|
Athmonum
Athmonum or Athmonon (), also Athmonia (Ἀθμονία), was a deme of ancient Attica, situated on the site of Marousi (Amarousion). The name of the modern village has been derived from Amarysia, a surname of Artemis, who was worshipped under this designation at Athmonum. An inscription found near Marousi, in which the ''temenos'' of this goddess is mentioned, puts the matter beyond dispute. Athmonum also possessed a very ancient temple of Aphrodite Urania. The inhabitants of this deme appear to have been considered clever wine-dressers.Aristophanes, ''Pac.'' 190. See also * List of ancient Greek cities This is an incomplete list of ancient Greek cities, including colonies outside Greece, and including settlements that were not sovereign '' poleis''. Many colonies outside Greece were soon assimilated to some other language but a city is included h ... References Populated places in ancient Attica Former populated places in Greece Demoi {{AncientAttica-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marousi
Marousi or Maroussi (), also known as Amarousio (), is a city and a suburb in the northeastern part of the Athens#Athens Urban Area, Athens urban area, Greece. Marousi dates back to the era of the History of Athens, ancient Athenian Republic; its ancient name was ''Athmonum, Athmonon'' () and it represented one of the 10 Athenian sub-cities. The area held a main ancient temple, where Amarysia Artemis, the goddess of hunting, was adored. Consequently the city's modern name derives from that of the goddess, ''Amarysia'', which denotes the origin of the worship back in Amarynthos, Euboea. Its mayor is Theodoros Ampatzoglou, re-elected in 2023.Municipality of Maroussi, Municipal elections – October 2023 Ministry of Interior Geography Marousi is situated ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deme
In Ancient Greece, a deme or (, plural: ''demoi'', δήμοι) was a suburb or a subdivision of Classical Athens, Athens and other city-states. Demes as simple subdivisions of land in the countryside existed in the 6th century BC and earlier, but did not acquire particular significance until the reforms of Cleisthenes in 508 BC. In those reforms, enrollment in the citizen-lists of a deme became the requirement for citizenship; prior to that time, citizenship had been based on membership in a phratry, or family group. At this same time, demes were established in the main city of Athens itself, where they had not previously existed; in all, at the end of Cleisthenes' reforms, Classical Athens, Athens was divided into 139 demes., Three other demes were created subsequently: Berenikidai (224/223 BC), Apollonieis (201/200 BC), and Antinoeis (AD 126/127). The establishment of demes as the fundamental units of the state weakened the ''genos, gene'', or aristocratic family groups, that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
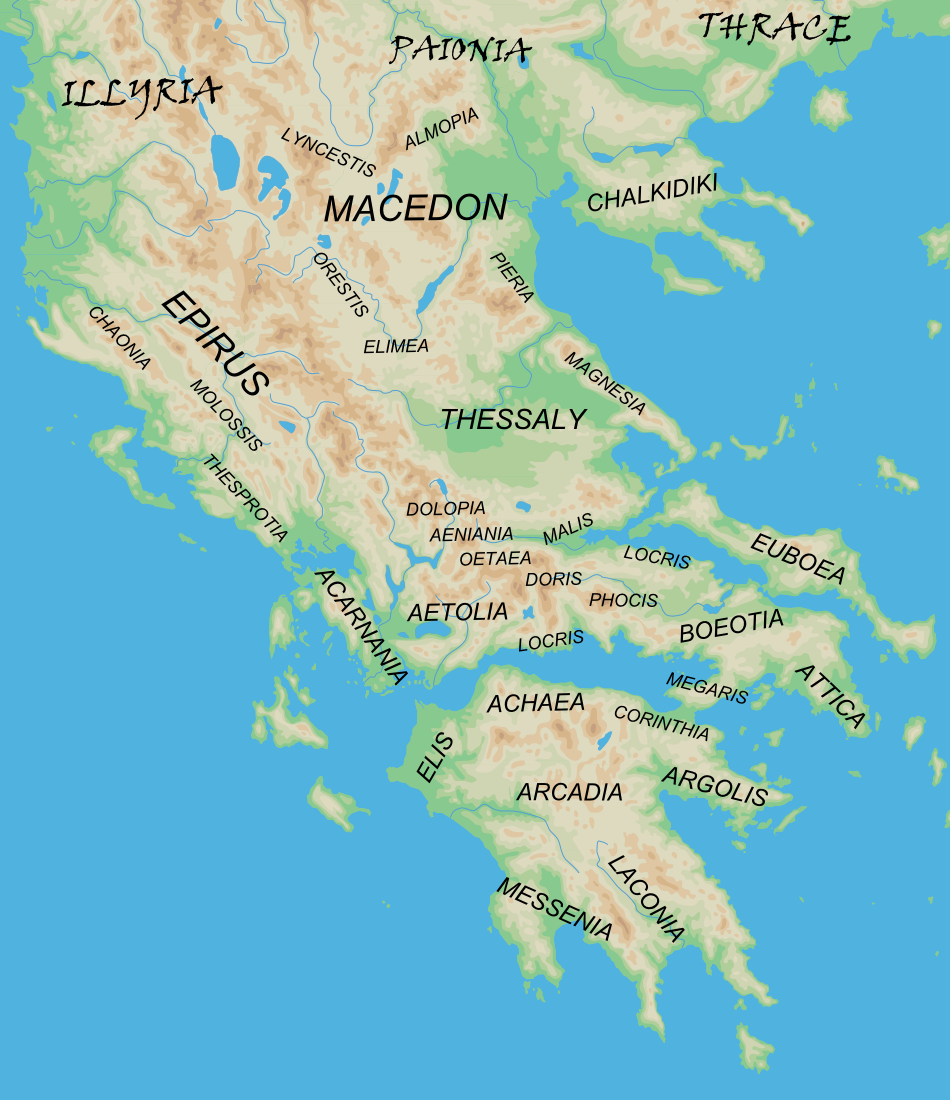
Ancient Attica
The regions of ancient Greece were sub-divisions of the Hellenic world as conceived by the ancient Greeks, shown by their presence in the works of ancient historians and geographers or in surviving legends and myths. Conceptually, there is no clear theme to the structure of these regions. Some, particularly in the Peloponnese, can be seen primarily as distinct geo-physical units, defined by physical boundaries such as mountain ranges and rivers. Conversely, the division of central Greece between Boeotia, Phocis, Doris and the three parts of Locris, seems to be attributable to ancient tribal divisions and not major geographical features. Both types of regions retained their identity throughout the Greek Dark Ages and its tumultuous changes in the local population and culture, giving them a less political and more symbolic presence. Other geographical divisions not identified with the aforementioned areas did, however, change over time, suggesting a closer connection with tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artemis
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Artemis (; ) is the goddess of the hunting, hunt, the wilderness, wild animals, transitions, nature, vegetation, childbirth, Kourotrophos, care of children, and chastity. In later times, she was identified with Selene, the Lunar deity, personification of the Moon.Smiths.v. Artemis/ref> She was often said to roam the forests and mountains, attended by her entourage of nymphs. The goddess Diana (mythology), Diana is her Religion in ancient Rome, Roman equivalent. In Greek tradition, Artemis is the daughter of Zeus and Leto, and twin sister of Apollo. In most accounts, the twins are the products of an extramarital liaison. For this, Zeus' wife Hera forbade Leto from giving birth anywhere on solid land. Only the island of Delos gave refuge to Leto, allowing her to give birth to her children. In one account, Artemis is born first and then proceeds to assist Leto in the birth of the second twin, Apollo. Artemis was a kouro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temenos
A ''temenos'' ( Greek: ; plural: , ''temenē''). is a piece of land cut off and assigned as an official domain, especially to kings and chiefs, or a piece of land marked off from common uses and dedicated to a god, such as a sanctuary, holy grove, or holy precinct. A ''temenos'' enclosed a sacred space called a ''hieron''. It was usually surrounded by a wall, ditch, or line of stones. All things inside of the demarcated area belonged to the designated god. Greeks could find asylum within a sanctuary and be under the protection of the deity and could not be moved against their will. Etymology The word derives from the Greek verb (''temnō''), "I cut". The earliest attested form of the word is the Mycenaean Greek , ''te-me-no'', written in Linear B syllabic script. The Latin language equivalent was '' fanum''. In religious discourse in English, ''temenos'' has also come to refer to a territory, plane, receptacle or field of deity or divinity. Examples * The race-course of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphrodite Urania
Aphrodite Urania (, Latinized as Venus Urania) was an epithet of the Greek goddess Aphrodite, signifying a "heavenly" or "spiritual" aspect descended from the sky-god Ouranos to distinguish her from the more earthly epithet of Aphrodite Pandemos, "Aphrodite for all the people". The two were used (mostly in literature) to differentiate the more "celestial" love of body and soul from purely physical lust. Plato represented her as a daughter of the Greek god Uranus, conceived and born without a mother. Hesiod described this aspect as being born from the severed genitals of Uranus and emerging from the sea foam. Etymology and names According to Herodotus, the Arabs called this aspect of the goddess " Alitta" or "Alilat" ( or ). The most distinctively Western Asian title of the Greek Aphrodite is Urania, the Semitic "queen of the heavens". It has been explained by reference to the lunar character of the goddess, but more probably signifies "she whose seat is in heaven", whence s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristophanes
Aristophanes (; ; ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Ancient Greek comedy, comic playwright from Classical Athens, Athens. He wrote in total forty plays, of which eleven survive virtually complete today. The majority of his surviving plays belong to the genre of comic drama known as Old Comedy and are considered its most valuable examples. Aristophanes' plays were performed at the religious festivals of Athens, mostly the City Dionysia and the Lenaia, and several of them won the first prize in their respective competitions. Also known as "The Father of Comedy" and "the Prince of Ancient Comedy", Aristophanes wrote plays that often dealt with real-life figures, including Euripides and Alcibiades, and contemporary events, such as the Peloponnesian War. He has been said to recreate the life of ancient Athens more convincingly than any other author. His plays are characterized by preposterous premises, explicit language, wordplays, and political satire. His powers of ridicule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ancient Greek Cities
This is an incomplete list of ancient Greek cities, including colonies outside Greece, and including settlements that were not sovereign '' poleis''. Many colonies outside Greece were soon assimilated to some other language but a city is included here if at any time its population or the dominant stratum within it spoke Greek. Also included are some cities that were not Greek-speaking or Hellenic, but contributed to the Hellenic culture of the region. A B C D E G H I J K L M N O P R S T V Z See also * Greek colonisation Greek colonisation refers to the expansion of Archaic Greeks, particularly during the 8th–6th centuries BC, across the Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea. The Archaic expansion differed from the Iron Age migrations of the Greek Dark Ag ... * Adjectival and demonymic forms of regions in Greco-Roman antiquity * List of cities in ancient Epirus * Greek cities in Thrace and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populated Places In Ancient Attica
Population is a set of humans or other organisms in a given region or area. Governments conduct a census to quantify the resident population size within a given jurisdiction. The term is also applied to non-human animals, microorganisms, and plants, and has specific uses within such fields as ecology and genetics. Etymology The word ''population'' is derived from the Late Latin ''populatio'' (a people, a multitude), which itself is derived from the Latin word ''populus'' (a people). Use of the term Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined feature in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species which inhabit the same geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where interbreeding is possible between any opposite-sex pair within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Populated Places In Greece
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being used in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose cone to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built unt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |