|
Ashby Puerorum
Ashby Puerorum is a small village and former civil parish, now in the parish of Greetham with Somersby, in the East Lindsey district of Lincolnshire, England. The village situated north-west from Partney, east from Horncastle, to the north of the A158 road, and to the west of Bag Enderby. In 1931 the parish had a population of 97. On 1 April 1936 the parish was abolished and merged with Somersby. Bishop Oliver Sutton (1280–1299) was responsible for the renaming of this village, coining the name Ashby Puerorum or "the Little Boys' Ashby". This came about after the bishop assigned the revenues of the vicarage of Ashby to the upkeep of the boys in the cathedral choir. Ashby Puerorum Grade II* listed Anglican church is dedicated to St Andrew. The church is chiefly Early English with Perpendicular In geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if they intersect at right angles, i.e. at an angle of 90 degrees or π/2 radians. The condition of perpendicul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greetham With Somersby
Greetham with Somersby is a civil parish in the East Lindsey district of Lincolnshire, England. It is situated approximately north-east from the market town of Horncastle. The parish comprises the villages of Greetham, Somersby, Ashby Puerorum, Bag Enderby and the hamlet of Holbeck. Greetham with Somersby is crossed by no major roads, although the A158 Lincoln to Skegness road forms part of the southern parish boundary. The summits of Millam's Hill and Melbourne's Hill – at and – are the highest points in a parish generally between and 260 feet above sea level. Two small streams flow eastward into the River Lymn which flows south-eastwards through the east of the parish. The 2001 Census recorded a Greetham with Somersby population of 161, including Ashby Puerorum and increasing to 167 at the 2011 Census. Community politics is in the hand of a Parish meeting A parish meeting is a meeting all the electors in a civil parish in England are entitled to attend. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oliver Sutton (bishop)
Oliver Sutton (died 1299) was a medieval Bishop of Lincoln, in England. Sutton was the nephew of Henry of Lexington, Bishop of Lincoln from 1253 to 1258.Greenway Fasti Ecclesiae Anglicanae 1066–1300: Volume 3: Lincoln: Bishops of Lincoln'' He was Dean of Lincoln before 30 June 1275.Greenway Fasti Ecclesiae Anglicanae 1066–1300: Volume 3: Lincoln: Deans' Sutton was elected to the see of Lincoln on 6 February 1280 and consecrated on 19 May 1280Fryde, et al. ''Handbook of British Chronology'' p. 255 at Lambeth. He was enthroned at Lincoln Cathedral Lincoln Cathedral, also called Lincoln Minster, and formally the Cathedral Church of the Blessed Virgin Mary of Lincoln, is a Church of England cathedral in Lincoln, England, Lincoln, England. It is the seat of the bishop of Lincoln and is the Mo ... on 8 September 1280. Sutton died on 13 November 1299 at Nettleham. Citations * Rosalind Hill, ''The Rolls and Register of Bishop Oliver Sutton 1280-1299'' (published in eight volum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villages In Lincolnshire
A village is a human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Although villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighborhoods. Villages are normally permanent, with fixed dwellings; however, transient villages can occur. Further, the dwellings of a village are fairly close to one another, not scattered broadly over the landscape, as a dispersed settlement. In the past, villages were a usual form of community for societies that practice subsistence agriculture and also for some non-agricultural societies. In Great Britain, a hamlet earned the right to be called a village when it built a church.Dr Greg Stevenson, "Wha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effigy
An effigy is a sculptural representation, often life-size, of a specific person or a prototypical figure. The term is mostly used for the makeshift dummies used for symbolic punishment in political protests and for the figures burned in certain traditions around New Year, Carnival and Easter. In European cultures, effigies were used in the past for punishment in formal justice when the perpetrator could not be apprehended, and in popular justice practices of social shaming and exclusion. Additionally, "effigy" is used for certain traditional forms of sculpture, namely tomb effigies, funeral effigies and coin effigies. There is a large overlap and exchange between the ephemeral forms of effigies. Traditional holiday effigies are often politically charged, for instance, when the generalised figures Año Viejo (the Old Year) or Judas in Latin America are substituted by the effigy of a despised politician. Traditional forms are also borrowed for political protests. In India, for i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Gothic Architecture
English Gothic is an architectural style that flourished from the late 12th until the mid-17th century. The style was most prominently used in the construction of Gothic cathedrals and churches, cathedrals and churches. Gothic architecture, Gothic architecture's defining features are Pointed arch (architecture), pointed arches, rib vaults, buttresses, and extensive use of stained glass. Combined, these features allowed the creation of buildings of unprecedented height and grandeur, filled with light from large stained glass windows. Important examples include Westminster Abbey, Canterbury Cathedral and Salisbury Cathedral. The Gothic style endured in England much longer than in Continental Europe. The Gothic style was introduced from France, where the various elements had first been used together within a single building at the choir (architecture), choir of the Abbey of Saint-Denis north of Paris, completed in 1144. The earliest large-scale applications of Gothic architecture i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Andrew
Andrew the Apostle ( ; ; ; ) was an apostle of Jesus. According to the New Testament, he was a fisherman and one of the Apostles in the New Testament, Twelve Apostles chosen by Jesus. The title First-Called () used by the Eastern Orthodox Church stems from the Gospel of John, where Andrew, initially a disciple of John the Baptist, follows Jesus and, recognising him as the Messiah, introduces his brother Simon Peter to him. According to Eastern Orthodox tradition, the apostolic successor to Andrew is the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople. Life Early life The name "Andrew (name), Andrew" (meaning ''manly, brave'', from ), like other Greek names, appears to have been common among the Jews and other Hellenization, Hellenised people since the second or third century B.C.MacRory, Joseph; "Saint An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglican
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the largest branches of Christianity, with around 110 million adherents worldwide . Most are members of national or regional Ecclesiastical province#Anglican Communion, ecclesiastical provinces of the international Anglican Communion, one of the largest Christian bodies in the world, and the world's third-largest Christian communion. When united and uniting churches, united churches in the Anglican Communion and the breakaway Continuing Anglican movement were not counted, there were an estimated 97.4 million Anglicans worldwide in 2020. Adherents of Anglicanism are called ''Anglicans''; they are also called ''Episcopalians'' in some countries. The provinces within the Anglican ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Listed Building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building is a structure of particular architectural or historic interest deserving of special protection. Such buildings are placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Historic Environment Division of the Department for Communities in Northern Ireland. The classification schemes differ between England and Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland (see sections below). The term has also been used in the Republic of Ireland, where buildings are protected under the Planning and Development Act 2000, although the statutory term in Ireland is "Record of Protected Structures, protected structure". A listed building may not be demolished, extended, or altered without permission from the local planning authority, which typically consults the relevant central government agency. In England and Wales, a national amenity society must be notified of any work to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
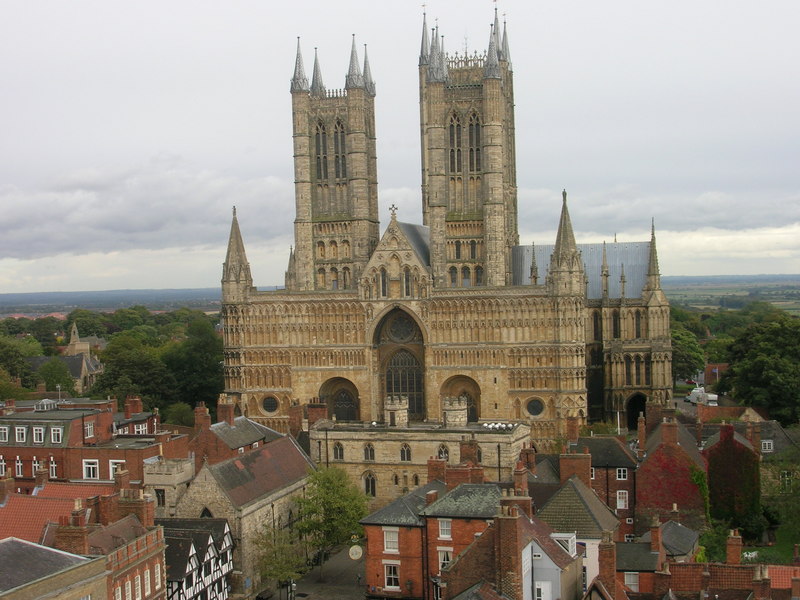
Lincoln Cathedral
Lincoln Cathedral, also called Lincoln Minster, and formally the Cathedral Church of the Blessed Virgin Mary of Lincoln, is a Church of England cathedral in Lincoln, England, Lincoln, England. It is the seat of the bishop of Lincoln and is the Mother Church#Cathedral, mother church of the diocese of Lincoln. The cathedral is governed by its Dean of Lincoln, dean and Chapter (religion), chapter, and is a Listed building, grade I listed building. The earliest parts of the current building date to 1072, when bishop Remigius de Fécamp moved his seat from Dorchester on Thames to Lincoln. The building was completed in 1092, but severely damaged in 1185 East Midlands earthquake, an earthquake in 1185. It was rebuilt over the following centuries in different phases of the English Gothic architecture, Gothic style, with significant surviving parts of the cathedral in English Gothic architecture#Early English Gothic, Early English, Decorated Gothic, Decorated and Perpendicular architecture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somersby, Lincolnshire
Somersby is a village in the civil parish of Greetham with Somersby, in the East Lindsey district of Lincolnshire, England. It is situated north-west from Spilsby and east-north-east from Horncastle. The village lies in the Lincolnshire Wolds The Lincolnshire Wolds which also includes the Lincolnshire Wolds National Landscape are a range of low hills in the county of Lincolnshire, England which runs roughly parallel with the North Sea coast, from the Humber Estuary just west of the t ..., a designated Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty; the parish covers about . In 1971 the parish had a population of 119. On 1 April 1987 the parish was abolished and merged with Greetham, Lincolnshire, Greetham to form "Greetham with Somersby". Tennyson Alfred, Lord Tennyson, Poet Laureate, was born and brought up in Somersby, the son of the rector (ecclesiastical), rector, and the fourth of twelve children. When he wrote ''The Babbling Brook'' he was referring to a small stream here. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Lindsey
East Lindsey is a Non-metropolitan district, local government district in Lincolnshire, England. Its council is based in Horncastle and the largest town is Skegness. Other towns include Alford, Lincolnshire, Alford, Burgh le Marsh, Coningsby, Louth, Lincolnshire, Louth, Mablethorpe, Spilsby, Sutton on Sea, Wainfleet All Saints, Wragby and Woodhall Spa. The district also covers a large rural area, including many smaller settlements. The district lies on the east coast, bordering the North Sea. The north-west of the district includes part of the Lincolnshire Wolds, a designated Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. The neighbouring districts are Borough of Boston, Boston, North Kesteven, West Lindsey and North East Lincolnshire. History The district was created on 1 April 1974 under the Local Government Act 1972, covering nine former districts which were all abolished at the same time: *Alford Urban District *Horncastle Rural District *Horncastle Urban District *Municipal Borough o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Vision Of Britain Through Time
The Great Britain Historical GIS (or GBHGIS) is a spatially enabled database that documents and visualises the changing human geography of the British Isles, although is primarily focussed on the subdivisions of the United Kingdom mainly over the 200 years since the first census in 1801. The project is currently based at the University of Portsmouth, and is the provider of the website ''A Vision of Britain through Time''. NB: A "GIS" is a geographic information system, which combines map information with statistical data to produce a visual picture of the iterations or popularity of a particular set of statistics, overlaid on a map of the geographic area of interest. Original GB Historical GIS (1994–99) The first version of the GB Historical GIS was developed at Queen Mary, University of London between 1994 and 1999, although it was originally conceived simply as a mapping extension to the existing Labour Markets Database (LMDB). The system included digital boundaries for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |