|
Attacin
Attacin is a glycine-rich protein of about 20 kDa belonging to the group of antimicrobial peptides (AMP). It is active against Gram-negative bacteria. Attacin was first discovered in ''Hyalophora cecropia ''Hyalophora cecropia'', the cecropia moth, is North America's largest native moth. It is a member of the family Saturniidae, or giant silk moths. Females have been documented with a wingspan of or more. These moths can be found predominately ac ...'', but is widely conserved in different insects from butterflies to fruit flies. See also * Diptericin, a structurally related antimicrobial peptide References {{Reflist Insect immunity Antimicrobial peptides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
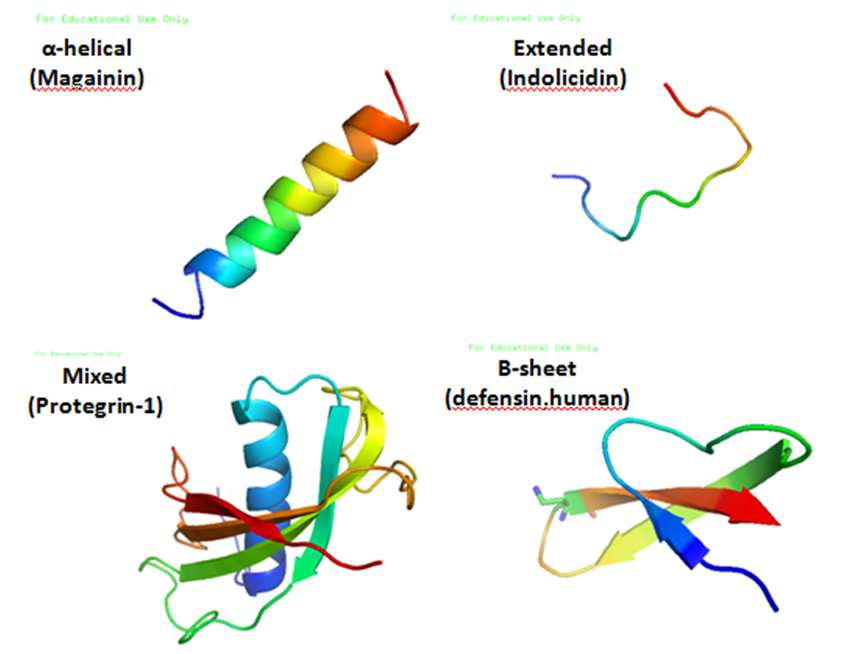
Antimicrobial Peptides
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), also called host defence peptides (HDPs) are part of the innate immune response found among all classes of life. Fundamental differences exist between Prokaryote, prokaryotic and eukaryota, eukaryotic cells that may represent targets for antimicrobial peptides. These peptides are potent, broad spectrum antimicrobials which demonstrate potential as novel therapeutic agents. Antimicrobial peptides have been demonstrated to kill Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria, enveloped viruses, fungi and even transformed or cancerous cells. Unlike the majority of conventional antibiotics it appears that antimicrobial peptides frequently destabilize biological membranes, can form transmembrane channels, and may also have the ability to enhance immunity by functioning as immunomodulators. Structure Antimicrobial peptides are a unique and diverse group of molecules, which are divided into subgroups on the basis of their amino acid composition and structure. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diptericin
Diptericin is a 9 kDa antimicrobial peptide (AMP) of flies first isolated from the blowfly '' Phormia terranova''. It is primarily active against Gram-negative bacteria, disrupting bacterial membrane integrity. The structure of this protein includes a proline-rich domain with similarities to the AMPs drosocin, pyrrhocoricin, and abaecin, and a glycine-rich domain with similarity to attacin. Diptericin is an iconic readout of immune system activity in flies, used ubiquitously in studies of ''Drosophila'' immunity. Diptericin is named after the insect order Diptera. Structure and function Diptericins are found throughout Diptera, but are most extensively characterized in ''Drosophila'' fruit flies. The mature structures of diptericins are unknown, though previous efforts to synthesize Diptericin have suggested Diptericin in '' Protophormia terraenovae'' is one linear peptide. Yet ''Drosophila melanogaster's'' Diptericin B peptide is likely cleaved into two separate peptides. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG). Glycine disrupts the formation of alpha-helices in secondary protein structure. Its small side chain causes it to favor random coils instead. Glycine is also an inhibitory neurotransmitter – interference with its release within the spinal cord (such as during a '' Clostridium tetani'' infection) can cause spastic paralysis due to uninhibited muscle contraction. It is the only achiral proteinogenic amino acid. It can fit into both hydrophilic and hydrophobic environments, due to its minimal side chain of only one hydrogen atom. History and etymology Glycine was discovered in 1820 by French chemist Henri Braconnot when he hydrolyzed gelatin by boiling it with sulfuric acid. He originally called it "sugar of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-negative Bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the Crystal violet, crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelope consists of a thin peptidoglycan gram-negative cell wall, cell wall sandwiched between an inner (Cytoplasm, cytoplasmic) Cell membrane, membrane and an Bacterial outer membrane, outer membrane. These bacteria are found in all environments that support life on Earth. Within this category, notable species include the model organism ''Escherichia coli'', along with various pathogenic bacteria, such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', ''Chlamydia trachomatis'', and ''Yersinia pestis''. They pose significant challenges in the medical field due to their outer membrane, which acts as a protective barrier against numerous Antibiotic, antibiotics (including penicillin), Detergent, detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyalophora Cecropia
''Hyalophora cecropia'', the cecropia moth, is North America's largest native moth. It is a member of the family Saturniidae, or giant silk moths. Females have been documented with a wingspan of or more. These moths can be found predominately across the east of North America, with occurrences as far west as Washington and north into the majority of Canadian provinces. Cecropia moth larvae are most commonly found on maple trees, but they have also been found on cherry and birch trees among many others. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae''. Life cycle Like other members of the giant silk moth family, the adult cecropia moth lacks functional mouth parts and a digestive system. Due to this, they survive approximately two weeks. To find a mate, the female cecropia moth emits pheromones which the male detects with its sensitive antennae. Male cecropia moths can detect these pheromones from up to a mile away, although a ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insect Immunity
Insects (from Latin ') are hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes, and a pair of antennae. Insects are the most diverse group of animals, with more than a million described species; they represent more than half of all animal species. The insect nervous system consists of a brain and a ventral nerve cord. Most insects reproduce by laying eggs. Insects breathe air through a system of paired openings along their sides, connected to small tubes that take air directly to the tissues. The blood therefore does not carry oxygen; it is only partly contained in vessels, and some circulates in an open hemocoel. Insect vision is mainly through their compound eyes, with additional small ocelli. Many insects can hear, using tympanal organs, which may be on the legs or other parts of the body. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |