|
Asthenia
Weakness is a symptom of many different medical conditions. The causes are many and can be divided into conditions that have true or perceived muscle weakness. True muscle weakness is a primary symptom of a variety of skeletal muscle diseases, including muscular dystrophy and inflammatory myopathy. It occurs in neuromuscular junction disorders, such as myasthenia gravis. Pathophysiology Muscle cells work by detecting a flow of electrical impulses from the brain, which signals them to contract through the release of calcium by the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Fatigue (reduced ability to generate force) may occur due to the nerve, or within the muscle cells themselves. New research from scientists at Columbia University suggests that muscle fatigue is caused by calcium leaking out of the muscle cell. This makes less calcium available for the muscle cell. In addition, the Columbia researchers propose that an enzyme activated by this released calcium eats away at muscle fibers. Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a long-term neuromuscular junction disease that leads to varying degrees of skeletal muscle weakness. The most commonly affected muscles are those of the eyes, face, and swallowing. It can result in double vision, drooping eyelids, and difficulties in talking and walking. Onset can be sudden. Those affected often have a large thymus or develop a thymoma. Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease of the neuromuscular junction which results from antibodies that block or destroy nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (AChR) at the junction between the nerve and muscle. This prevents nerve impulses from triggering muscle contractions. Most cases are due to immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) and IgG3 antibodies that attack AChR in the postsynaptic membrane, causing complement-mediated damage and muscle weakness. Rarely, an inherited genetic defect in the neuromuscular junction results in a similar condition known as congenital myasthenia. Babies of mothers wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
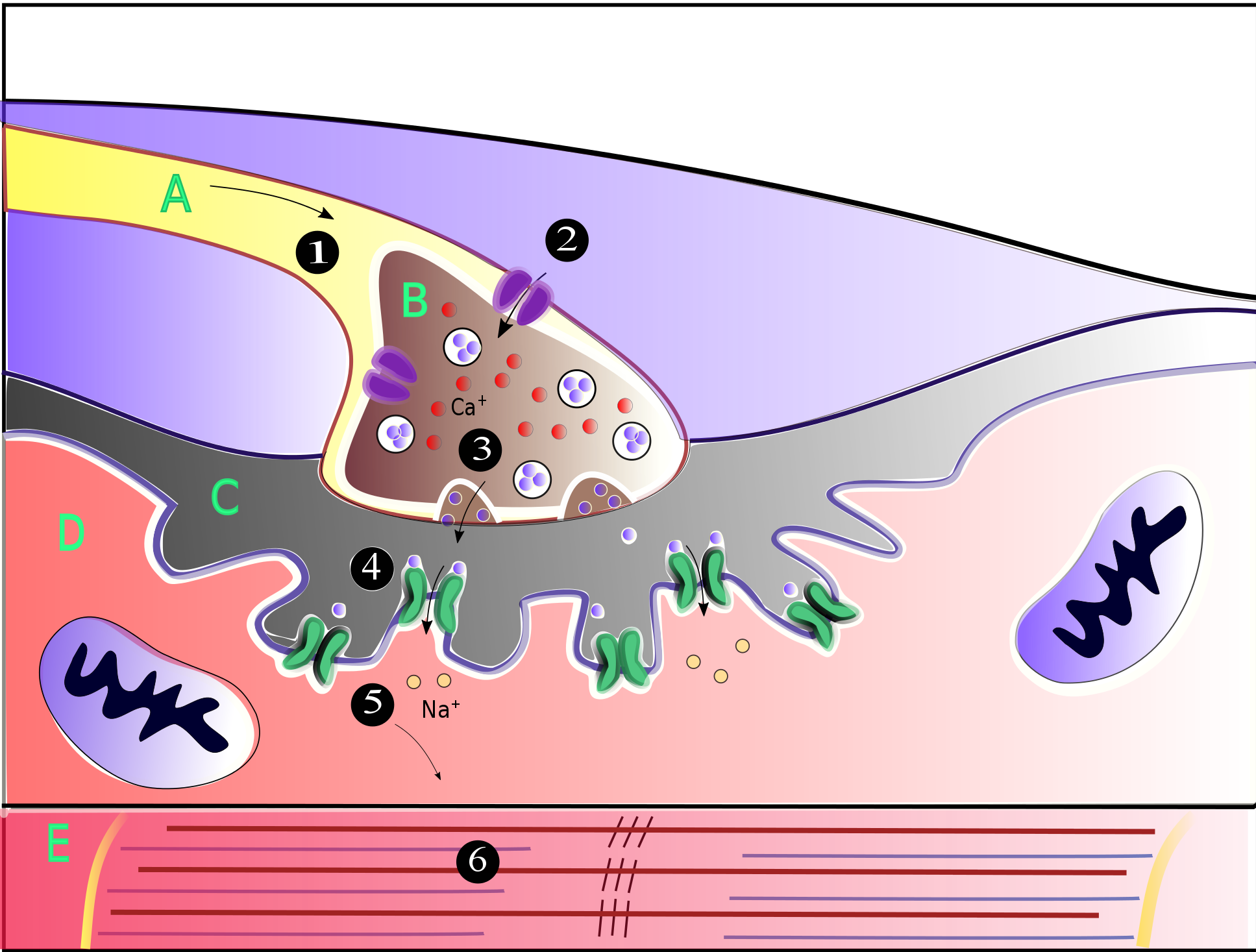
Neuromuscular Junction
A neuromuscular junction (or myoneural junction) is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber. It allows the motor neuron to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction. Muscles require innervation to function—and even just to maintain muscle tone, avoiding atrophy. In the neuromuscular system, nerves from the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system are linked and work together with muscles. Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-gated calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron. Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmins) on synaptic vesicles, triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft. In vertebrates, motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), a small molecule neurotransmitter, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Weakness
Muscle weakness is a lack of muscle strength. Its causes are many and can be divided into conditions that have either true or perceived muscle weakness. True muscle weakness is a primary symptom of a variety of skeletal muscle diseases, including muscular dystrophy and inflammatory myopathy. It occurs in neuromuscular junction disorders, such as myasthenia gravis. Muscle weakness can also be caused by low levels of potassium and other electrolytes within muscle cells. It can be temporary or long-lasting (from seconds or minutes to months or years). The term myasthenia is from my- from Greek μυο meaning "muscle" + -asthenia ἀσθένεια meaning " weakness". Types Neuromuscular fatigue can be classified as either "central" or "peripheral" depending on its cause. Central muscle fatigue manifests as an overall sense of energy deprivation, while peripheral muscle fatigue manifests as a local, muscle-specific inability to do work. Neuromuscular fatigue Nerves control the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuromuscular Disease
A neuromuscular disease is any disease affecting the peripheral nervous system (PNS), the neuromuscular junctions, or skeletal muscles, all of which are components of the motor unit. Damage to any of these structures can cause muscle atrophy and weakness. Issues with sensation can also occur. Neuromuscular diseases can be acquired or genetic. Mutations of more than 650 genes have shown to be causes of neuromuscular diseases. Other causes include nerve or muscle degeneration, autoimmunity, toxins, medications, malnutrition, metabolic derangements, hormone imbalances, infection, nerve compression/entrapment, comprised blood supply, and trauma. Signs and symptoms Symptoms of neuromuscular disease may include numbness, paresthesia, muscle atrophy, a pseudoathletic appearance, exercise intolerance, myalgia (muscle pain), fasciculations (muscle twitches), myotonia (delayed muscle relaxation), hypotonia (lack of resistance to passive movement), fixed muscle weakness (a static s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammatory Myopathy
Inflammatory myopathy, also known as idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM), is disease featuring muscle weakness, inflammation of muscles (myositis), and in some types, muscle pain (myalgia). The cause of much inflammatory myopathy is unknown (idiopathic), and such cases are classified according to their symptoms and signs, electromyography, MRI, and laboratory findings. It can also be associated with underlying cancer. The main classes of idiopathic inflammatory myopathy are polymyositis (PM), dermatomyositis (DM) (including juvenile, amyopathic, and sine-dermatitis form), inclusion-body myositis (IBM), immune-mediated necrotising myopathy (IMNM), and focal autoimmune myositis. Diagnosis Idiopathic inflammatory myopathy is a diagnosis of exclusion. There are a number of known causes of myopathy, and it is only once these have been ruled out that a clinician should assign an idiopathic inflammatory myopathy. The usual criteria for a diagnosis of PM are weakness in muscles of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurology
Neurology (from , "string, nerve" and the suffix wikt:-logia, -logia, "study of") is the branch of specialty (medicine) , medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the nervous system, which comprises the Human brain, brain, the spinal cord and the peripheral nervous system , peripheral nerves. Neurological practice relies heavily on the field of neuroscience, the scientific study of the nervous system, using various techniques of neurotherapy. IEEE Brain (2019). "Neurotherapy: Treating Disorders by Retraining the Brain". ''The Future Neural Therapeutics White Paper''. Retrieved 23.01.2025 from: https://brain.ieee.org/topics/neurotherapy-treating-disorders-by-retraining-the-brain/#:~:text=Neurotherapy%20trains%20a%20patient's%20brain,wave%20activity%20through%20positive%20reinforcement International Neuromodulation Society, Retrieved 23 January 2025 from: https://www.neuromodulation.com/ Val Danilov I (2023). "The O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mast Cell Activation Syndrome
Mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS) one of two types of mast cell activation disorder (MCAD); the other type is idiopathic MCAD. MCAS is an immunological condition in which mast cells, a type of white blood cell, inappropriately and excessively release chemical mediators, such as histamine, resulting in a range of chronic symptoms, sometimes including anaphylaxis or near-anaphylaxis attacks. Primary symptoms include cardiovascular, dermatological, gastrointestinal, neurological, and respiratory problems. Signs and symptoms Because degranulation events can be triggered in various locations within the body, MCAS can present with a wide range of symptoms in multiple body systems. These symptoms may range from digestive discomfort to chronic pain, mental issues, or full-scale anaphylactic reactions. Symptoms typically wax and wane over time, varying in severity and duration. Many signs and symptoms are the same as those for mastocytosis, because both conditions result in too many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyruvate
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell. Pyruvic acid can be made from glucose through glycolysis, converted back to carbohydrates (such as glucose) via gluconeogenesis, or converted to fatty acids through a reaction with acetyl-CoA. It can also be used to construct the amino acid alanine and can be converted into ethanol or lactic acid via fermentation. Pyruvic acid supplies energy to cells through the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle) when oxygen is present ( aerobic respiration), and alternatively ferments to produce lactate when oxygen is lacking. Chemistry In 1834, Théophile-Jules Pelouze distilled tartaric acid and isolated glutaric acid and another unknown organic acid. Jöns Jacob Berzelius characterized this other acid the following year and na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cori Cycle
The Cori cycle (also known as the lactic acid cycle), named after its discoverers, Carl Ferdinand Cori and Gerty Cori, is a metabolic pathway in which lactic acid, lactate, produced by anaerobic glycolysis in muscles, is transported to the liver and converted to glucose, which then returns to the muscles and is cyclically metabolized back to lactate. Process Muscular activity requires Adenosine triphosphate, ATP, which is provided by the breakdown of glycogen in the skeletal muscles. The breakdown of glycogen, known as glycogenolysis, releases glucose in the form of glucose-1-phosphate, glucose 1-phosphate (G1P). The G1P is converted to G6P by phosphoglucomutase. G6P is readily fed into glycolysis, (or can go into the pentose phosphate pathway if G6P concentration is high) a process that provides ATP to the muscle cells as an energy source. During muscular activity, the store of ATP needs to be constantly replenished. When the supply of dioxygen, oxygen is sufficient, this energy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
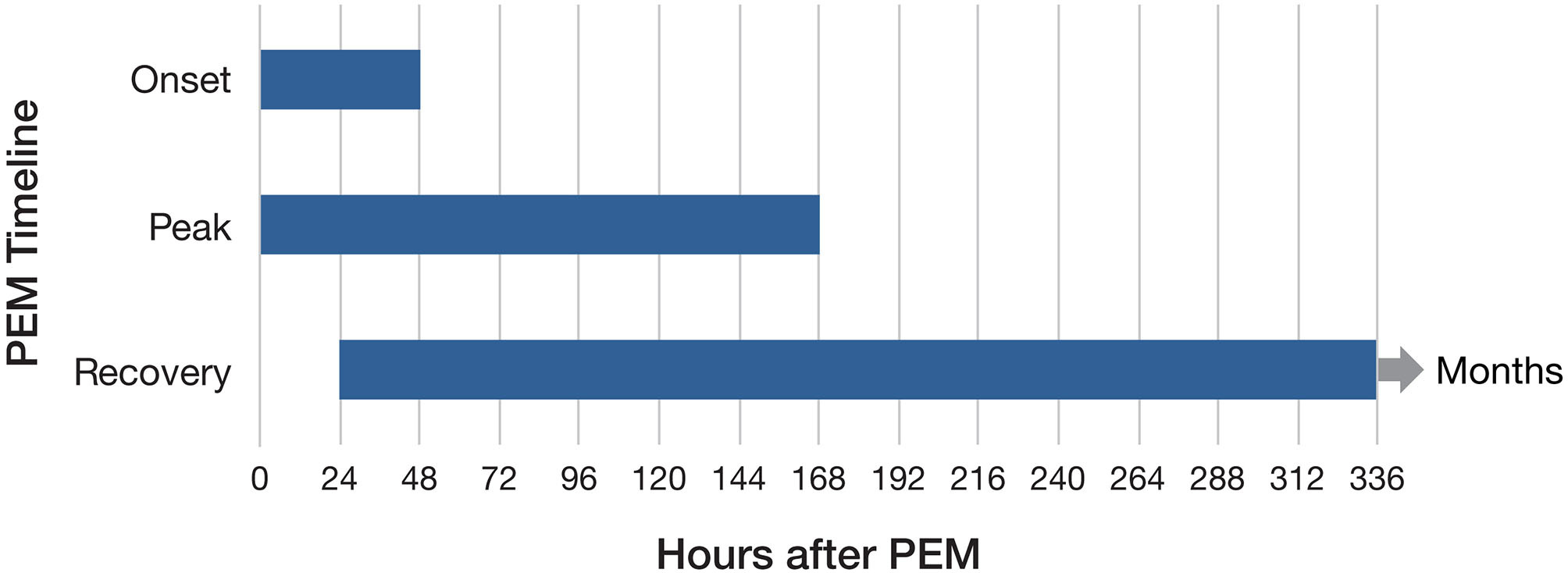
Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/chronic Fatigue Syndrome
Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) is a disabling Chronic condition, chronic illness. People with ME/CFS experience profound fatigue that does not go away with rest, as well as sleep issues and problems with memory or concentration. The Pathognomonic, hallmark symptom is post-exertional malaise (PEM), a worsening of the illness which can start immediately or hours to days after even minor physical or mental activity. This "crash" can last from hours or days to several months. Further common symptoms include orthostatic intolerance, dizziness or faintness when upright and pain. The cause of the disease is unknown. ME/CFS often starts after an infection, such as infectious mononucleosis, mononucleosis. It can run in families, but no genes that contribute to ME/CFS have been confirmed. ME/CFS is associated with changes in the nervous and immune systems, as well as in energy production. Diagnosis is based on distinctive symptoms, and a differential diag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ritonavir
Ritonavir, sold under the brand name Norvir, is an antiretroviral medication used along with other medications to treat HIV/AIDS. This combination treatment is known as highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). Ritonavir is a protease inhibitor, though it now mainly serves to boost the potency of other protease inhibitor (pharmacology), protease inhibitors. It may also be used in combination with other medications to treat hepatitis C and COVID-19. It is taken Oral administration, by mouth. Common side effects of ritonavir include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, diarrhea, and numbness of the hands and feet. Serious side effects include liver complications, pancreatitis, allergic reactions, and arrhythmias. Serious interactions may occur with a number of other medications including amiodarone and simvastatin. At low doses, it is considered to be acceptable for use during pregnancy. Ritonavir is of the protease inhibitor class. However, it is also commonly used to inhibi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organ (anatomy)
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of Tissue (biology), tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the biological organization, hierarchy of life, an organ lies between Tissue (biology), tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type Cell (biology), cells to act together in a function. Tissues of different types combine to form an organ which has a specific function. The Gastrointestinal tract, intestinal wall for example is formed by epithelial tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Two or more organs working together in the execution of a specific body function form an organ system, also called a biological system or body system. An organ's tissues can be broadly categorized as parenchyma, the functional tissue, and stroma (tissue), stroma, the structural tissue with supportive, connective, or ancillary functions. For example, the gland's tissue that makes the hormones is the parenchyma, whereas the stroma includes the nerve t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |