|
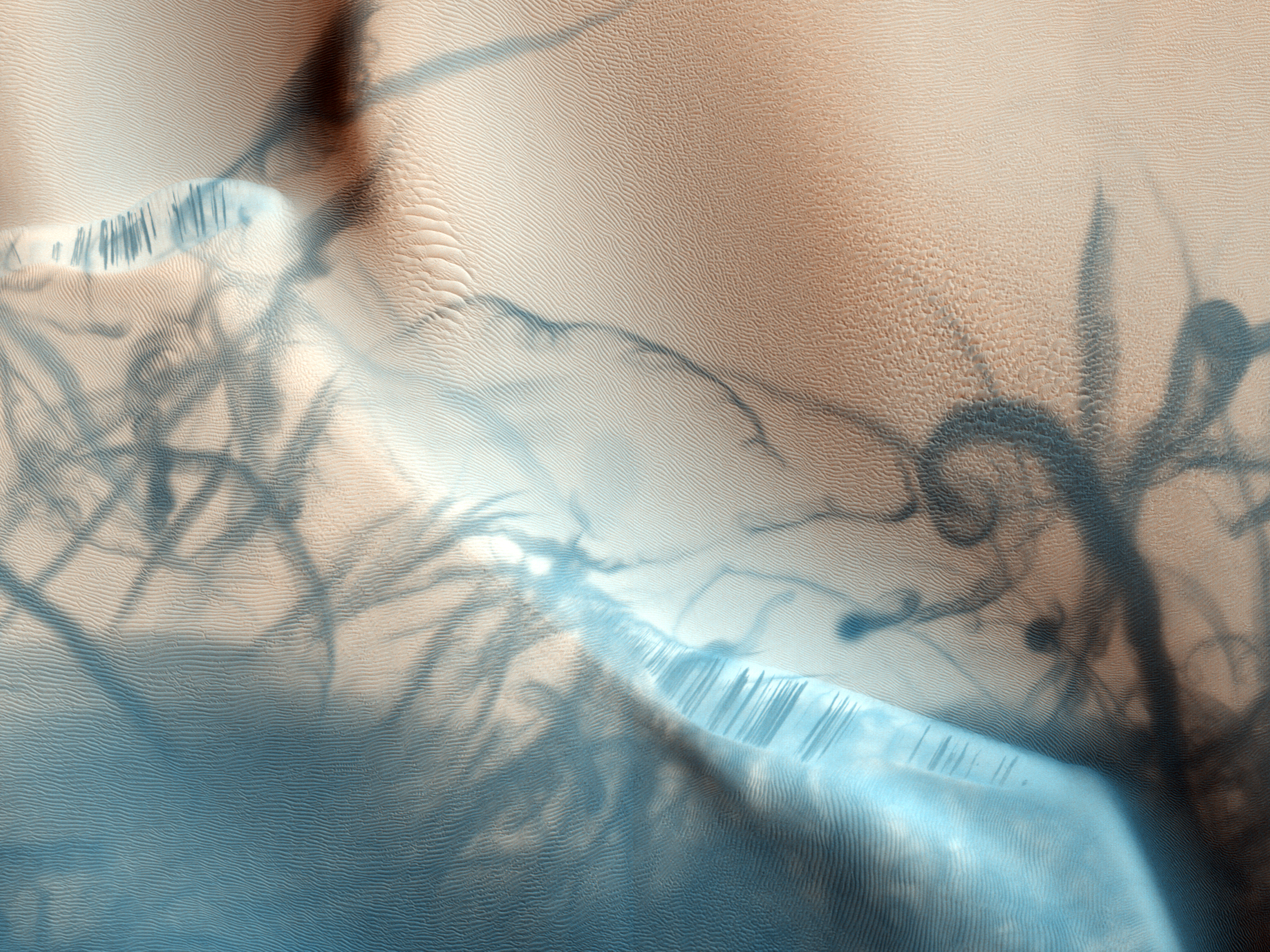
Astapus Colles
Astapus Colles is a group of hills in the Casius quadrangle of Mars, located at 35.5 North and 272.3 West. It is 580 km across and was named after an albedo feature at 35N, 269W. The term "Colles" is used for small hills or knobs. Geology Astapus Colles is 80 km thick and rich in ice. It mostly lies on top of the Vastitas Borealis interior unit, although it also overlies portions of the Vastitas Borealis marginal unit; both of these units together make up the greater Vastitas Borealis region. Features of Astapus Colles are both glacial and periglacial in nature, including scalloped depressions, rimless depressions, polygonal ground, raised rims, and potentially pingos and pingo scars. Formation Astapus Colles was formed in the late Amazonian period The geological history of Mars follows the physical evolution of Mars as substantiated by observations, indirect and direct measurements, and various inference techniques. Methods dating back to 17th century tech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HiRISE
High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is a camera on board the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' which has been orbiting and studying Mars since 2006. The 65 kg (143 lb), US$40 million instrument was built under the direction of the University of Arizona's Lunar and Planetary Laboratory by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp. It consists of a 0.5m (19.7 in) aperture reflecting telescope, the largest so far of any deep space mission, which allows it to take pictures of Mars with resolutions of 0.3m/pixel (1ft/pixel), resolving objects below a meter across. HiRISE has imaged Mars exploration rovers on the surface, including the ''Opportunity'' rover and the ongoing ''Curiosity'' mission. History In the late 1980s, of Ball Aerospace & Technologies began planning the kind of high-resolution imaging needed to support sample return and surface exploration of Mars. In early 2001 he teamed up with Alfred McEwen of the University of Arizona to propose such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casius Quadrangle
The Casius quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the north-central portion of Mars’ eastern hemisphere and covers 60° to 120° east longitude (240° to 300° west longitude) and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Casius quadrangle is also referred to as MC-6 (Mars Chart-6). Casius quadrangle contains part of Utopia Planitia and a small part of Terra Sabaea. The southern and northern borders of the Casius quadrangle are approximately 3,065 km and 1,500 km wide, respectively. The north to south distance is about 2,050 km (slightly less than the length of Greenland). The quadrangle covers an approximate area of 4.9 million square km, or a little over 3% of Mars’ surface area. Origin of name Casius is the name of a telescopic albedo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vastitas Borealis
(Latin 'northern waste') is the largest lowland region of Mars. It is in the northerly latitudes of the planet and encircles the northern polar region. Vastitas Borealis is often simply referred to as the northern plains, northern lowlands or the North polar erg of Mars. The plains lie 4–5 km below the mean radius of the planet, and is centered at . A small part of Vastitas Borealis lies in the Ismenius Lacus quadrangle. The region was named by Eugene Antoniadi, who noted the distinct albedo feature of the Northern plains in his book ''La Planète Mars'' (1930). The name was officially adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1973. Although it is not an officially recognized feature, the North Polar Basin makes up most of the lowlands in the Northern Hemisphere of Mars. As a result, Vastitas Borealis lies within the North Polar Basin, while Utopia Planitia, another very large basin, is adjacent to it. Some scientists have speculated the plains were covered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacial Landform
Glacial landforms are landforms created by the action of glaciers. Most of today's glacial landforms were created by the movement of large ice sheets during the Quaternary glaciations. Some areas, like Fennoscandia and the southern Andes, have extensive occurrences of glacial landforms; other areas, such as the Sahara, display rare and very old fossil glacial landforms. Erosional landforms As the glaciers expand, due to their accumulating weight of snow and ice they crush and abrade and scour surfaces such as rocks and bedrock. The resulting erosional landforms include striations, cirques, glacial horns, arêtes, trim lines, U-shaped valleys, roches moutonnées, overdeepenings and hanging valleys. * Cirque: Starting location for mountain glaciers * Cirque stairway: a sequence of cirques * U-shaped, or trough, valley: U-shaped valleys are created by mountain glaciers. When filled with ocean water so as to create an inlet, these valleys are called fjords. * Arête: spiky ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periglaciation
Periglaciation (adjective: "periglacial", also referring to places at the edges of glacial areas) describes geomorphic processes that result from seasonal thawing of snow in areas of permafrost, the runoff from which refreezes in ice wedges and other structures. "Periglacial" suggests an environment located on the margin of past glaciers. However, freeze and thaw cycles influence landscapes outside areas of past glaciation. Therefore, periglacial environments are anywhere that freezing and thawing modify the landscape in a significant manner. Tundra is a common ecological community in periglacial areas. History Periglaciation became a distinct subject within the study of geology after Walery Łoziński, a Polish geologist, introduced the term in 1909. Łoziński drew upon the early work of Johan Gunnar Andersson. According to Alfred Jahn, his introduction of his work at the 1910 International Geological Congress held in Stockholm caused significant discussion. In the field trip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polygonal Patterned Ground
Polygonal, patterned ground is quite common in some regions of Mars. It is commonly believed to be caused by the sublimation of ice from the ground. Sublimation is the direct change of solid ice to a gas. This is similar to what happens to dry ice on the Earth. Places on Mars that display polygonal ground may indicate where future colonists can find water ice. Low center polygons have been proposed as a marker for ground ice. Patterned ground forms in a mantle layer, called latitude dependent mantle, that fell from the sky when the climate was different. On Mars, researches have found patterned ground that formed from fractures and patterned ground formed by the arrangement of boulders. It is not yet clear what caused boulders to form patterns, but it does not seem that fractures caused the boulders to move around. Esp 037167 1445mantle.jpg, Surface showing appearance with and without mantle covering, as seen by HiRISE, under the HiWish program. Location is Terra Sire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pingo
Pingos are intrapermafrost ice-cored hills, high and in diameter. They are typically conical in shape and grow and persist only in permafrost environments, such as the Arctic and subarctic. A pingo is a periglacial landform, which is defined as a non-glacial landform or process linked to colder climates. It is estimated that there are more than 11,000 pingos on Earth. The Tuktoyaktuk peninsula area has the greatest concentration of pingos in the world with a total of 1,350 pingos. There is currently remarkably limited data on pingos. History In 1825, John Franklin made the earliest description of a pingo when he climbed a small pingo on Ellice Island in the Mackenzie Delta. However, it was in 1938 that the term ''pingo'' was first borrowed from the Inuvialuit by the Arctic botanist Alf Erling Porsild in his paper on Earth mounds of the western Arctic coast of Canada and Alaska. Porsild Pingo in Tuktoyaktuk is named in his honour. The term pingos, which in Inuvialuktun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amazonian (Mars)
The Amazonian is a geologic system and time period on the planet Mars characterized by low rates of meteorite and asteroid impacts and by cold, hyperarid conditions broadly similar to those on Mars today.Carr, M.H. (2006), The Surface of Mars. Cambridge Planetary Science Series, Cambridge University Press. The transition from the preceding Hesperian period is somewhat poorly defined. The Amazonian is thought to have begun around 3 billion years ago, although error bars on this date are extremely large (~500 million years). The period is sometimes subdivided into the Early, Middle, and Late Amazonian. The Amazonian continues to the present day. The Amazonian period has been dominated by impact crater formation and Aeolian processes with ongoing isolated volcanism occurring in the Tharsis and Cerberus Fossae, including signs of activity as recently as a tens of thousands of years ago in the latter and within the past few million years on Olympus Mons, implying they may sti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |