|
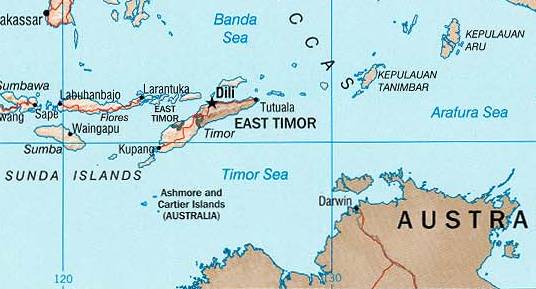
Ashmore Islands
The Territory of Ashmore and Cartier Islands is an uninhabited Australian States and territories of Australia#External territories, external territory consisting of four low-lying tropical islands in two separate reefs (Ashmore and Cartier), as well as the Territorial waters#Territorial sea, territorial sea generated by the islands. The territory is located in the Indian Ocean situated on the edge of the continental shelf, about off the northwest coast of Australia and south of the Indonesian island of Rote Island, Rote. Ashmore Reef is called ''Pulau Pasir'' by Indonesians and ''Nusa Solokaek'' in the Rotenese language. Both names have the meaning "sand island". Geography The territory comprises Ashmore Reef, which includes West, Middle and East Island (Ashmore and Cartier Islands), East Islands, in addition to two lagoons, as well as Cartier Reef, which includes Cartier Islands, Cartier Island. Ashmore Reef covers approximately and Cartier Reef , both measurements ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of Australia
The national flag of Australia is based on the British Blue Ensign—a blue field with the Union Jack in the upper hoist quarter—augmented with a large white seven-pointed star (the Commonwealth Star) and a representation of the Crux, Southern Cross constellation, made up of five white stars (Epsilon Crucis, one small five-pointed star and four, larger, seven-pointed stars). Australia also has a number of other #Other Australian flags, official flags representing its States and territories of Australia, states and territories, Indigenous Australians, Indigenous peoples and government bodies. The original version of the flag first flew as the Commonwealth blue ensign on 3 September 1901, after being selected alongside a merchant naval Australian red ensign, red ensign in 1901 Federal Flag Design Competition, a competition held following Federation of Australia, Federation. A slightly simplified version as approved by King Edward VII was officially adopted in 1903. It was later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pearling In Western Australia
Pearling in Western Australia includes the harvesting and farming of both pearl A pearl is a hard, glistening object produced within the soft tissue (specifically the mantle (mollusc), mantle) of a living Exoskeleton, shelled mollusk or another animal, such as fossil conulariids. Just like the shell of a mollusk, a pear ...s and pearl shells (for mother of pearl) along the north-western coast of Western Australia. The practice of collecting pearl shells existed well before History of Western Australia#Colonial era, British settlement. After settlement, Aboriginal people were used as slave labour in the emerging commercial industry, a practice known as blackbirding. After 1886, with the rise of 'Standard diving dress, hard hat' diving, Asian divers from coastal and island regions became most common, leading to the pearling industry being the sole exception to the White Australia Policy of 1901. Pearl hunting, Pearling centred first around Nickol Bay and Exmouth Gulf and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christmas Island
Christmas Island, officially the Territory of Christmas Island, is an States and territories of Australia#External territories, Australian external territory in the Indian Ocean comprising the island of the same name. It is about south of Java and Sumatra and about north-west of the closest point on the mainland Australia, Australian mainland. It has an area of . Christmas Island's geographic isolation and history of minimal human disturbance has led to a high level of endemism among its flora and fauna, which is of interest to scientists and naturalists. The territory derives its name from its discovery on Christmas Day 1643 by Captain William Mynors. The first European to sight Christmas Island was Richard Rowe of the ''Thomas'' in 1615. Mynors gave it its name. It was first settled in the late 19th century, after abundant phosphate deposits were found, originally deposited as guano, leading Britain to annex the island in 1888 and begin commercial mining in 1899. The J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of Infrastructure, Transport, Regional Development, Communications And The Arts
The Department of Infrastructure, Transport, Regional Development, Communications, Sport and the Arts (DITRDCSA), previously Department of Infrastructure, Transport, Regional Development, Communications and the Arts (DITRDCA) is a department of the Australian Federal Government responsible for delivering Australian Government policy and programs for infrastructure, transport, regional development, communications, cultural affairs, and the arts. The department was formed on 1 July 2022 from the Department of Infrastructure, Transport, Regional Development and Communications, under an Administrative Arrangements Order made on 1 July 2022. It was renamed to its current name on 13 May 2025, gaining the sport and recreation policy and functions from the Department of Health and Aged Care. However, land and planning policy and cities and urban policy were transferred to the Treasury. Ministers After the 2022 Australian election, under the Albanese government, the department nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canberra
Canberra ( ; ) is the capital city of Australia. Founded following the Federation of Australia, federation of the colonies of Australia as the seat of government for the new nation, it is Australia's list of cities in Australia, largest inland city, and the list of cities in Australia by population, eighth-largest Australian city by population. The city is located at the northern end of the Australian Capital Territory at the northern tip of the Australian Alps, the country's highest mountain range. Canberra's estimated population was 473,855. The area chosen for the capital had been inhabited by Aboriginal Australians for up to 21,000 years, by groups including the Ngunnawal and Ngambri. history of Australia (1788–1850), European settlement commenced in the first half of the 19th century, as evidenced by surviving landmarks such as St John the Baptist Church, Reid, St John's Anglican Church and Blundells Cottage. On 1 January 1901, federation of the colonies of Australi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOU Box
The MOU Box, or sometimes the MOU 74 Box, refers to a tract of marine waters in the Timor Sea, lying within Australia's Exclusive Economic Zone, that is subject to a 1974 memorandum of understanding (MoU), and subsequent agreements, between Australia and Indonesia related to traditional fishing rights consistent with UNDRIP. The MOU Box covers an area of about including Scott and Seringapatam Reefs, Browse Island, and Ashmore and Cartier Islands. Australia declared a marine protected area around Ashmore Island in 1983, and around Cartier Island in 2000. Agreement The bilateral agreement establishing the MOU Box is officially known as the Australia–Indonesia Memorandum of Understanding regarding the Operations of Indonesian Traditional Fishermen in Areas of the Australian Fishing Zone and Continental Shelf – 1974. From 2001 cooperation under the Agreement has taken place through the Working Group on Marine Affairs and Fisheries, which brings together representatives of fishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Migration Zone
The Australian migration zone is a legal device created by the Australian Government for the purpose of Visa policy of Australia, Australia's visa policy and Immigration to Australia, immigration policy, as the territory in which Australia's visa policy applies. The Australian migration zone covers such States and territories of Australia, Australian controlled territories as the government may determine. Prior to 2001, the Australian migration zone consisted of the mainland, as well as some Dependent territory#Australia, external territories. Norfolk Island, for example, was not part of the Australian migration zone until 2016. Under Australia’s universal visa policy, a non-Australian nationality law, citizen must hold an Australian visa within the Australian migration zone. Without such a visa, or a bridging visa, the non-citizen is an unlawful non-citizen and treated as an "unauthorised arrival". However, the main effect of the migration zone is that unauthorised arrivals ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environment Protection And Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999
The ''Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999'' (Cth) is an Act of the Parliament of Australia that provides a framework for protection of the Australian environment, including its biodiversity and its natural and culturally significant places. Enacted on 16 July 2000, it established a range of processes to help protect and promote the recovery of threatened species and ecological communities, and preserve significant places from decline. The Act is administered by the Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water. Lists of threatened species are drawn up under the Act, and these lists, the primary reference to threatened species in Australia, are available online through the Species Profile and Threats Database (SPRAT). As an Act of the Australian Parliament, it relies for its constitutional validity upon the legislative powers of the Parliament granted by the Australian Constitution, and key provisions of the Act are largely ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Age
''The Age'' is a daily newspaper in Melbourne, Australia, that has been published since 1854. Owned and published by Nine Entertainment, ''The Age'' primarily serves Victoria (Australia), Victoria, but copies also sell in Tasmania, the Australian Capital Territory and border regions of South Australia and southern New South Wales. It is delivered both in print and digital formats. The newspaper shares some articles with its sister paper ''The Sydney Morning Herald''. ''The Age'' is considered a newspaper of record for Australia, and has variously been known for its investigative reporting, with its journalists having won dozens of Walkley Awards, Australia's most prestigious journalism prize. , ''The Age'' had a monthly readership of 5.4 million. , this had fallen to 4.55 million. History Foundation ''The Age'' was founded by three Melbourne businessmen: brothers John and Henry Cooke (who had arrived from New Zealand in the 1840s) and Walter Powell. The first editi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert Johnson (Australian Politician)
Herbert Victor Johnson (25 October 1889 – 10 July 1962) was an Australian politician. He was a member of the Australian Labor Party (ALP) and served in the House of Representatives from 1940 to 1948. He was Minister for the Interior in the Chifley government from 1945 to 1949. Early life Johnson was born on 25 October 1889 in Northampton, Western Australia. He was the son of Catherine (née Hartigan) and Arthur Johnson. His father had been transported to Western Australia as a convict in 1867 for theft and later became a farmer. Johnson's mother committed suicide when he was an infant, leaving nine children. His father later remarried and had a further five children. Johnson received his education at a local convent school. He left school at a young age and began working as a shearer in the Murchison, Gascoyne and North-West. He claimed a world record for sheep shearing of "3761 sheep in 17½ days" in 1914. Labour movement Johnson joined the Australian Workers' Union (AWU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Territory (Self-Government) Act 1978
The ''Northern Territory (Self-Government) Act 1978'' is an Act of the Parliament of Australia that granted limited self-government to the Northern Territory. Although Australian territories can not have Constitutions, the self-government act functions in much the same way as the constitutions of the States. References {{reflist External links Northern Territory (Self-Government) Act 1978from AustLII The Australasian Legal Information Institute (AustLII) is an institution operated jointly by the Faculties of Law of the University of Technology Sydney and the University of New South Wales. Its public policy purpose is to improve access to just ... Acts of the Parliament of Australia Northern Territory Government 1978 in Australian law ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-government
Self-governance, self-government, self-sovereignty or self-rule is the ability of a person or group to exercise all necessary functions of regulation without intervention from an external authority. It may refer to personal conduct or to any form of institution, such as family units, social groups, affinity groups, legal bodies, industry bodies, religions, and political entities of various degrees. Self-governance is closely related to various philosophical and socio-political concepts such as autonomy, independence, self-control, self-discipline, and sovereignty. In the context of nation states, self-governance is called national sovereignty which is an important concept in international law. In the context of administrative division, a self-governing territory is called an autonomous region. Self-governance is also associated with political contexts in which a population or demographic becomes independent from colonial rule, absolute government, absolute monarchy, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |