|
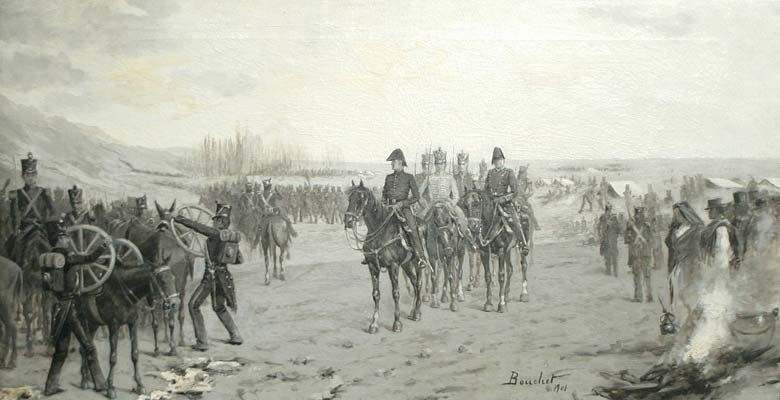
Attack On The Brazilian Fort In Punta Del Este
The Attack on the Brazilian Fort in Punta del Este was a short-lived military operation during the Cisplatine War, led by Brigadier General Juan Antonio Lavalleja. The operation took place between August 17 and 19, 1827, in the region now known as Punta del Este in Uruguay. It aimed to expel Brazilian forces stationed at a strategically constructed fort in the area. Background The Cisplatine War (1825–1828) was fought between the Empire of Brazil and the United Provinces of the Rio de la Plata (now Argentina and Uruguay) over control of the Cisplatina province (modern-day Uruguay). By early 1827, the Brazilian military had established an outpost in Punta del Este, a small, rocky peninsula in southern Uruguay surrounded by sand dunes. The Brazilian government of Montevideo deployed resources and personnel to the site as part of a broader campaign to maintain control of the region. This fort, located near the intersection of Gorlero Avenue and 27th Street, posed a threat to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cisplatine War
The Cisplatine War was an armed conflict fought in the 1820s between the Empire of Brazil and the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata over control of Brazil's Cisplatina province. It was fought in the aftermath of the United Provinces' and Brazil's independence from Spain and Portugal, respectively, and resulted in the independence of Cisplatina as the Uruguay, Oriental Republic of Uruguay. In 1816, the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves carried out an Portuguese conquest of the Banda Oriental, invasion of the Banda Oriental and, after defeating the local resistance led by José Gervasio Artigas, annexed it under the name of Cisplatina. After Independence of Brazil, Brazil's independence in 1822, Cisplatina remained as part of Brazil. Wishing to gain control of the region, the United Provinces sent a diplomatic mission to Brazil in 1823 to negotiate a peaceful Brazilian withdrawal, but it failed. In 1825, a group of patriots known as the Thirty-Three Orien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José De San Martín
José Francisco de San Martín y Matorras (; 25 February 177817 August 1850), nicknamed "the Liberator of Argentina, Chile and Peru", was an Argentine general and the primary leader of the southern and central parts of South America's successful struggle for independence from the Spanish Empire who served as the Protector of Peru. Born in Yapeyú, Corrientes, in modern-day Argentina, he left the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata at the early age of seven to study in Málaga, Spain. In 1808, after taking part in the Peninsular War against France, San Martín contacted South American supporters of independence from Spain in London. In 1812, he set sail for Buenos Aires and offered his services to the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata, present-day Argentina and other countries. After the Battle of San Lorenzo and time commanding the Army of the North during 1814, he organized a plan to defeat the Spanish forces that menaced the United Provinces from the north, us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
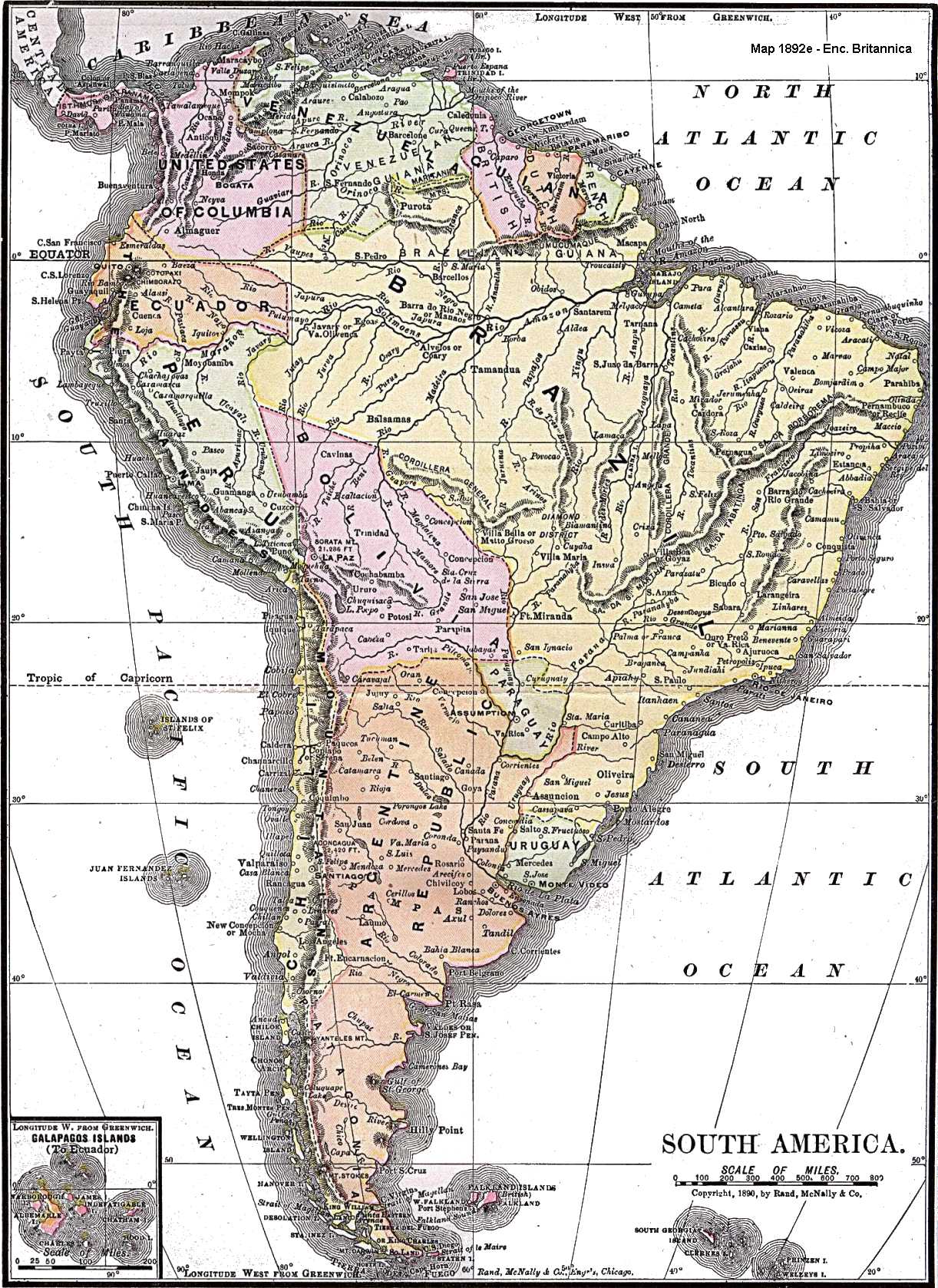
History Of South America
The history of South America is the study of the past, particularly the written record, oral histories, and traditions, passed down from generation to generation on the continent of South America. The continent continues to be home to indigenous peoples, some of whom built high civilizations prior to the arrival of Europeans in the late 1400s and early 1500s. South America has a history that has a wide range of human cultures and forms of civilization. The Norte Chico civilization in Peru dating back to about 3500 BCE is the oldest civilization in the Americas and one of the first six independent civilizations in the world; it was contemporaneous with the Egyptian pyramids. It predated the Mesoamerican Olmec by nearly two millennia. Indigenous peoples' thousands of years of independent life were disrupted by European colonization from Spain and Portugal and by demographic collapse. The resulting civilizations, however, were very different from those of their colonizers, both in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |