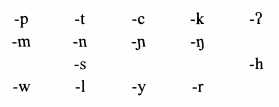|
Aslian
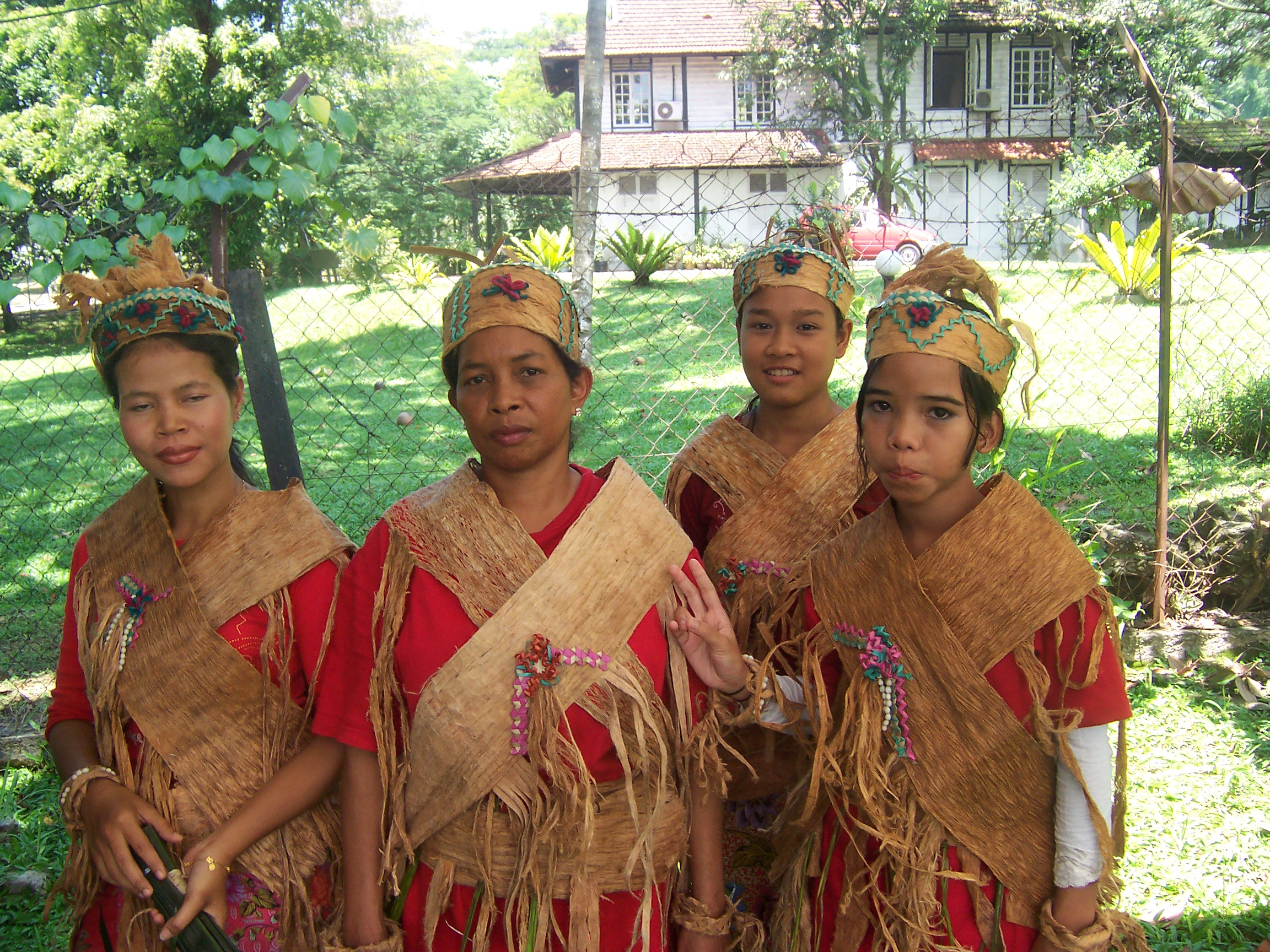
The Aslian languages () are the southernmost branch of Austroasiatic languages spoken on the Malay Peninsula. They are the languages of many of the ''Orang Asli'', the aboriginal inhabitants of the peninsula. The total number of native speakers of Aslian languages is about fifty thousand and all are in danger of extinction. Aslian languages recognized by the Malaysian administration include Kensiu, Kintaq, Jahai, Minriq, Batek, Cheq Wong, Lanoh, Temiar, Semai, Jah Hut, Mah Meri, Semaq Beri, Semelai and Temoq.Geoffrey Benjamin (1976Austroasiatic Subgroupings and Prehistory in the Malay PeninsulaJenner ''et al'' Part I, pp. 37–128 History and origin Aslian languages originally appeared on the western side of the main mountains and eventually spread eastwards into Kelantan, Terengganu and Pahang. The nearest relatives to the Aslian languages are Monic and Nicobarese.Blench, R. (2006)Why are Aslian speakers Austronesian in culture. Paper presented at the Preparatory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orang Asli
The Orang Asli are a Homogeneity and heterogeneity, heterogeneous Indigenous peoples, indigenous population forming a national minority in Malaysia. They are the oldest inhabitants of Peninsular Malaysia. As of 2017, the Orang Asli accounted for 0.7% of the population of Peninsular Malaysia. Although seldom mentioned in the country's demographics, the Orang Asli are a distinct group, alongside the Malaysian Malays, Malays, Malaysian Chinese, Chinese, Malaysian Indians, Indians, and the Orang Asal, indigenous East Malaysians of Sabah and Sarawak. Their special status is enshrined in law. Orang Asli settlements are scattered among the mostly Malay population of the country, often in mountainous areas or the jungles of the rainforest. While outsiders often perceive them as a single group, there are many distinctive groups and tribes, each with its own language, culture and customary land. Each group considers itself independent and different from the other communities. What main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austroasiatic Languages
The Austroasiatic languages ( ) are a large language family spoken throughout Mainland Southeast Asia, South Asia and East Asia. These languages are natively spoken by the majority of the population in Vietnam and Cambodia, and by minority populations scattered throughout parts of Thailand, Laos, India, Myanmar, Malaysia, Bangladesh, Nepal, and southern China. Approximately 117 million people speak an Austroasiatic language, of which more than two-thirds are Vietnamese language, Vietnamese speakers. Of the Austroasiatic languages, only Vietnamese language, Vietnamese, Khmer language, Khmer, and Mon language, Mon have lengthy, established presences in the historical record. Only two are presently considered to be the national languages of sovereign states: Vietnamese in Vietnam, and Khmer in Cambodia. The Mon language is a recognized indigenous language in Myanmar and Thailand, while the Wa language is a "recognized national language" in the de facto autonomous Wa State within M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Aslian Language
Proto-Aslian is the reconstructed proto-language of the Aslian languages of Peninsular Malaysia and southern Thailand. It has been reconstructed by Timothy Phillips (2012).Phillips, Timothy C. 2012. ''Proto-Aslian: towards an understanding of its historical linguistic systems, principles and processes''. Ph.D. thesis, Institut Alam Dan Tamadun Melayu Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Bangi. Reconstructed forms The 289 reconstructed Proto-Aslian forms below are from Phillips (2012:259-262). * * əeew 'water, river' * * a(n)ɨŋ 'spider' * * /grɯɯɲ 'termite' * * əiik 'to swallow' * * əɛɛs 'liver' * * �aɯɯʔ 'pig' * * əoom 'nest' * * əit 'to close (eyes)' * * /nay 'one' * * əam 'to plant' * * /həc 'to whistle' * * aay 'new' * * aam 'right (side)' * * amɯɯs 'to sweep' * * �aiɛʔ 'earth' * * �ənɛɛn 'cooked' * * '(iterative)' * * '(nominalizer agentive)' * * '(nominalizer)' * * '(causative)' * * '(plural/comparative)' * *baay 'to dig' * *bakaʔ 'descendant' * *baliiŋ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kensiu Language
Kensiu (Kensiw) is an Austroasiatic language of the Jahaic (Northern Aslian) subbranch. It is spoken by a small community of 300 people in Yala Province in southern Thailand and also reportedly by a community of approximately 300 speakers in Western Malaysia in Perak and Kedah states. Speakers of this language are Negritos who are known as the Maniq people or Mani of Thailand. In Malaysia, they are counted among the Orang Asli. History The Thai Maniq and the Malaysian Semang are reportedly the first modern humans to enter the Malay Peninsula. After the Negrito, the next wave of migrants to arrive were speakers of the Mon–Khmer languages, most likely from southwestern China. Over the millennia, the Negrito lost their original languages and adopted the Mon–Khmer languages of their neighbors, which they still speak today. Geographic distribution The Maniq settle around the mountainous jungle areas in Southern Thailand and Northern Malaysia. They are considered the original ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jahaic Languages
The Jahaic or Northern Aslian languages (also called Jehaic or Semang) are a group of Aslian languages spoken by about 5,000 people in inland areas of Peninsular Malaysia, with a few pockets in southern Thailand. The most distinctive language in the group is the outlier Cheq Wong, which is spoken south of the Central Aslian language Semai. The other languages apart from Ten'edn can be split into two divisions: * Cheq Wong *Northern Aslian proper **Eastern *** Batek (Batek Deq and Batek Nong), Mintil (Batek Tanɨm) *** Jahai (Jehai), Minriq (Menriq) *** Jedek **Western *** Kintaq *** Kensiu (Maniq) (unclassified) Ten'edn (Mos, Maniq) The name Maniq (Məniʔ, Maniʔ) can refer to either Kensiu or Tonga, both of which also go by the name of Mos. Some Aslian languages are already extinct, such as Wila' (also called Bila' or Lowland Semang), a language or various languages recorded having been spoken on the Province Wellesley coast opposite Penang in the early 19th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Aslian Languages
The Southern Aslian languages are a sub-branch of the Aslian branch of the Austroasiatic language family. They have also been referred to as the Semelaic languages, but this label is no longer used. The four languages that make up the branch are: : Semelai, Semaq Beri, Mah Meri (Betise’), and Temoq .Aslian Sidwell, Paul; Australian National University
The Australian National University (ANU) is a public university, public research university and member of the Group of Eight (Australian universities), Group of Eight, located in Canberra, the capital of Australia. Its main campus in Acton, A ... ; April 2006; Accessed 31 January 200 ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jah Hut Language
Jah Hut (Jah Het) is an Austroasiatic language spoken around the Krau river in peninsular Malaysia by the Jah Hut, one of the indigenous Orang Asli peoples. Classification Jah Hut belongs to the Aslian branch of the Austroasiatic language family. Previously thought to be a member of the Central Aslian sub-branch, Jah Hut is now considered an isolate. Dialects * Kerdau * Krau * Ketiar Krau * Kuala Tembeling * Pulau Guai * Cheres * Ulu Tembeling Phonology Jah Hut has 9 vowels and 19 consonants. Morphology Jah Hut does not contain open major syllables in word-final positions. Conversely, the language contains 15 consonants that can be used to close a syllable. Further, in the context in which a nasalized vowel or consonant occurs earlier in a given word, the final stop is broken down into a nasal and glottal stop. Does not contain restrictions on non-homorganic stop clusters, meaning that many words begin with consonants that don’t phonetically match. (i.e. words t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mah Meri Language
Mah Meri, also known as Besisi, Cellate, Hmaʼ Btsisiʼ, Maʼ Betisek, and pejoratively as Orang Sabat, is an Austroasiatic language spoken in the Malay Peninsula. Along with Semaq Beri, Semelai and Temoq, Mah Meri belongs to the Southern Aslian branch of the Aslian languages. Mah Meri is the only remaining Aslian language spoken in a coastal area (on the coasts of Negeri Sembilan and Selangor) and its speaker population is 3,675 as recorded at the Orang Asli Museum in Gombak. A dictionary of the Mah Meri language has been compiled by Nicole Kruspe. Kruspe, N., & Zainal, A. (2010)A Dictionary of Mah Meri as Spoken at Bukit Bangkong ''Oceanic Linguistics Special Publications'', (36), Iii-410. https://www.jstor.org/stable/25822793 Phonology Vowels Source: Kruspe, N., & Hajek, J. (2009)Mah Meri''Journal of the International Phonetic Association'', 39(2), 241-248doi:10.1017/S0025100309003946/ref> Voice register Source: There are two voice registers in Mah Meri: Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semaq Beri Language
Semaq Beri (Semoq Beri) is an Austroasiatic language spoken in the Malay Peninsula in the states of Pahang and Terengganu. It belongs to the Southern division of the Aslian The Aslian languages () are the southernmost branch of Austroasiatic languages spoken on the Malay Peninsula. They are the languages of many of the ''Orang Asli'', the aboriginal inhabitants of the peninsula. The total number of native speakers o ... languages, along with Semelai, Temoq, and Mah Meri. A preliminary description of the Semaq Beri language by Nicole Kruspe was published in 2014. References External links *http://projekt.ht.lu.se/rwaai RWAAI (Repository and Workspace for Austroasiatic Intangible Heritage) * http://hdl.handle.net/10050/00-0000-0000-0003-66DE-7@view Semaq Beri in RWAAI Digital Archive {{AustroAsiatic-lang-stub Languages of Malaysia Aslian languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kintaq Language
Kintaq, or Kentaq Bong, is an Austroasiatic language spoken in Malaysia and Thailand Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa .... It belongs to the Northern Aslian sub-branch of the Aslian languages. The small number of speakers is decreasing. References External links RWAAI(Repository and Workspace for Austroasiatic Intangible Heritage) * http://hdl.handle.net/10050/00-0000-0000-0003-EBC8-D@view Kintaq in RWAAI Digital Archive Languages of Malaysia Languages of Thailand Aslian languages {{AustroAsiatic-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semelai Language
Semelai is an Austroasiatic language spoken in the Malay Peninsula by Semelai people. It belongs to the Southern branch of the Aslian language subgrouping. The Semelai people reside predominantly around the Bera, Serting and associated river systems in the states of Pahang, Negeri Sembilan and Johor Johor, also spelled Johore,'' is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state of Malaysia in the south of the Malay Peninsula. It borders with Pahang, Malacca and Negeri Sembilan to the north. Johor has maritime borders with Singapore .... Phonology Semelai has 32 consonants and 20 vowels. * Stops /p t c k/ are heard as ̚ t̚ c̚ k̚word-final position. * Palatal sounds /c ɟ/ are slightly affricated as ᶝ ɟᶽwhen in word-initial position. * /s/ may occur as or �within free variation. * Nasals /m n ɲ ŋ/ can occur as prestopped ��m ᵈn ᶡɲ ᶢŋwhen in word-final position. * /r/ can be heard as �when in word-final position. When preceded by a nasal / ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenaboi Language
Kĕnaboi is an extinct unclassified language of Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia that may be a language isolate or an Austroasiatic language belonging to the Aslian branch. It is attested in what appears to be two dialects, based on word lists of about 250 lexical items, presumably collected around 1870–90. Background In Walter William Skeat and Charles Otto Blagden's 1906 work "Pagan Races of the Malay Peninsula", the contents of three previously unpublished wordlists appear, two of which were collected by D.F.A. Hervey, a former government official in Malacca. There is no indication as to when these word lists were collected; however, there is a possibility that these wordlists were collected around the 1870s to 1890s. Hervey collected his Kenaboi lexicon in Alor Gajah, Malacca from speakers living in Gunung Dato', which is a mountain situated in Rembau District, southern Negeri Sembilan. Based on the ethnonym, the Kenaboi may have originated from the Kenaboi River valley of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |