|
Atari BASIC
Atari BASIC is an interpreter for the BASIC programming language that shipped with the Atari 8-bit family of 6502-based home computers. Unlike most American BASICs of the home computer era, Atari BASIC is not a derivative of Microsoft BASIC and differs in significant ways. It includes keywords for Atari-specific features and lacks support for string arrays, for example. The language was distributed as an 8 KB ROM cartridge for use with the 1979 Atari 400 and 800 computers. Starting with the 600XL and 800XL in 1983, BASIC is built into the system. Despite the Atari 8-bit computers running at a higher speed than most of its contemporaries, several technical decisions placed Atari BASIC near the bottom in performance benchmarks. The original authors addressed most of these issues in a series of improved versions: BASIC A+ (1981), BASIC XL (1983), and BASIC XE (1985). A host of third-party interpreters and compilers like Turbo-Basic XL also appeared. The complete, anno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BASIC Programming Language
BASIC (Beginners' All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) is a family of general-purpose, high-level programming languages designed for ease of use. The original version was created by John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz at Dartmouth College in 1963. They wanted to enable students in non-scientific fields to use computers. At the time, nearly all computers required writing custom software, which only scientists and mathematicians tended to learn. In addition to the program language, Kemeny and Kurtz developed the Dartmouth Time Sharing System (DTSS), which allowed multiple users to edit and run BASIC programs simultaneously on remote terminals. This general model became very popular on minicomputer systems like the PDP-11 and Data General Nova in the late 1960s and early 1970s. Hewlett-Packard produced an entire computer line for this method of operation, introducing the HP2000 series in the late 1960s and continuing sales into the 1980s. Many early video games trace their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Game Console
A video game console is an electronic device that outputs a video signal or image to display a video game that can be played with a game controller. These may be home consoles, which are generally placed in a permanent location connected to a television or other display devices and controlled with a separate game controller, or handheld consoles, which include their own display unit and controller functions built into the unit and which can be played anywhere. Hybrid consoles combine elements of both home and handheld consoles. Video game consoles are a specialized form of a home computer geared towards video game playing, designed with affordability and accessibility to the general public in mind, but lacking in raw computing power and customization. Simplicity is achieved in part through the use of game cartridges or other simplified methods of distribution, easing the effort of launching a game. However, this leads to ubiquitous proprietary formats that creates competi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floating Point
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic that represents real numbers approximately, using an integer with a fixed precision, called the significand, scaled by an integer exponent of a fixed base. For example, 12.345 can be represented as a base-ten floating-point number: 12.345 = \underbrace_\text \times \underbrace_\text\!\!\!\!\!\!^ In practice, most floating-point systems use base two, though base ten ( decimal floating point) is also common. The term ''floating point'' refers to the fact that the number's radix point can "float" anywhere to the left, right, or between the significant digits of the number. This position is indicated by the exponent, so floating point can be considered a form of scientific notation. A floating-point system can be used to represent, with a fixed number of digits, numbers of very different orders of magnitude — such as the number of meters between galaxies or between protons in an atom. For this reason, floating-poi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time-sharing System
In computing, time-sharing is the sharing of a computing resource among many users at the same time by means of multiprogramming and multi-tasking.DEC Timesharing (1965), by Peter Clark, The DEC Professional, Volume 1, Number 1 Its emergence as the prominent model of computing in the 1970s represented a major technological shift in the history of computing. By allowing many users to interact concurrently with a single computer, time-sharing dramatically lowered the cost of providing computing capability, made it possible for individuals and organizations to use a computer without owning one, and promoted the interactive use of computers and the development of new interactive applications. History Batch processing The earliest computers were extremely expensive devices, and very slow in comparison to later models. Machines were typically dedicated to a particular set of tasks and operated by control panels, the operator manually entering small programs via switches in order t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-100 Bus
The S-100 bus or Altair bus, IEEE 696-1983 ''(withdrawn)'', is an early computer bus designed in 1974 as a part of the Altair 8800. The bus was the first industry standard expansion bus for the microcomputer industry. computers, consisting of processor and peripheral cards, were produced by a number of manufacturers. The bus formed the basis for homebrew computers whose builders (e.g., the Homebrew Computer Club) implemented drivers for CP/M and MP/M. These microcomputers ran the gamut from hobbyist toy to small business workstation and were common in early home computers until the advent of the IBM PC. Architecture The bus is a passive backplane of 100-pin printed circuit board edge connectors wired in parallel. Circuit cards measuring 5 × 10-inches serving the functions of CPU, memory, or I/O interface plugged into these connectors. The bus signal definitions closely follow those of an 8080 microprocessor system, since the Intel 8080 microprocessor was the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
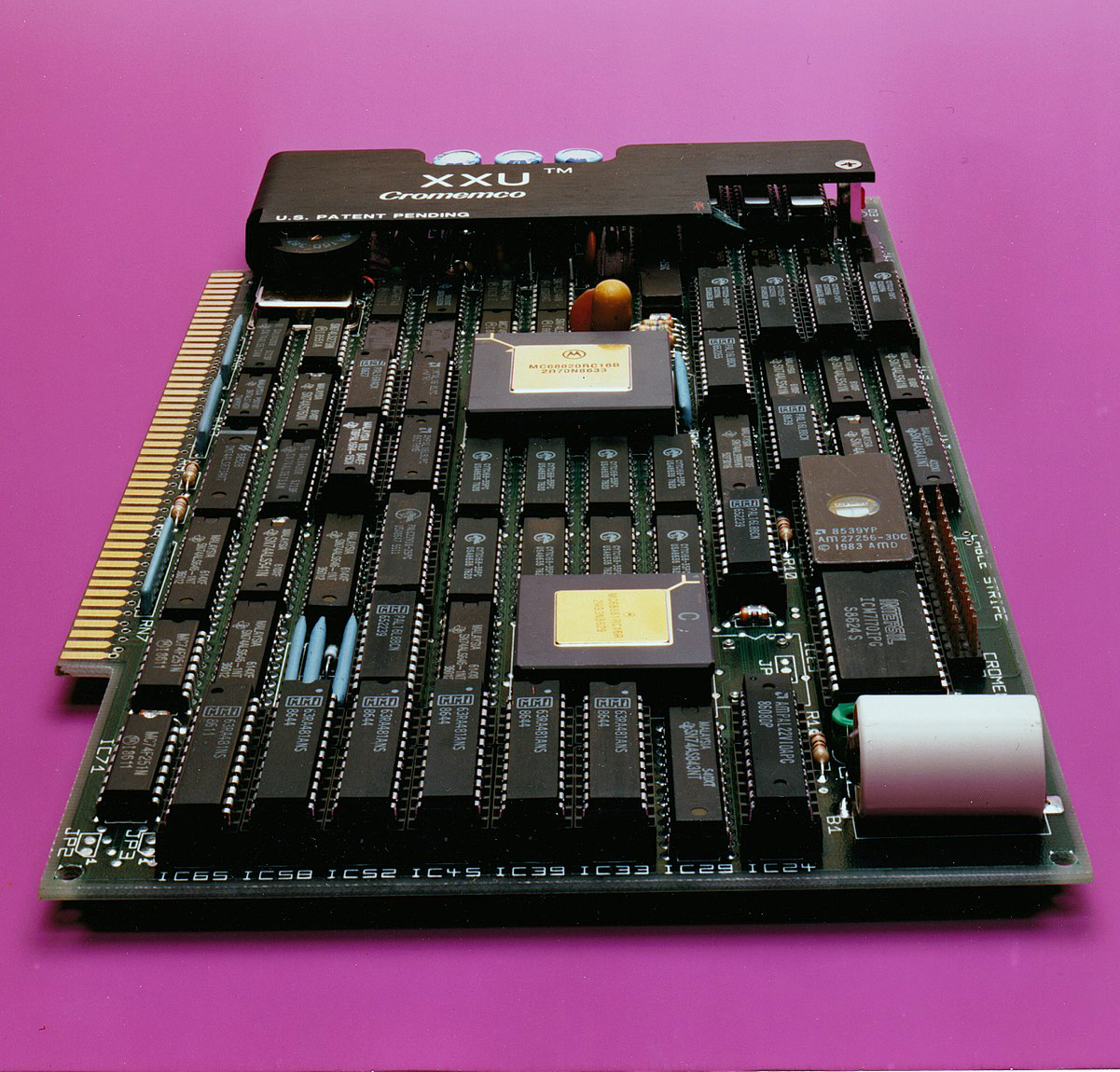
Cromemco
Cromemco was a Mountain View, California microcomputer company known for its high-end Z80-based S-100 bus computers and peripherals in the early days of the personal computer revolution. The company began as a partnership in 1974 between Harry Garland and Roger Melen, two Stanford Ph.D. students. The company was named for their residence at Stanford University ( Crothers Memorial, a Stanford dormitory reserved for engineering graduate students). Cromemco was incorporated in 1976 and their first products were the Cromemco Cyclops digital camera, and the Cromemco Dazzler color graphics interface - both groundbreaking at the time - before they moved on to making computer systems. In December 1981, ''Inc.'' magazine named Cromemco in the top ten fastest-growing privately held companies in the U.S. Early history The collaboration that was to become Cromemco began in 1970 when Harry Garland and Roger Melen, graduate students at Stanford University, began working on a series of artic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zilog Z80
The Z80 is an 8-bit computing, 8-bit microprocessor introduced by Zilog as the startup company's first product. The Z80 was conceived by Federico Faggin in late 1974 and developed by him and his 11 employees starting in early 1975. The first working samples were delivered in March 1976, and it was officially introduced on the market in July 1976. With the revenue from the Z80, the company built its own Semiconductor fabrication plant, chip factories and grew to over a thousand employees over the following two years. The Zilog Z80 is a backward compatible, software-compatible extension and enhancement of the Intel 8080 and, like it, was mainly aimed at embedded systems. Although used in that role, the Z80 also became one of the most widely used central processing unit, CPUs in desktop computers and home computers from the 1970s to the mid-1980s. It was also common in military applications, musical equipment such as synthesizers (like the Roland Jupiter-8), and coin-operated a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basic Computing Language For Atari 8-bit Computers
BASIC (Beginners' All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) is a family of general-purpose, high-level programming languages designed for ease of use. The original version was created by John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz at Dartmouth College in 1963. They wanted to enable students in non-scientific fields to use computers. At the time, nearly all computers required writing custom software, which only scientists and mathematicians tended to learn. In addition to the program language, Kemeny and Kurtz developed the Dartmouth Time Sharing System (DTSS), which allowed multiple users to edit and run BASIC programs simultaneously on remote terminals. This general model became very popular on minicomputer systems like the PDP-11 and Data General Nova in the late 1960s and early 1970s. Hewlett-Packard produced an entire computer line for this method of operation, introducing the HP2000 series in the late 1960s and continuing sales into the 1980s. Many early video games trace their histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumer Electronics Show
CES (; formerly an initialism for Consumer Electronics Show) is an annual trade show organized by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA). Held in January at the Las Vegas Convention Center in Winchester, Nevada, United States, the event typically hosts presentations of new products and technologies in the consumer electronics industry. History The first CES was held in June 1967 in New York City. It was a spinoff from the Chicago Music Show, which, until then, had served as the main event for exhibiting consumer electronics. The event had 17,500 attenders and over 100 exhibitors; the kickoff speaker was Motorola chairman Bob Galvin. From 1978 to 1994, CES was held twice each year: once in January in Las Vegas known for ''Winter Consumer Electronics Show (WCES)'' and once in June in Chicago, known as ''Summer Consumer Electronics Show (SCES)''. The winter show was successfully held in Las Vegas in 1995 as planned. However, since the summer Chicago shows were beginning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple II+
The Apple II (stylized as ) is an 8-bit home computer and one of the world's first highly successful mass-produced microcomputer products. It was designed primarily by Steve Wozniak; Jerry Manock developed the design of Apple II's foam-molded plastic case, Rod Holt developed the switching power supply, while Steve Jobs's role in the design of the computer was limited to overseeing Jerry Manock's work on the plastic case. It was introduced by Jobs and Wozniak at the 1977 West Coast Computer Faire, and marks Apple's first launch of a personal computer aimed at a consumer market—branded toward American households rather than businessmen or computer hobbyists. ''Byte'' magazine referred to the Apple II, Commodore PET 2001, and TRS-80 as the "1977 Trinity". As the Apple II had the defining feature of being able to display color graphics, the Apple logo was redesigned to have a spectrum of colors. The Apple II is the first model in the Apple II series, followed by App ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
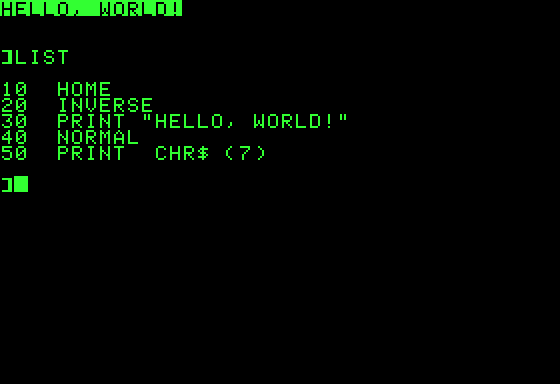
Applesoft BASIC
Applesoft BASIC is a dialect of Microsoft BASIC, developed by Marc McDonald and Ric Weiland, supplied with the Apple II series of computers. It supersedes Integer BASIC and is the BASIC in ROM in all Apple II series computers after the original Apple II model. It is also referred to as FP BASIC (from floating point) because of the Apple DOS command used to invoke it, instead of INT for Integer BASIC. Applesoft BASIC was supplied by Microsoft and its name is derived from the names of both Apple Computer and Microsoft. Apple employees, including Randy Wigginton, adapted Microsoft's interpreter for the Apple II and added several features. The first version of Applesoft was released in 1977 on cassette tape and lacked proper support for high-resolution graphics. Applesoft II, which was made available on cassette and disk and in the ROM of the Apple II Plus and subsequent models, was released in 1978. It is this latter version, which has some syntax differences and support for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOS 6502
The MOS Technology 6502 (typically pronounced "sixty-five-oh-two" or "six-five-oh-two") William Mensch and the moderator both pronounce the 6502 microprocessor as ''"sixty-five-oh-two"''. is an 8-bit microprocessor that was designed by a small team led by Chuck Peddle for MOS Technology. The design team had formerly worked at Motorola on the Motorola 6800 project; the 6502 is essentially a simplified, less expensive and faster version of that design. When it was introduced in 1975, the 6502 was the least expensive microprocessor on the market by a considerable margin. It initially sold for less than one-sixth the cost of competing designs from larger companies, such as the 6800 or Intel 8080. Its introduction caused rapid decreases in pricing across the entire processor market. Along with the Zilog Z80, it sparked a series of projects that resulted in the home computer revolution of the early 1980s. Popular video game consoles and home computers of the 1980s and early 1990s, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |