|
Athlon
AMD Athlon is the brand name applied to a series of x86, x86-compatible microprocessors designed and manufactured by AMD, Advanced Micro Devices. The original Athlon (now called Athlon Classic) was the first seventh-generation x86 processor and the first desktop processor to reach speeds of one gigahertz (GHz). It made its debut as AMD's high-end processor brand on June 23, 1999. Over the years AMD has used the Athlon name with the 64-bit Athlon 64 architecture, the Athlon II, and Accelerated Processing Unit (APU) chips targeting the Socket AM1 desktop System on a chip, SoC architecture, and Socket AM4 Zen (microarchitecture). The modern Zen-based Athlon with a Radeon, Radeon Graphics processor was introduced in 2019 as AMD's highest-performance entry-level processor. Brand history K7 design and development The first Athlon processor was a result of AMD's development of K7 processors in the 1990s. AMD founder and then-CEO Jerry Sanders (businessman), Jerry Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athlon Logo
AMD Athlon is the brand name applied to a series of x86-compatible microprocessors designed and manufactured by Advanced Micro Devices. The original Athlon (now called Athlon Classic) was the first seventh-generation x86 processor and the first desktop processor to reach speeds of one gigahertz (GHz). It made its debut as AMD's high-end processor brand on June 23, 1999. Over the years AMD has used the Athlon name with the 64-bit Athlon 64 architecture, the Athlon II, and Accelerated Processing Unit (APU) chips targeting the Socket AM1 desktop SoC architecture, and Socket AM4 Zen (microarchitecture). The modern Zen-based Athlon with a Radeon Graphics processor was introduced in 2019 as AMD's highest-performance entry-level processor. Brand history K7 design and development The first Athlon processor was a result of AMD's development of K7 processors in the 1990s. AMD founder and then-CEO Jerry Sanders aggressively pursued strategic partnerships and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athlon 64
The Athlon 64 is a ninth-generation, AMD64-architecture microprocessor produced by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), released on September 23, 2003. It is the third processor to bear the name ''Athlon'', and the immediate successor to the Athlon XP. The Athlon 64 was the second processor to implement the AMD64 architecture (after the Opteron) and the first 64-bit processor targeted at the average consumer. Variants of the Athlon 64 have been produced for Socket 754, Socket 939, Socket 940, and Socket AM2. It was AMD's primary consumer CPU, and primarily competed with Intel's Pentium 4, especially the ''Prescott'' and ''Cedar Mill'' core revisions. The Athlon 64 is AMD's first AMD K8, K8, eighth-generation processor core for desktop and mobile computers. Despite being natively 64-bit, the AMD64 architecture is backward-compatible with 32-bit x86 instructions. The Athlon 64 line was succeeded by the dual-core Athlon 64 X2 and Athlon X2 lines. Background The Athlon 64 was originally cod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athlon II
Athlon II is a family of AMD multi-core 45 nm central processing units, which is aimed at the budget to mid-range market and is a complementary product lineup to the Phenom II. Features The Athlon II series is based on the AMD K10 architecture and derived from the Phenom II series. However, unlike its Phenom siblings, it does not contain any L3 Cache. There are two principal Athlon II dies: the dual-core Regor die with 1 MB L2 Cache per core and the four-core Propus with 512 KB per core. Regor is a native dual-core design with lower TDP and additional L2 to offset the removal of L3 cache. The Athlon II x2 200e-220 chips have less L2 cache than the rest of the Regor line. The triple-core ''Rana'' is derived from the Propus quad-core design, with one core disabled. In some cases, the Phenom II Deneb die is used with disabled L3 cache and cores in the case. Includes: AMD Direct Connect Architecture AMD Wide Floating Point Accelerator AMD Digital Media XPress 2.0 Tech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentium III
The Pentium III (marketed as Intel Pentium III Processor, informally PIII or P3) brand refers to Intel's 32-bit x86 desktop and mobile CPUs based on the sixth-generation P6 microarchitecture introduced on February 28, 1999. The brand's initial processors were very similar to the earlier Pentium II-branded processors. The most notable differences were the addition of the Streaming SIMD Extensions (SSE) instruction set (to accelerate floating point and parallel calculations), and the introduction of a controversial serial number embedded in the chip during manufacturing. Even after the release of the Pentium 4 in late 2000, the Pentium III continued to be produced with new models introduced up until early 2003. They were then discontinued in April 2004 for desktop units and May 2007 for mobile units. Processor cores Similarly to the Pentium II it superseded, the Pentium III was also accompanied by the Celeron brand for lower-end versions, and the Xeon for high-end (server and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accelerated Processing Unit
AMD Accelerated Processing Unit (APU), formerly known as Fusion, is a series of 64-bit microprocessors from Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), combining a general-purpose AMD64 central processing unit ( CPU) and 3D integrated graphics processing unit (IGPU) on a single die. AMD announced the first generation APUs, ''Llano'' for high-performance and ''Brazos'' for low-power devices, in January 2011 and launched the first units on June 14. The second generation ''Trinity'' for high-performance and ''Brazos-2'' for low-power devices were announced in June 2012. The third generation ''Kaveri'' for high performance devices were launched in January 2014, while ''Kabini'' and ''Temash'' for low-power devices were announced in the summer of 2013. Since the launch of the Zen microarchitecture, Ryzen and Athlon APUs have released to the global market as Raven Ridge on the DDR4 platform, after Bristol Ridge a year prior. AMD has also supplied semi-custom APUs for consoles starting with the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket AM1
Socket AM1 is a CPU socket, socket designed by AMD, launched in April 2014 for desktop System on a chip, SoCs in the value segment. Socket AM1 is intended for a class of CPUs that contain both an integrated GPU and a chipset, essentially forming a complete System_on_a_chip, SoC implementation, and as such has pins for display, PCI Express, SATA, and other I/O interfaces directly in the socket. AMD's first compatible CPUs, designated as AMD Accelerated Processing Unit, APUs, are 4 socketable chips in the Jaguar_(microarchitecture)#Desktop, ''Kabini'' family of the Jaguar microarchitecture, marketed under the Athlon and Sempron names and announced on April 9, 2014. Socket AM1 was initially branded as ''Socket FS1b'' before its release. The brand names are Athlon and Sempron. The underlying microarchitectures are Jaguar_(microarchitecture), Jaguar and Puma (microarchitecture), Puma. All products are system on a chip, SoCs, this means the List of AMD chipsets#Fusion controller hubs ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circuitry required to perform the functions of a computer's central processing unit (CPU). The IC is capable of interpreting and executing program instructions and performing arithmetic operations. The microprocessor is a multipurpose, Clock signal, clock-driven, Processor register, register-based, digital integrated circuit that accepts binary code, binary data as input, processes it according to instruction (computing), instructions stored in its computer memory, memory, and provides results (also in binary form) as output. Microprocessors contain both combinational logic and sequential logic, sequential digital logic, and operate on numbers and symbols represented in the binary number system. The integration of a whole CPU on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket AM4
Socket AM4 is a PGA microprocessor socket used by AMD's central processing units (CPUs) built on the Zen (including Zen+, Zen 2 and Zen 3) and Excavator microarchitectures. ''AM4'' was launched in September 2016 and was designed to replace the sockets AM3+, FM2+ and FS1b as a single platform. It has 1331 pin slots and is the first from AMD to support DDR4 memory as well as achieve unified compatibility between high-end CPUs (previously using Socket AM3+) and AMD's lower-end APUs (on various other sockets). In 2017, AMD made a commitment to using the AM4 platform with socket 1331 until 2020. AM5 succeeded the AM4 platform in late 2022 with the introduction of the Ryzen 7000 series, however, AMD has continued to release new CPUs for AM4 even after the release of AM5. Features * Support for Zen (including Zen+, Zen 2 and Zen 3) based family of CPUs and APUs (Ryzen, Athlon), as well as for some A-Series APUs and Athlon X4 CPUs (Bristol Ridge based on the Excavator micro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
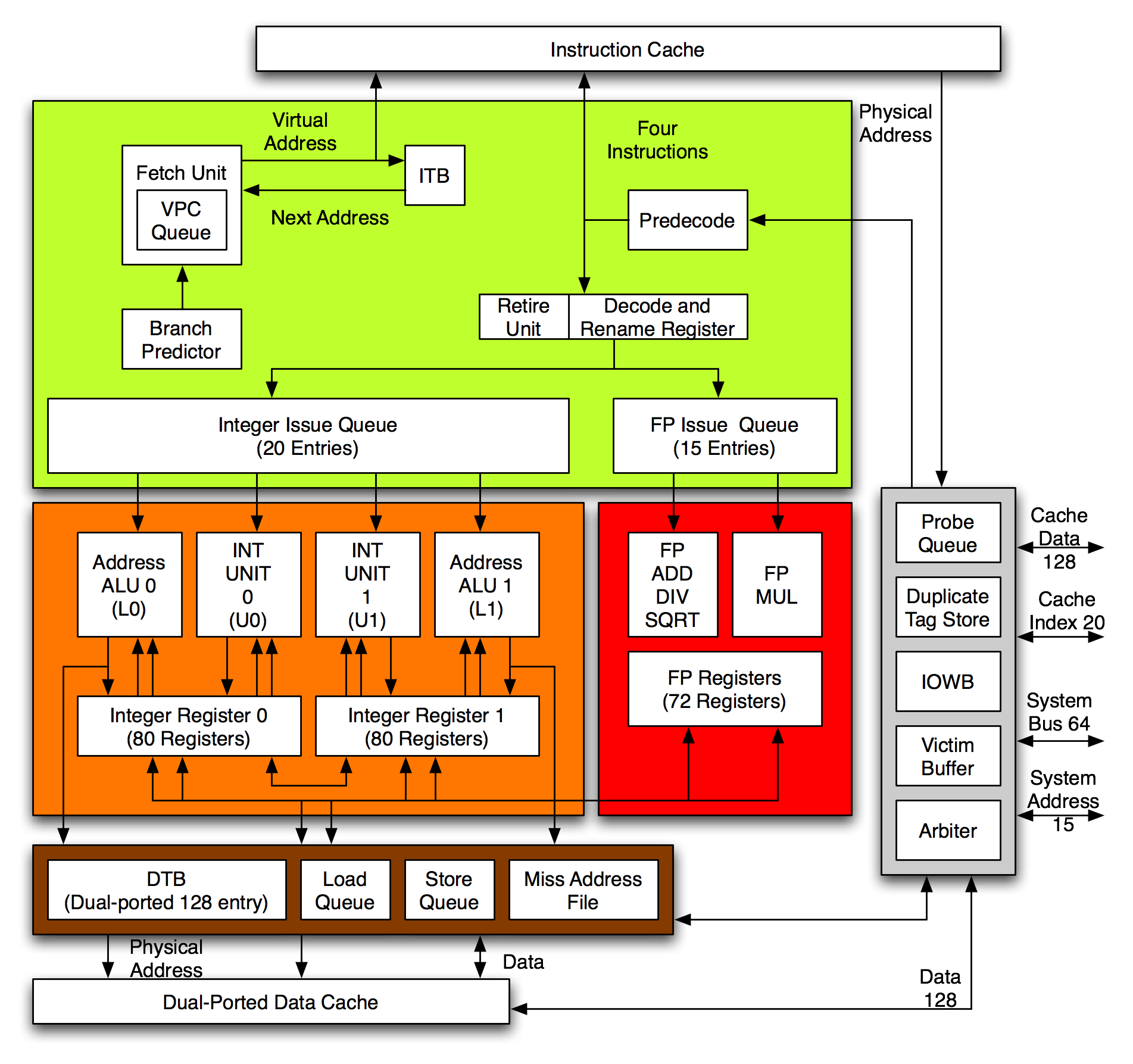
Alpha 21264
The Alpha 21264, also known by its code name, EV6, is a RISC microprocessor developed by Digital Equipment Corporation launched on 19 October 1998. The 21264 implemented the Alpha instruction set architecture (ISA). Description The Alpha 21264 is a four-issue superscalar microprocessor with out-of-order execution and speculative execution. It has a peak execution rate of six instructions per cycle and could sustain four instructions per cycle. It has a seven-stage instruction pipeline. Out of order execution At any given stage, the microprocessor could have up to 80 instructions in various stages of execution, surpassing any other contemporary microprocessor. Decoded instructions are held in instruction queues and are issued when their operands are available. The integer queue contained 20 entries and the floating-point queue 15. Each queue could issue as many instructions as there were pipelines. Ebox The Ebox executes integer, load and store instructions. It has tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirk Meyer
Derrick R. "Dirk" Meyer (born November 24, 1961) is a former chief executive officer of Advanced Micro Devices, serving in the position from July 18, 2008 to January 10, 2011. Education He received a bachelor's degree in computer engineering from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and a master's degree in business administration from Boston University Graduate School of Management. Career He was a co-architect of the Alpha 21064 and Alpha 21264 microprocessors during his employment at DEC and also worked at Intel in its microprocessor design group. Meyer joined AMD in 1996, where he personally led the team that designed and developed the Athlon processor. Meyer was formerly president and chief executive officer of AMD. At one time, he was the chief operating officer. In this role, he shared leadership and management of AMD with former Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of AMD Hector Ruiz. Prior to this role, Meyer served as president and chief operating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
180 Nm
The 180 nm process is a MOSFET (CMOS) semiconductor process technology that was commercialized around the 1998–2000 timeframe by leading semiconductor companies, starting with TSMC and Fujitsu, then followed by Sony, Toshiba, Intel, AMD, Texas Instruments and IBM. History The origin of the 180 nm value is historical, as it reflects a trend of 70% scaling every 2–3 years. The naming is formally determined by the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors (ITRS). Some of the first CPUs manufactured with this process include Intel Coppermine family of Pentium III processors. This was the first technology using a gate length shorter than that of light used for contemporary lithography, which had a wavelength of 193 nm. Some more recent microprocessors and microcontrollers (e.g. PIC) are using this technology because it is typically low cost and does not require upgrading of existing equipment. In 2022, Google sponsored open-source hardware projects usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NexGen
NexGen, Inc. was a private semiconductor company based in Milpitas, California, that designed x86 microprocessors until it was purchased by AMD on January 16, 1996. NexGen was a fabless design house that designed its chips but relied on other companies for production. NexGen's chips were produced by IBM's IBM Microelectronics, Microelectronics division in Burlington, Vermont, alongside PowerPC and DRAM parts. The company was best known for the unique implementation of the x86 architecture in its processors. NexGen's CPUs were designed very differently from other processors based on the x86 instruction set at the time: the processor would translate code designed to run on the traditionally Complex instruction set computing, CISC-based x86 architecture to run on the chip's internal Reduced instruction set computing, RISC architecture. The architecture was used in later AMD chips such as the AMD K6, K6, and to an extent most x86 processors today implement a "hybrid" architecture si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |