizure is a sudden, brief disruption of brain activity caused by abnormal, excessive, or synchronous neuronal firing. Depending on the regions of the brain involved, seizures can lead to changes in movement, sensation, behavior, awareness, or consciousness. Symptoms vary widely. Some seizures involve subtle changes, such as brief lapses in attention or awareness (as seen in absence seizures), while others cause generalized convulsions with loss of consciousness ( tonic–clonic seizures). Most seizures last less than two minutes and are followed by a postictal period of confusion, fatigue, or other symptoms. A seizure lasting longer than five minutes is a medical emergency known as status epilepticus. Seizures are classified as provoked, when triggered by a known cause such as fever, head trauma, or metabolic imbalance, or unprovoked, when no immediate trigger is identified. Recurrent unprovoked seizures define the neurological condition epilepsy. Clinical features Seizur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of Non-communicable disease, non-communicable Neurological disorder, neurological disorders characterized by a tendency for recurrent, unprovoked Seizure, seizures. A seizure is a sudden burst of abnormal electrical activity in the brain that can cause a variety of symptoms, ranging from brief lapses of awareness or muscle jerks to prolonged convulsions. These episodes can result in physical injuries, either directly, such as broken bones, or through causing accidents. The diagnosis of epilepsy typically requires at least two unprovoked seizures occurring more than 24 hours apart. In some cases, however, it may be diagnosed after a single unprovoked seizure if clinical evidence suggests a high risk of recurrence. Isolated seizures that occur without recurrence risk or are provoked by identifiable causes are not considered indicative of epilepsy. The underlying cause is often unknown, but epilepsy can result from brain injury, stroke, infections, Brain tumor, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
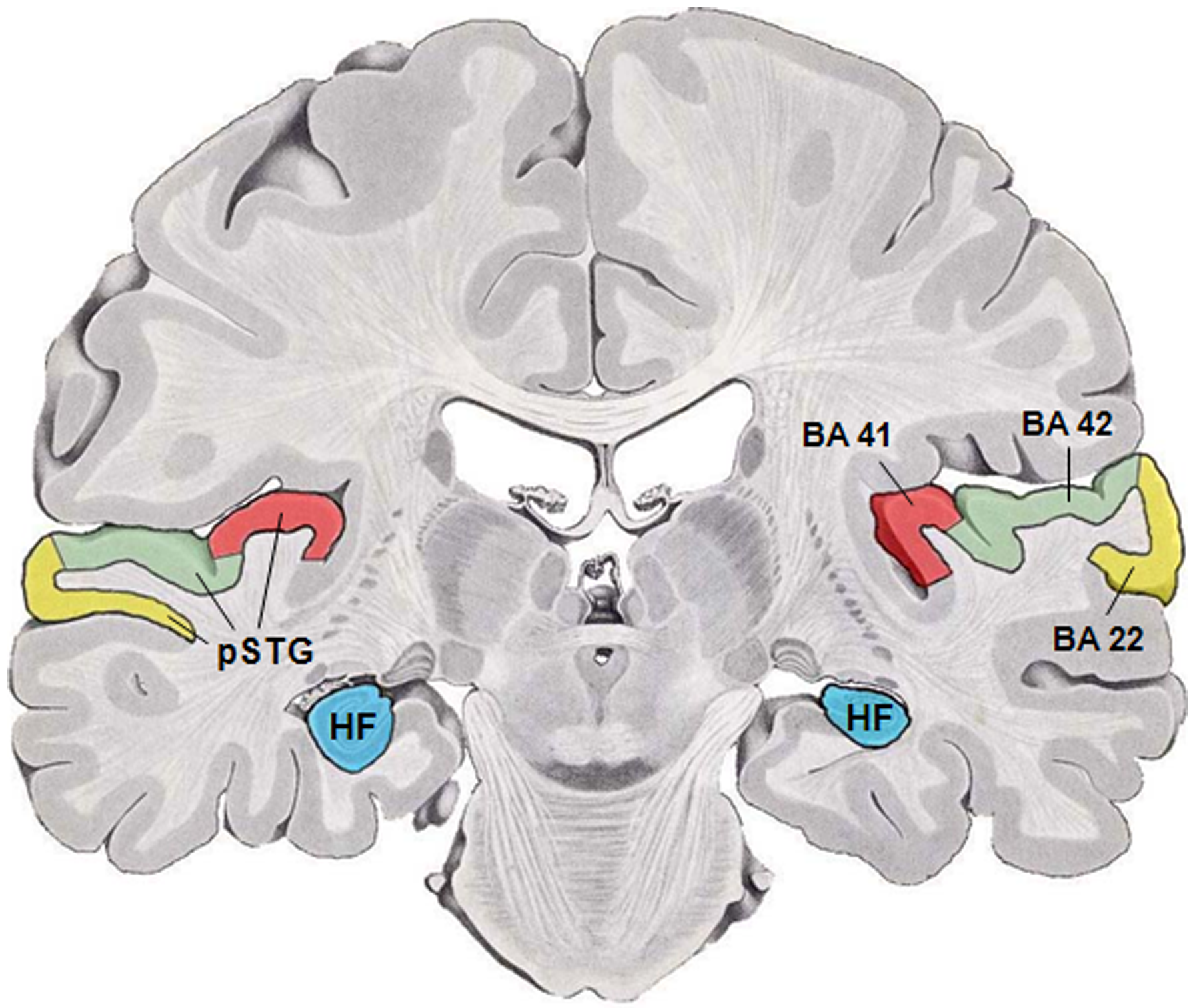 |
Auditory Cortex
The auditory cortex is the part of the temporal lobe that processes auditory information in humans and many other vertebrates. It is a part of the auditory system, performing basic and higher functions in hearing, such as possible relations to language switching.Cf. Pickles, James O. (2012). ''An Introduction to the Physiology of Hearing'' (4th ed.). Bingley, UK: Emerald Group Publishing Limited, p. 238. It is located bilaterally, roughly at the upper sides of the temporal lobes – in humans, curving down and onto the medial surface, on the superior temporal plane, within the lateral sulcus and comprising parts of the transverse temporal gyri, and the superior temporal gyrus, including the planum polare and planum temporale (roughly Brodmann areas 41 and 42, and partially 22). The auditory cortex takes part in the spectrotemporal, meaning involving time and frequency, analysis of the inputs passed on from the ear. The cortex then filters and passes on the information to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Myelin
Myelin Sheath ( ) is a lipid-rich material that in most vertebrates surrounds the axons of neurons to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) pass along the axon. The myelinated axon can be likened to an electrical wire (the axon) with insulating material (myelin) around it. However, unlike the plastic covering on an electrical wire, myelin does not form a single long sheath over the entire length of the axon. Myelin ensheaths part of an axon known as an internodal segment, in multiple myelin layers of a tightly regulated internodal length. The ensheathed segments are separated at regular short unmyelinated intervals, called nodes of Ranvier. Each node of Ranvier is around one micrometre long. Nodes of Ranvier enable a much faster rate of conduction known as saltatory conduction where the action potential recharges at each node to jump over to the next node, and so on till it reaches the axon terminal. At the terminal the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Deafness
Deafness has varying definitions in cultural and medical contexts. In medical contexts, the meaning of deafness is hearing loss that precludes a person from understanding spoken language, an audiological condition. In this context it is written with a lower case ''d''. It later came to be used in a cultural context to refer to those who primarily communicate with a deafness aid or through sign language regardless of hearing ability, often capitalized as ''Deaf'' and referred to as "big D Deaf" in speech and sign. The two definitions overlap but are not identical, as hearing loss includes cases that are not severe enough to impact spoken language comprehension, while cultural Deafness includes hearing people who use sign language, such as children of deaf adults. Medical context In a medical context, deafness is defined as a degree of hearing difficulties such that a person is unable to understand speech, even in the presence of amplification. In profound deafness, eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Landau–Kleffner Syndrome
Landau–Kleffner syndrome (LKS), also called infantile acquired aphasia, acquired epileptic aphasia, or aphasia with convulsive disorder, is a rare neurological syndrome that develops during childhood. It is named after William Landau and Frank Kleffner, who characterized it in 1957 with a diagnosis of six children. Reproduced as Signs and symptoms Landau–Kleffner syndrome is characterized by the sudden or gradual development of aphasia (the inability to understand or express language) and an abnormal electroencephalogram (EEG). LKS affects the parts of the brain that control comprehension and speech (Broca's area and Wernicke's area). The disorder usually occurs in children between the ages of 3 and 7 years. There appears to be a male dominance in the diagnosis of the syndrome (ratio of 1.7:1, men to women). Typically, children with LKS develop normally, but then lose their language skills. While many affected individuals have clinical seizures, some only have electrogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Birth Trauma (physical)
Birth trauma refers to damage of the tissues and organs of a newly delivered child, often as a result of physical pressure or trauma during childbirth. It encompasses the long term consequences, often of cognitive nature, of damage to the brain or cranium. Medical study of birth trauma dates to the 16th century, and the morphological consequences of mishandled delivery are described in Renaissance-era medical literature. Birth injury occupies a unique area of concern and study in the medical canon. In ICD-10 "birth trauma" occupied 49 individual codes (P10–Р15). However, there are often clear distinctions to be made between brain damage caused by birth trauma and that induced by intrauterine asphyxia. It is also crucial to distinguish between "birth trauma" and "birth injury". Birth injuries encompass any systemic damages incurred during delivery (Intrauterine hypoxia, hypoxic, toxic, biochemical, infection factors, etc.), but "birth trauma" focuses largely on mechanical damage. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Short Circuit
A short circuit (sometimes abbreviated to short or s/c) is an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path with no or very low electrical impedance. This results in an excessive current flowing through the circuit. The opposite of a short circuit is an open circuit, which is an infinite resistance (or very high impedance) between two nodes. Definition A short circuit is an abnormal connection between two nodes of an electric circuit intended to be at different voltages. This results in an electric current limited only by the Thévenin equivalent resistance of the rest of the network which can cause circuit damage, overheating, fire or explosion. Although usually the result of a fault, there are cases where short circuits are caused intentionally, for example, for the purpose of voltage-sensing crowbar circuit protectors. In circuit analysis, a ''short circuit'' is defined as a connection between two nodes that forces them to be at the sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Dominance (genetics)
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second is called recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes ( autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance, such as incomp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is a partial or total inability to hear. Hearing loss may be present at birth or acquired at any time afterwards. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears. In children, hearing problems can affect the ability to acquire spoken language, and in adults it can create difficulties with social interaction and at work. Hearing loss can be temporary or permanent. Hearing loss related to age usually affects both ears and is due to cochlear hair cell loss. In some people, particularly older people, hearing loss can result in loneliness. Hearing loss may be caused by a number of factors, including: genetics, ageing, exposure to noise, some infections, birth complications, trauma to the ear, and certain medications or toxins. A common condition that results in hearing loss is chronic ear infections. Certain infections during pregnancy, such as cytomegalovirus, syphilis and rubella, may also cause hearing loss in the child. Hearing loss is diagnosed when hearing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |