|
Atomistix Virtual NanoLab
Atomistix Virtual NanoLab (VNL) is a commercial point-and-click software for simulation and analysis of physical and chemical properties of nanoscale devices. Virtual NanoLab is developed and sold commercially by QuantumWise A/S. QuantumWise was then acquired by Synopsys in 2017. Features With its graphical interface, Virtual NanoLab provides a user-friendly approach to atomic-scale modeling. The software contains a set of interactive instruments that allows the user to design nanosystems, to set up and execute numerical calculations, and to visualize the results. Samples such as molecules, nanotubes, crystalline systems, and two-probe systems (i.e. a nanostructure coupled to two electrodes) are built with a few mouse clicks. Virtual NanoLab contains a 3D visualization tool, the Nanoscope, where atomic geometries and computed results can be viewed and analyzed. One can for example plot Bloch functions of nanotubes and crystals, molecular orbitals, electron densities, and eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomistix
Atomistix A/S was a software company developing tools for atomic scale modelling. It was headquartered in Copenhagen, Denmark, with a subsidiary for Asia Pacific in Singapore and for the Americas in California. In September 2008 Atomistix A/S went bankrupt, but in December 2008 the newly founded company QuantumWise announced that they had acquired all assets from the Atomistix estate and would continue the development and marketing of the products Atomistix ToolKit and Atomistix Virtual NanoLab. QuantumWise was then acquired by Synopsys in 2017. History The company was founded in October 2003 by Dr. Kurt Stokbro, Dr. Jeremy Taylor and Dr. Thomas Magnussen. Dr. Stokbro and Dr. Taylor are co-authors on the article introducing the electron transport method and program TranSIESTA (based on the SIESTA program for academic research. This method, and methods used in Dr. Taylor Ph.D. research, was the starting point for Atomistix first product, TranSIESTA-C. The C refers to the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density Functional Theory
Density-functional theory (DFT) is a computational quantum mechanical modelling method used in physics, chemistry and materials science to investigate the electronic structure (or nuclear structure) (principally the ground state) of many-body systems, in particular atoms, molecules, and the condensed phases. Using this theory, the properties of a many-electron system can be determined by using functionals, i.e. functions of another function. In the case of DFT, these are functionals of the spatially dependent electron density. DFT is among the most popular and versatile methods available in condensed-matter physics, computational physics, and computational chemistry. DFT has been very popular for calculations in solid-state physics since the 1970s. However, DFT was not considered accurate enough for calculations in quantum chemistry until the 1990s, when the approximations used in the theory were greatly refined to better model the exchange and correlation interactio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics Software
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Chemistry Software
Computation is any type of arithmetic or non-arithmetic calculation that follows a well-defined model (e.g., an algorithm). Mechanical or electronic devices (or, historically, people) that perform computations are known as '' computers''. An especially well-known discipline of the study of computation is computer science. Physical process of Computation Computation can be seen as a purely physical process occurring inside a closed physical system called a computer. Examples of such physical systems are digital computers, mechanical computers, quantum computers, DNA computers, molecular computers, microfluidics-based computers, analog computers, and wetware computers. This point of view has been adopted by the physics of computation, a branch of theoretical physics, as well as the field of natural computing. An even more radical point of view, pancomputationalism (inaudible word), is the postulate of digital physics that argues that the evolution of the universe is itself a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Science
Computational science, also known as scientific computing or scientific computation (SC), is a field in mathematics that uses advanced computing capabilities to understand and solve complex problems. It is an area of science that spans many disciplines, but at its core, it involves the development of models and simulations to understand natural systems. * Algorithms ( numerical and non-numerical): mathematical models, computational models, and computer simulations developed to solve science (e.g., biological, physical, and social), engineering, and humanities problems * Computer hardware that develops and optimizes the advanced system hardware, firmware, networking, and data management components needed to solve computationally demanding problems * The computing infrastructure that supports both the science and engineering problem solving and the developmental computer and information science In practical use, it is typically the application of computer simulation and other f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
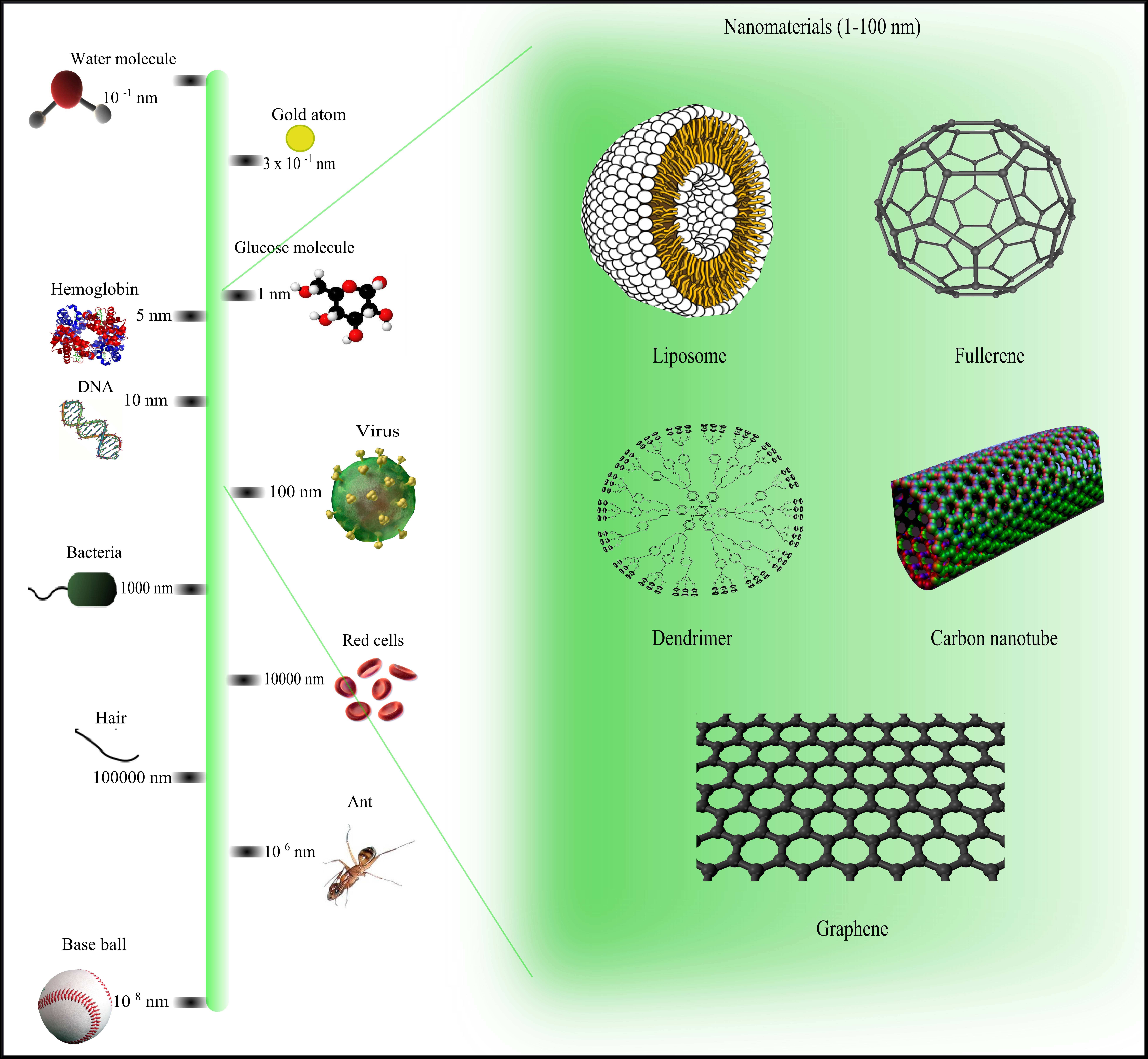
Nanotechnology Companies
Nanotechnology, also shortened to nanotech, is the use of matter on an atomic, molecular, and supramolecular scale for industrial purposes. The earliest, widespread description of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabrication of macroscale products, also now referred to as molecular nanotechnology. A more generalized description of nanotechnology was subsequently established by the National Nanotechnology Initiative, which defined nanotechnology as the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). This definition reflects the fact that quantum mechanical effects are important at this quantum-realm scale, and so the definition shifted from a particular technological goal to a research category inclusive of all types of research and technologies that deal with the special properties of matter which occur below the given size threshold. It is therefore common to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NanoLanguage
NanoLanguage is a scripting interface built on top of the interpreted programming language Python, and is primarily intended for simulation of physical and chemical properties of nanoscale systems. Introduction Over the years, several electronic-structure codes based on density functional theory have been developed by different groups of academic researchers; VASP, Abinit, SIESTA, and Gaussian are just a few examples. The input to these programs is usually a simple text file written in a code-specific format with a set of code-specific keywords. NanoLanguage was introduced by Atomistix A/S as an interface to Atomistix ToolKit (version 2.1) in order to provide a more flexible input format. A NanoLanguage script (or input file) is just a Python program and can be anything from a few lines to a script performing complex numerical simulations, communicating with other scripts and files, and communicating with other software (e.g. plotting programs). NanoLanguage is not a proprietary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ab Initio
''Ab initio'' ( ) is a Latin term meaning "from the beginning" and is derived from the Latin ''ab'' ("from") + ''initio'', ablative singular of ''initium'' ("beginning"). Etymology Circa 1600, from Latin, literally "from the beginning", from ablative case of ''initium'' "entrance", "beginning", related to verb ''inire'' "to go into", "enter upon", "begin". Uses ''Ab initio'' (abbreviation: ''ab init.'') is used in several contexts, including the following: Law In law, ''ab initio'' refers to something being the case from the start or from the instant of the act rather than from when the court declared it so. For instance, the term "void ''ab initio''" means "to be treated as invalid from the outset." E.g., in many jurisdictions, if a person signs a contract under duress, that contract is treated as being "void ''ab initio''". Typically, documents or acts which are void ''ab initio'' cannot be fixed and if a jurisdiction, a document, or an act is so declared at law to be vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green's Functions
In mathematics, a Green's function is the impulse response of an inhomogeneous linear differential operator defined on a domain with specified initial conditions or boundary conditions. This means that if \operatorname is the linear differential operator, then * the Green's function G is the solution of the equation \operatorname G = \delta, where \delta is Dirac's delta function; * the solution of the initial-value problem \operatorname y = f is the convolution (G \ast f). Through the superposition principle, given a linear ordinary differential equation (ODE), \operatorname y = f, one can first solve \operatorname G = \delta_s, for each , and realizing that, since the source is a sum of delta functions, the solution is a sum of Green's functions as well, by linearity of . Green's functions are named after the British mathematician George Green, who first developed the concept in the 1820s. In the modern study of linear partial differential equations, Green's functions ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomistix ToolKit
Atomistix ToolKit (ATK) is a commercial software for atomic-scale modeling and simulation of nanosystems. The software was originally developed by Atomistix A/S, and was later acquired by QuantumWise following the Atomistix bankruptcy. QuantumWise was then acquired by Synopsys in 2017. Atomistix ToolKit is a further development of TranSIESTA-C, which in turn in based on the technology, models, and algorithms developed in the academic codes TranSIESTA, and McDCal, employing localized basis sets as developed in SIESTA. Features Atomistix ToolKit combines density functional theory with non-equilibrium Green's functions for first principles electronic structure and transport calculations of *electrode—nanostructure—electrode systems (two-probe systems) *molecules *periodic systems (bulk crystals and nanotubes) The key features are *Calculation of transport properties of two-probe systems under an applied bias voltage *Calculation of energy spectra, wave functions, el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology, also shortened to nanotech, is the use of matter on an atomic, molecular, and supramolecular scale for industrial purposes. The earliest, widespread description of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabrication of macroscale products, also now referred to as molecular nanotechnology. A more generalized description of nanotechnology was subsequently established by the National Nanotechnology Initiative, which defined nanotechnology as the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). This definition reflects the fact that quantum mechanical effects are important at this quantum-realm scale, and so the definition shifted from a particular technological goal to a research category inclusive of all types of research and technologies that deal with the special properties of matter which occur below the given size threshold. It is therefore commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Density
In quantum chemistry, electron density or electronic density is the measure of the probability of an electron being present at an infinitesimal element of space surrounding any given point. It is a scalar quantity depending upon three spatial variables and is typically denoted as either \rho(\textbf r) or n(\textbf r). The density is determined, through definition, by the normalised N-electron wavefunction which itself depends upon 4N variables (3N spatial and N spin coordinates). Conversely, the density determines the wave function modulo up to a phase factor, providing the formal foundation of density functional theory. According to quantum mechanics, due to the uncertainty principle on an atomic scale the exact location of an electron cannot be predicted, only the probability of its being at a given position; therefore electrons in atoms and molecules act as if they are "smeared out" in space. For one-electron systems, the electron density at any point is proportional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |