|
Attercliffe Riverside
Attercliffe is an industrial suburb of northeast Sheffield, England on the south bank of the River Don. The suburb falls in the Darnall ward of Sheffield City Council. History The name Attercliffe can be traced back as far as an entry in the Domesday Book of 1086 - Ateclive – meaning “at the cliff”, a small escarpment that lay alongside the River Don. This cliff can be seen in images from the 19th century, but is no longer visible.J. Edward Vickers, ''The Ancient Suburbs of Sheffield'', pp.7–10 (1971) Westforth or Washford Bridge, at the Sheffield end of the village, was first recorded in a will of 1535. It was rebuilt in wood in 1608 and 1647, then in stone in 1672, 1789 and 1794.G. R. Vine, The Story of Old Attercliffe' (pt. 2) Historically a part of the parish of Sheffield, Attercliffe Chapel was built in 1629 as the first place of worship in the settlement. The Town School was built in 1779, and Christ Church was built in 1826 but destroyed during the Sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Of Sheffield
The City of Sheffield is a metropolitan borough with City status in the United Kingdom, city status in South Yorkshire, England. The metropolitan borough includes the administrative centre of Sheffield, the town of Stocksbridge and the larger village of Chapeltown, South Yorkshire, Chapeltown and part of the Peak District. It has a population of (), making it technically the third List of English districts by population, largest city in England by population behind Birmingham and City of Leeds, Leeds, since London is not considered a single entity. It is governed by Sheffield City Council. The current city boundaries were set on 1 April 1974 by the provisions of the Local Government Act 1972, as part of a reform of local government in England. The city is a Merger (politics), merger of two former local government districts; the unitary County Borough of Sheffield, City and County Borough of Sheffield combined with the Urban district (Great Britain and Ireland), urban district ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timothy Jollie
Timothy Jollie, (c. 1659–1714), was a nonconformist minister and notable educator in the north of England. Biography Timothy Jollie, son of Thomas Jollie, was born at Altham, Accrington, Lancashire, about 1659. On 27 August 1673 he entered the dissenting academy of Richard Frankland at Rathmell, Yorkshire. He left it in December 1675 to study in London, where he became a member of the independent church at Girdlers' Hall, Basinghall Street, under George Griffith. In 1679 he was called to an independent church in a newly erected meeting-house at Snig Hall, Sheffield. He was ordained on 28 April 1681 by his father, with Oliver Heywood and two other ministers, at the house of Abel Yates in Sheffield. Heywood notes the occasion as remarkable, seeing that an independent church, with but two objectors, allowed their pastor to be ordained by presbyters. In 1682 Jollie was arrested under the Five Miles Act, fined £20, taken to York, and bound over to appear at the next assizes. Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turnpike Trust
Turnpike trusts were bodies set up by individual Acts of Parliament in the United Kingdom, Acts of Parliament, with powers to collect road toll road, tolls for maintaining the principal roads in Kingdom of Great Britain, Britain from the 17th but especially during the 18th and 19th centuries. At the peak, in the 1830s, over 1,000 trusts administered around of turnpike road in England and Wales, taking tolls at almost 8,000 toll-gates and side-bars. During the early 19th century the concept of the turnpike trust was adopted and adapted to manage roads within the British Empire (Ireland, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, India, and South Africa) and in the United States. Turnpikes declined with the Railway mania, coming of the railways and then the Local Government Act 1888 gave responsibility for maintaining main roads to county councils and county borough councils. Etymology The term "turnpike" originates from the similarity of the gate used to control access to the road, to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
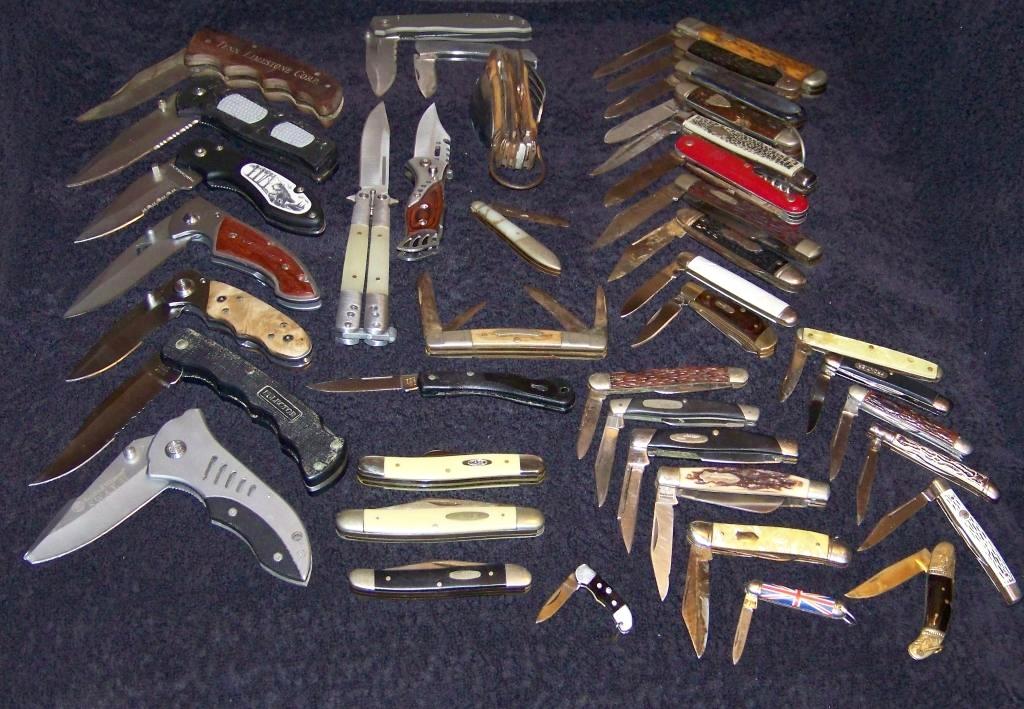
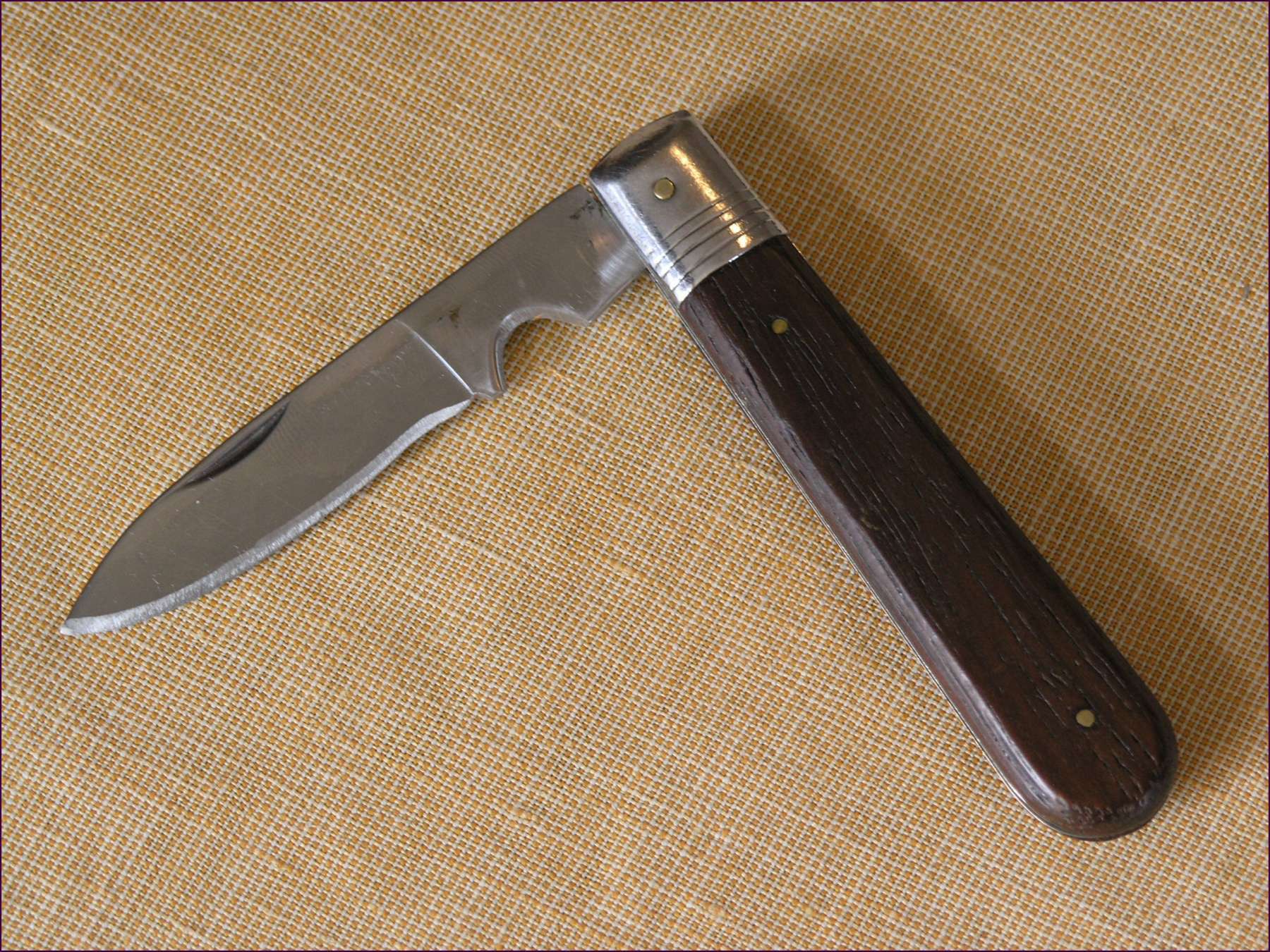
Pocket Knives
A pocketknife (also spelled as pocket knife) is a knife with one or more blades that fold into the handle. They are also known as jackknives, folding knives, Everyday carry, EDC knife, or may be referred to as a penknife, though a penknife may also be a specific kind of pocketknife. A typical blade length is . Pocketknives are versatile tools, and may be used for anything from whittling and Wood carving, woodcarving, to butchering Game (hunting), small game, gutting and filleting small fish, aiding in the preparation of tinder and kindling for fires, boring holes in soft material, to opening an envelope, cutting twine, slicing fruits and vegetables or as a means of self-defense. Pocketknives may also be used in conjunction with other tools and equipment for woodcraft and bushcraft. Specialised designs are also used for mushroom hunting and gardening. Pocketknives designed for gardening include pruning knives, which are folding knives with long curved blades used for pruning, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penknife
Penknife, or pen knife, is a small folding knife. Today ''penknife'' is also the common British English term for both a pocketknife, which can have single or multiple blades, and for multi-tools, with additional tools incorporated into the design. History Originally, penknives were used for thinning and pointing quills (cf. ''penna'', Latin for ''feather'') to prepare them for use as dip pens and, later, for repairing or re-pointing the Nib (pen), nib. A penknife might also be used to sharpen a pencil, prior to the invention of the pencil sharpener. In the mid-1800s, penknives were necessary to slice the uncut edges of newspapers and books. A penknife did not necessarily have a folding blade, but might resemble a scalpel or chisel by having a short, fixed blade at the end of a long handle. During the 20th century there has been a proliferation of multi-function pocketknives with assorted blades and gadgets, the most famous of which is the Swiss Army knife, referred to in Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maze
A maze is a path or collection of paths, typically from an entrance to a goal. The word is used to refer both to branching tour puzzles through which the solver must find a route, and to simpler non-branching ("unicursal") patterns that lead unambiguously through a convoluted layout to a goal. The term "labyrinth" is generally synonymous with "maze", but can also connote specifically a unicursal pattern. The pathways and walls in a maze are typically fixed, but puzzles in which the walls and paths can change during the game are also categorised as mazes or tour puzzles. Construction Mazes have been built with a variety of materials. Some are relatively permanent, like Hedge maze, hedges, Turf maze, turf, walls, rooms, tiles, and paving stones or bricks. Others are deliberately transitory, like Corn maze, corn stalks, Straw maze, straw bales, books, snow, or in fields of crops such as cereal, corn or maize. Maize mazes can be very large; they are usually kept only for one g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
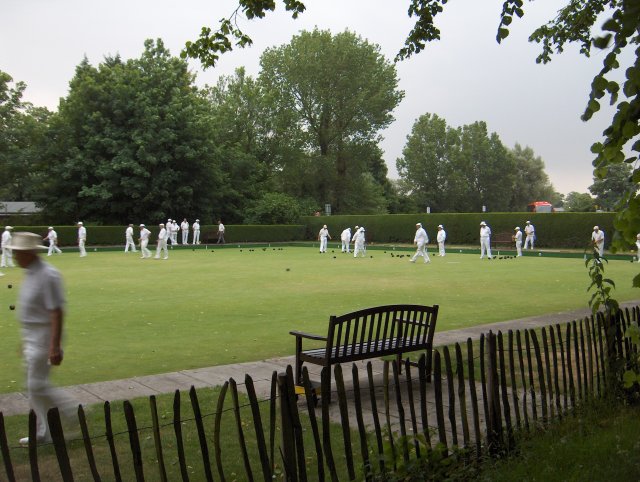
Bowling Green
A bowling green is a finely laid, close-mown and rolled stretch of turf for playing the game of bowls. Before 1830, when Edwin Beard Budding of Thrupp, near Stroud, UK, invented the lawnmower, lawns were often kept cropped by grazing sheep on them. The world's oldest surviving bowling green is the Southampton Old Bowling Green, which was first used in 1299. When the French adopted "boulingrin" in the 17th century, it was understood to mean a sunk geometrically shaped piece of perfect grass, framed in gravel walks, which often formed the centre of a regularly planted wood called a '' bosquet'', somewhat like a highly formalized glade; it might have a central pool or fountain. The diarist Samuel Pepys Samuel Pepys ( ; 23 February 1633 – 26 May 1703) was an English writer and Tories (British political party), Tory politician. He served as an official in the Navy Board and Member of Parliament (England), Member of Parliament, but is most r ... relates a conversation h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Racecourse
A race track (racetrack, racing track or racing circuit) is a facility built for racing of vehicles, athletes, or animals (e.g. horse racing or greyhound racing). A race track also may feature grandstands or concourses. Race tracks are also used in the study of animal locomotion. A ''racetrack'' is a permanent facility or building. ''Racecourse'' is an alternate term for a horse racing track, found in countries such as the United Kingdom, India, Australia, Hong Kong, and the United Arab Emirates. Race tracks built for bicycles are known as ''velodromes''. ''Circuit'' is a common alternate term for race track, given the circuit configuration of most race tracks, allowing races to occur over several laps. Some race tracks may also be known as ''speedways'', or ''raceways''. A ''race course'', as opposed to a ''racecourse'', is a nonpermanent track for sports, particularly road running, water sports, road racing, or rallying. Many sports usually held on race tracks also can occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
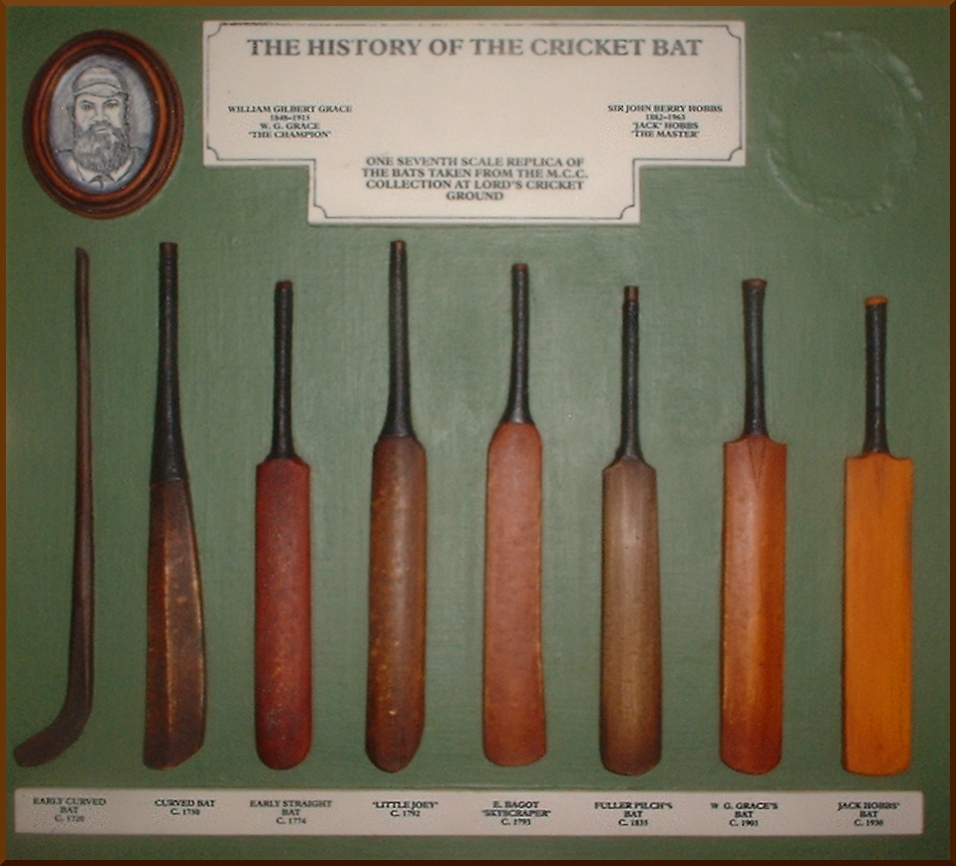
Cricket Ground
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field, at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails (small sticks) balanced on three stumps. Two players from the batting team, the striker and nonstriker, stand in front of either wicket holding bats, while one player from the fielding team, the bowler, bowls the ball toward the striker's wicket from the opposite end of the pitch. The striker's goal is to hit the bowled ball with the bat and then switch places with the nonstriker, with the batting team scoring one run for each of these swaps. Runs are also scored when the ball reaches the boundary of the field or when the ball is bowled illegally. The fielding team aims to prevent runs by dismissing batters (so they are "out"). Dismissal can occur in various ways, including being bowled (when the ball hits the striker's wicket and dislodges the bails), and by the fielding side either catchi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleasure Garden
A pleasure garden is a park or garden that is open to the public for recreation and entertainment. Pleasure gardens differ from other public gardens by serving as venues for entertainment, variously featuring such attractions as concert halls, bandstands, amusement rides, zoos, and menageries. Historically a "pleasure garden" or ''pleasure ground'' meant private flower gardens, shrub gardens or formal wooded areas such as bosquets, that were planted for enjoyment, with ornamental plants and neat paths for walking. These were distinguished from the areas in a large garden planted as lawns or a landscaped park, or the "useful" areas of the kitchen garden and woodland. Pleasure gardens provided a cool and refreshing refuge from the summer heat. The Mediterranean gardens were also maintained in the winter season, with winter rain allowing for the upkeep of rose and almond trees in northern Italy. This made the gardens a welcome retreat throughout the year. The two meanings of the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishop Of Canterbury
The archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop and a principal leader of the Church of England, the Primus inter pares, ceremonial head of the worldwide Anglican Communion and the bishop of the diocese of Canterbury. The first archbishop was Augustine of Canterbury, the "Apostle to the English", who was sent to England by Pope Gregory the Great and arrived in 597. The position is currently vacant following the resignation of Justin Welby, the List of Archbishops of Canterbury, 105th archbishop, effective 7 January 2025.Orders in Council, 18 December 2024, page 42 During the vacancy the official functions of the office have been delegated primarily to the archbishop of York, Stephen Cottrell, with some also undertaken by the bishop of London, Sarah Mullally, and the bishop of Dover, Rose Hudson-Wilkin. From Augustine until William Warham, the archbishops of Canterbury were in full communion with the Catholic Church and usually received the pallium from the pope. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford Dictionary Of National Biography
The ''Dictionary of National Biography'' (''DNB'') is a standard work of reference on notable figures from History of the British Isles, British history, published since 1885. The updated ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' (''ODNB'') was published on 23 September 2004 in 60 volumes and online, with 50,113 biographical articles covering 54,922 lives. First series Hoping to emulate national biography, biographical collections published elsewhere in Europe, such as the (1875), in 1882 the publisher George Murray Smith, George Smith (1824–1901), of Smith, Elder & Co., planned a universal dictionary that would include biographical entries on individuals from world history. He approached Leslie Stephen, then editor of the ''Cornhill Magazine'', owned by Smith, to become the editor. Stephen persuaded Smith that the work should focus only on subjects from the United Kingdom and its present and former colonies. An early working title was the ''Biographia Britannica'', the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |