|
Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement
The Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement (APTA), previously known as the Bangkok Agreement and renamed 2 November 2005, was signed in 1975. It is the oldest preferential trade agreement between countries in the Asia-Pacific region. The APTA market covers 2.7 billion people and accounted for US$15 trillion in terms of gross domestic product in Fiscal Year 2015–2016APTA’s key objectiveis to hasten economic development among the seven participating states opting trade and investment liberalization measures that will contribute to intra-regional trade and economic strengthening through the coverage of merchandise goods and services, synchronized investment regime and free flow of technology transfer making all the Participating States to be in equally winsome situation. Its aim is to promote economic development and cooperation through the adoption of trade liberalization measures. APTA is open to all members of the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Agreement
A trade agreement (also known as trade pact) is a wide-ranging taxes, tariff and trade treaty that often includes investment guarantees. It exists when two or more countries agree on terms that help them trade with each other. The most common trade agreements are of the preferential and free trade types, which are concluded in order to reduce (or eliminate) tariffs, quotas and other trade restrictions on items traded between the signatories. The logic of formal trade agreements is that they outline what is agreed upon and specify the punishments for deviation from the rules set in the agreement. Trade agreements therefore make misunderstandings less likely, and create confidence on both sides that cheating will be punished; this increases the likelihood of long-term cooperation. An international organization, such as the IMF, can further incentivize cooperation by monitoring compliance with agreements and reporting third countries of the violations. Monitoring by international ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia-Pacific Trade Agreements Database
ThAsia-Pacific Trade and Investment Agreements Database (APTIAD)is a resource for researchers and policymakers in the area of international trade and investment. The online database allows searches in two ways. One relates to the agreements themselves where users can search by agreements, members, key terms, types and scopes of agreements and their status. Another possibility is to search publications relevant to regional integration and trade agreements. For easier use of the database, users can download a glossary of related terms from thwebsite Trade Agreements Database ThTrade Agreements Databasecomponent of APTIAD is designed to give researchers and policymakers both an overview of, and easy access to, all the regional and bilateral trade agreements entered into or under negotiation by the countries of the Asia and Pacific region. As of June 2008 there were 136 such agreements, including those agreements that have not been notified to the WTO but for which there is official info ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
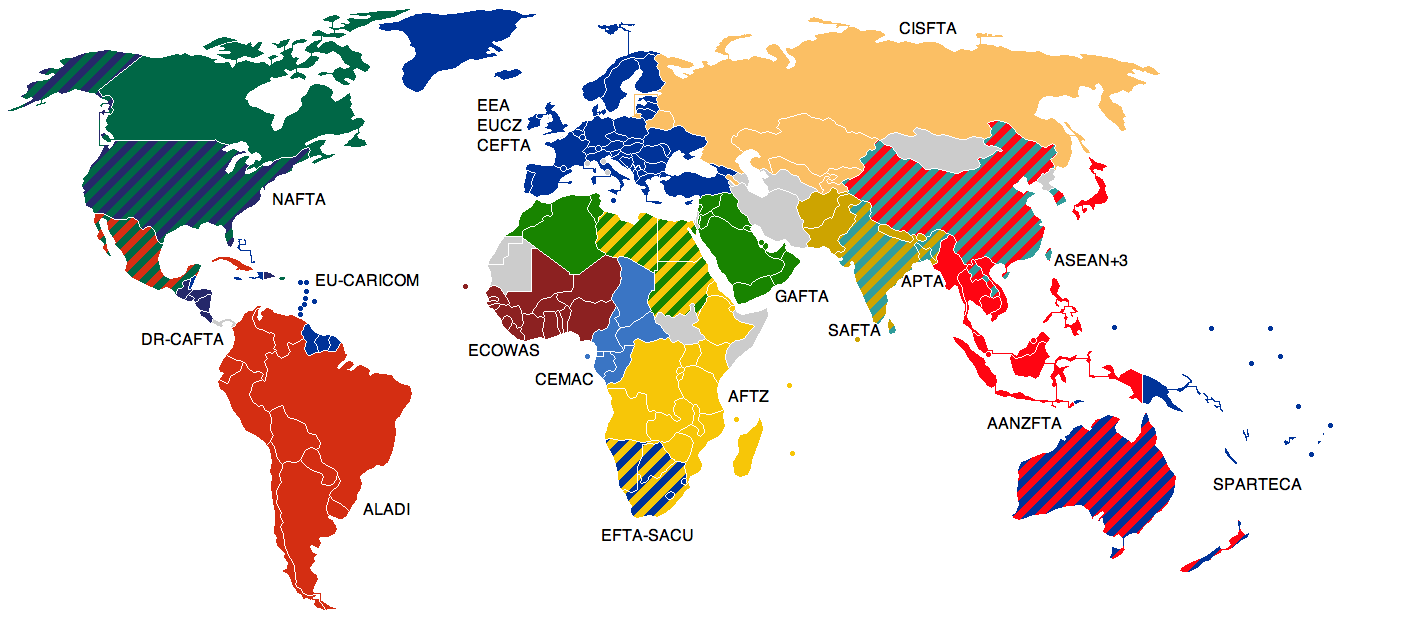
Trade Blocs
A trade bloc is a type of intergovernmental agreement, often part of a regional intergovernmental organization, where barriers to trade (tariffs and others) are reduced or eliminated among the participating states. Trade blocs can be stand-alone agreements between several states (such as the USMCA) or part of a regional organization (such as the European Union). Depending on the level of economic integration, trade blocs can be classified as preferential trading areas, free-trade areas, customs unions, common markets, or economic and monetary unions. Use Historic trading blocs include the Hanseatic League, a Northern European economic alliance between the 12th and 17th centuries, and the German Customs Union, formed on the basis of the German Confederation and subsequently the German Empire from 1871. Surges of trade bloc formation occurred in the 1960s and 1970s, as well as in the 1990s after the collapse of Communism. By 1997, more than 50% of all world commerce was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Trade Agreements
A free trade agreement (FTA) or treaty is an agreement according to international law to form a free-trade area between the cooperating states. There are two types of trade agreements: bilateral and multilateral. Bilateral trade agreements occur when two countries agree to loosen trade restrictions between the two of them, generally to expand business opportunities. Multilateral trade agreements are agreements among three or more countries, and are the most difficult to negotiate and agree. FTAs, a form of trade pacts, determine the tariffs and duties that countries impose on imports and exports with the goal of reducing or eliminating trade barriers, thus encouraging international trade. Such agreements usually "center on a chapter providing for preferential tariff treatment", but they also often "include clauses on trade facilitation and rule-making in areas such as investment, intellectual property, government procurement, technical standards and sanitary and phytosanitary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Of Independent States Free Trade Area
The Common Economic Space is the goal and the result of the process of economic integration of post-Soviet states envisaged by the Article 7 of the Agreement on the creation the Commonwealth of Independent States signed on 8 December 1991. According to Article 7, the High Contracting Parties indicate that through common coordinating institutions, their joint activities will consist in coordinating foreign policy activities, ''cooperation in the formation and development of a common economic space, common European and Eurasian markets, in the field of customs policy'', in the development of transport and communication systems, cooperation in the field of environmental protection, migration policy and the fight against organized crime. The former Soviet republics that became independent states were part of the economy of the Soviet Union with its common technical standards, common infrastructure, territorial proximity, chains of cooperation, and common legal heritage. Through the sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Of Bengal Initiative For Multi-Sectoral Technical And Economic Cooperation
The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) is an international organization of seven South Asian and Southeast Asian nations, housing 1.73 billion people and having a combined gross domestic product of US$5.2 trillion (2023). The BIMSTEC member states – Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Myanmar, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Thailand – are among the countries dependent on the Bay of Bengal. Fourteen priority sectors of cooperation have been identified and several BIMSTEC centers have been established to focus on those sectors. A BIMSTEC free trade agreement is under negotiation , referred to as similar to SAARC. Leadership is rotated in alphabetical order of country names. The permanent secretariat is in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Background On 6 June 1997, a new sub-regional grouping was formed in Bangkok under the name BIST-EC (Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka, and Thailand Economic Cooperation). Following the inclusion of Myanmar on 22 Decemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Islands Forum
The Pacific Islands Forum (PIF) is an inter-governmental organisation that aims to enhance cooperation among countries and territories of Oceania, including formation of a trade bloc and regional peacekeeping operations. It was founded in 1971 as the South Pacific Forum (SPF), and changed its name in 1999 to "Pacific Islands Forum", so as to be more inclusive of the Forum's Oceania-spanning membership of both north and south Pacific island countries, including Australia. The mission of the Pacific Islands Forum is "to work in support of Forum member governments, to enhance the economic and social well-being of the people of the South Pacific by fostering cooperation between governments and between international agencies, and by representing the interests of Forum members in ways agreed by the Forum". Its decisions are implemented by the ''Pacific Islands Forum Secretariat'' (PIFS), which grew out of the ''South Pacific Bureau for Economic Co-operation'' (SPEC). As well as its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Asian Free Trade Area
The South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA) is a 2004 agreement that created a free-trade area of 1.6 billion people in Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, the Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka with the vision of increasing economic cooperation and integration. One of the major goals was to reduce customs duties of all traded goods to zero by 2016. SAFTA required the developing countries in South Asia (India, Pakistan and Sri Lanka) to bring their duties down to 20 per cent in the first phase of the two-year period ending in 2007. In the final five-year phase ending in 2012, the 20-percent duty was reduced to zero in a series of annual cuts. The least developed countries in the region had an additional three years to reduce tariffs to zero. India and Pakistan ratified the treaty in 2009, whereas Afghanistan, as the eighth member state of the SAARC, ratified the SAFTA protocol on 4 May 2011. History SAPTA The establishment of an Inter-Governmental Group (IGG) to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Pacific Regional Trade And Economic Co-operation Agreement
The South Pacific Regional Trade and Economic Co-operation Agreement (SPARTECA) is a nonreciprocal trade agreement in which Australia and New Zealand offer duty-free and unrestricted access for specified products originating from the developing island member countries of the Pacific Islands Forum. The agreement was signed in 1980 in Tarawa, Kiribati, and subject to Rules of Origin regulations, designed to address the unequal trade relationships between the two groups. The textiles, clothing and footwear (TCF) industry has been a major beneficiary of SPARTECA through the preferential access to Australian and New Zealand markets. The agreement entered into force on 1 January 1981. TCF in Fiji The local Fiji textiles, clothing and footwear (TCF) industry has grown over the last 10 years and is now one of the major industries in Fiji. In 1997 the TCF industry accounted for 26% of Fiji’s total domestic exports; it contributed to some 3.5% of GDP and provided employment for about 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASEAN Free Trade Area
The ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) is a trade bloc agreement by the Association of Southeast Asian Nations supporting local trade and manufacturing in all ASEAN countries, and facilitating economic integration with regional and international allies. It stands as one of the largest and most important free trade areas (FTA) in the world, and together with its network of dialogue partners, drove some of the world's largest multilateral forums and blocs, including Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, East Asia Summit and Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership. The AFTA agreement was signed on 28 January 1992 in Singapore. When the AFTA agreement was originally signed, ASEAN had six members, namely, Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore and Thailand. Vietnam joined in 1995, Laos and Myanmar in 1997 and Cambodia in 1999. AFTA now comprises the ten countries of ASEAN. All the four latecomers were required to sign the AFTA agreement to join ASEAN, but were given longer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tariffs
A tariff or import tax is a duty imposed by a national government, customs territory, or supranational union on imports of goods and is paid by the importer. Exceptionally, an export tax may be levied on exports of goods or raw materials and is paid by the exporter. Besides being a source of revenue, import duties can also be a form of regulation of foreign trade and policy that burden foreign products to encourage or safeguard domestic industry. Protective tariffs are among the most widely used instruments of protectionism, along with import quotas and export quotas and other non-tariff barriers to trade. Tariffs can be fixed (a constant sum per unit of imported goods or a percentage of the price) or variable (the amount varies according to the price). Tariffs on imports are designed to raise the price of imported goods to discourage consumption. The intention is for citizens to buy local products instead, which, according to supporters, would stimulate their country's econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free-trade Area
A free trade area is the region encompassing a trade bloc whose member countries have signed a free trade agreement (FTA). Such agreements involve cooperation between at least two countries to reduce trade barriers, import quotas and tariffs, and to increase trade of goods and services with each other. If natural persons are also free to move between the countries, in addition to a free trade agreement, it would also be considered an open border. It can be considered the second stage of economic integration. Customs unions are a special type of free trade area. All such areas have internal arrangements which parties conclude in order to liberalize and facilitate trade among themselves. The crucial difference between customs unions and free trade areas is their approach to third parties. While a customs union requires all parties to establish and maintain identical external tariffs with regard to trade with non-parties, parties to a free trade area are not subject to this requiremen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |