|
Atilia (band)
Atilia (sometimes spelt Attilia) was the first wife of Marcus Porcius Cato Uticensis and mother of his two eldest children. Biography Early life It is not known for certain who Atilia's father was, but he was from the Atilii Serrani. He may have been Gaius Atilius Serranus the consul of 106 BC, or Gaius' son. Marriage Cato married Atilia c. 73 BC, after his intended wife, Aemilia Lepida married Quintus Caecilius Metellus Pius Scipio Nasica. In the words of Plutarch: :tiliawas the first woman with whom he made love, but not the only one, as was true of Laelius, the friend of Scipio Africanus; Laelius, indeed, was more fortunate, since in the course of his long life he only ever made love to one woman, the wife of his youth. Cato and Atilia had a son Marcus Porcius Cato, who later died in the second Battle of Philippi, and a daughter Porcia, who became the wife of her cousin Marcus Junius Brutus Marcus Junius Brutus (; ; 85 BC – 23 October 42 BC) was a Roman politician, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Atilius Serranus
Gaius Atilius Serranus (c. 149 – 87 BC) was a Roman senator, who served as consul in 106 BC as the colleague of Quintus Servilius Caepio. Career Although noted by Cicero as being a "a most stupid man" (), he managed to defeat Quintus Lutatius Catulus in the consular elections of the previous year. Before this, Serranus had presumably held the office of praetor by 109 BC, a necessary requirement in the senatorial career track. Serranus was one of the senators of consular rank who took up arms against the tribune Saturninus in 100 BC. He is probably the Atilius Serranus who was murdered on orders of Gaius Marius following the conclusion of the civil war in 87 BC. Family Serranus may have been the father or more likely grandfather of Atilia the wife of Cato the Younger. See also * List of Roman consuls This is a list of consuls known to have held office, from the beginning of the Roman Republic to the latest use of the title in Imperial times, together with those ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aemilia Lepida
Aemilia Lepida is a Latin feminine given name that was given to the daughters of various Aemilius Lepiduses (), men belonging to the Lepidus branch of the Aemilia (family) that was founded by the Marcus Aemilius Lepidus who served as consul in . The Aemila Lepidas () who appear in Roman historians were principally known for their engagements and marriages, with those in the late Republic and early Empire related to the Julio-Claudian dynasty. Aemilia Lepida (1st century BC), wife of Metellus Scipio This Aemilia was daughter of Mamercus Aemilius Lepidus Livianus, wife of Metellus Scipio and former fiancée of Cato. Her daughter was Cornelia Metella, last wife and widow of Pompey the Great. Although Aemilia Lepida was engaged to be married to Cato the Younger, she in fact married someone else, leaving Cato to marry Atilia. In the words of Plutarch: When atothought that he was old enough to marry — and up to that time he had consorted with no woman — he engaged him ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quintus Caecilius Metellus Pius Scipio Nasica
Quintus Caecilius Metellus Pius Scipio (c. 95 – 46 BC), often referred to as Metellus Scipio, was a Roman senator and military commander. During the civil war between Julius Caesar and the senatorial faction led by Pompey, he was a staunch supporter of the latter. He led troops against Caesar's forces, mainly in the battles of Pharsalus and Thapsus, where he was defeated. He later committed suicide. Ronald Syme called him "the last Scipio of any consequence in Roman history." Family connections and name The son of Publius Cornelius Scipio Nasica, praetor about 95 BC, and Licinia, Scipio was the grandson of Publius Cornelius Scipio Nasica, consul in 111, and Lucius Licinius Crassus, consul in 95. His great-grandfather was Scipio Nasica Serapio, the man who murdered Tiberius Gracchus in 133 BC. Through his mother Cornelia, Serapio was also the grandson of Scipio Africanus. Scipio's father died not long after his praetorship, and was survived by two sons and two daughters. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Laelius
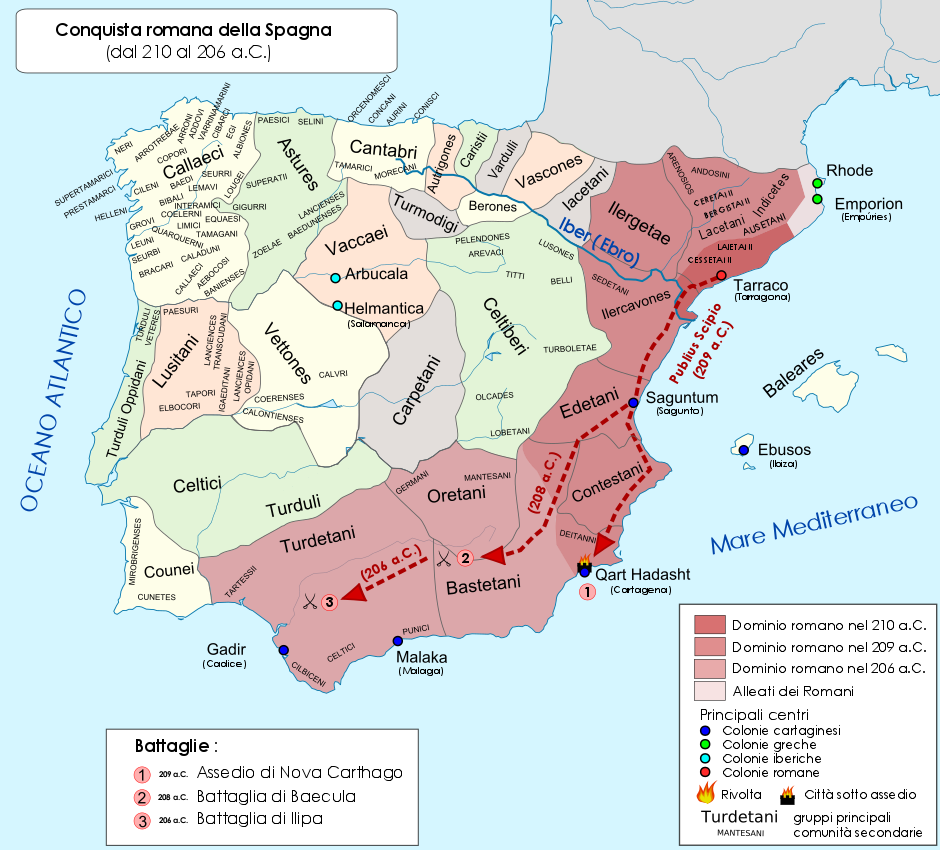
Gaius Laelius was a Roman general and statesman, and a friend of Scipio Africanus, whom he accompanied on his Iberian campaign (210–206 BC; the Roman Hispania, comprising modern Spain and Portugal) and his African campaign (204–202 BC). His command of the Roman fleet in the attack on New Carthage and command of the Roman cavalry at Zama contributed to Scipio's victories. Background According to some Roman historians, including Polybius (Polybius, X, 3), Laelius was a friend of Scipio from childhood; however, his family background is obscure. This obscurity unfortunately extends to how he became acquainted with Scipio in the first place. Livy suggested that he was not from a rich family, since he wanted command of the campaign against Antiochus the Great in 190 BC to repair (or more likely make) his family fortunes. Polybius suggests that Laelius was a companion of Scipio from their earliest days in the army together, since Laelius was apparently a witness to Scipio's rescue o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scipio Africanus
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus (, , ; 236/235–) was a Roman general and statesman who was one of the main architects of Rome's victory against Ancient Carthage, Carthage in the Second Punic War. Often regarded as one of the greatest military commanders and strategists of all time, his greatest military achievement was the defeat of Hannibal at the Battle of Zama in 202 BC. This victory in Africa earned him the honorific epithet ''Africanus'', literally meaning 'the African', but meant to be understood as a conqueror of Africa (Roman province), Africa. Scipio's conquest of Carthaginian Iberia culminated in the Battle of Ilipa in 206 BC against Hannibal's brother Mago Barca. Although considered a hero by the Roman people, primarily for his victories against Carthage, Scipio had many opponents, especially Cato the Elder, who hated him deeply. In 187 BC, he was tried in a show trial alongside his brother for bribes they supposedly received from the Seleucid king Antiochus III ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Porcius Cato (son Of Cato The Younger)
Marcus Porcius Cato (c. 73-42 BC), son of Cato the Younger by his first marriage to Atilia, was a Roman soldier and in his earlier years spent some time in politics with his father. Although he never achieved greatness, he was admired by close friends and relatives, and also served his father most loyally and shared his ideals. Marcus was renowned for being a man of gallantry and warm temperament. Biography He was the brother of Porcia Catonis, who was first married to Marcus Calpurnius Bibulus (co-consul with Caesar in 59 BC); she later married their half-cousin (on the maternal side) Marcus Junius Brutus. Marcus fought in the Battle of Thapsus, and after being defeated by Caesar's forces his father Cato committed suicide in 46 BC. Julius Caesar pardoned young Cato and allowed him to keep his father's property. In spite of being pardoned by Caesar and allowed to return home, Marcus joined his brother-in-law Brutus and his ally Gaius Cassius Longinus, who both assassinated Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Philippi
The Battle of Philippi was the final battle in the Liberators' civil war between the forces of Mark Antony and Octavian (of the Second Triumvirate) and the leaders of Julius Caesar's assassination, Brutus and Cassius, in 42 BC, at Philippi in Macedonia. The Second Triumvirate declared the civil war ostensibly to avenge Julius Caesar's assassination in 44 BC, but the underlying cause was a long-brewing conflict between the Optimates and the Populares. The battle, involving up to 200,000 men in one of the largest of the Roman civil wars, consisted of two engagements in the plain west of the ancient city of Philippi. The first occurred in the first week of October; Brutus faced Octavian, and Antony's forces fought those of Cassius. The Roman armies fought poorly, with low discipline, nonexistent tactical coordination and amateurish lack of command experience evident in abundance with neither side able to exploit opportunities as they developed. At first, Brutus pushed back Octa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porcia (wife Of Brutus)
Porcia ( – June 43 BC), occasionally spelled Portia, especially in 18th-century English literature, was a Roman Republic, Roman woman who lived in the 1st century BC. She was the daughter of Cato the Younger, Marcus Porcius Cato Uticensis (Cato the Younger) and his first wife Atilia. She is best known for being the second wife of Marcus Junius Brutus, the most famous of Assassination of Julius Caesar, Julius Caesar's assassins, and appears primarily in the Writings of Cicero, letters of Cicero. Biography Early life Porcia was born around 73 BC. She had an affectionate nature, was interested in philosophy, and was "full of an understanding courage."Plutarch, ''Marcus Brutus'', 13.4. Plutarch describes her as being prime of youth and beauty. When she was still very young, her father divorced her mother for adultery. At a young age she was married first to Marcus Calpurnius Bibulus, her father's political ally, between 58 BC and 53 BC. Porcia's father was a member of the Optimat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Junius Brutus
Marcus Junius Brutus (; ; 85 BC – 23 October 42 BC) was a Roman politician, orator, and the most famous of the assassins of Julius Caesar. After being adopted by a relative, he used the name Quintus Servilius Caepio Brutus, which was retained as his legal name. He is often referred to simply as Brutus. Early in his political career, Brutus opposed Pompey, who was responsible for Brutus' father's death. He also was close to Caesar. However, Caesar's attempts to evade accountability in the law courts put him at greater odds with his opponents in the Roman elite and the senate. Brutus eventually came to oppose Caesar and sided with Pompey against Caesar's forces during the ensuing civil war (49–45 BC). Pompey was defeated at the Battle of Pharsalus in 48, after which Brutus surrendered to Caesar, who granted him amnesty. With Caesar's increasingly monarchical and autocratic behaviour after the civil war, several senators who later called themselves ''liberatores'' (liber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcia (wife Of Cato)
Marcia (also Marzia or Martia; born 80 BC) was the second wife of Marcus Porcius Cato Uticensis (Cato the Younger) and the daughter of Lucius Marcius Philippus. Biography Early life Marcia is believed to have been born around 80 BC to Lucius Marcius Philippus and his first wife. She had two brothers named Lucius Marcius Philippus and Quintus Marcius Philippus.Sumner, "Lex Annalis", pp. 252–254. When her father married Atia, she became the step-sister of Octavia Minor and Gaius Octavius Thurinus (the future emperor Augustus). Marriages and children After Cato divorced his first wife Atilia because of rumors about her infidelity, in 63 BC, he married Marcia whom Plutarch described as "a woman of excellent reputation, about whom there was the most abundant talk". Marcia and Cato had two or three children; however, there is controversy about whether or not she was pregnant with this third child at the time of her second marriage to Hortensius. There is no indication t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st-century BC Roman Women
File:1st century collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Jesus is crucified by Roman authorities in Judaea (17th century painting). Four different men ( Galba, Otho, Vitellius, and Vespasian) claim the title of Emperor within the span of a year; The Great Fire of Rome (18th-century painting) sees the destruction of two-thirds of the city, precipitating the empire's first persecution against Christians, who are blamed for the disaster; The Roman Colosseum is built and holds its inaugural games; Roman forces besiege Jerusalem during the First Jewish–Roman War (19th-century painting); The Trưng sisters lead a rebellion against the Chinese Han dynasty (anachronistic depiction); Boudica, queen of the British Iceni leads a rebellion against Rome (19th-century statue); Knife-shaped coin of the Xin dynasty., 335px rect 30 30 737 1077 Crucifixion of Jesus rect 767 30 1815 1077 Year of the Four Emperors rect 1846 30 3223 1077 Great Fire of Rome rect 30 1108 1106 2155 Boudican re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |