|
Asbestos-related Diseases
Asbestos-related diseases are disorders of the lung and pleura caused by the inhalation of asbestos fibres. Asbestos-related diseases include non-malignant disorders such as asbestosis (pulmonary fibrosis due to asbestos), diffuse pleural thickening, pleural plaques, pleural effusion, rounded atelectasis and malignancies such as lung cancer and malignant mesothelioma. People who worked in jobs with high asbestos dust exposure are at the highest risk of developing asbestos-related disease. However, exposure to asbestos may also occur in the worker's home due to dust that has accumulated on the worker's clothing (para-occupational exposure). Asbestos-related diseases can also occur as a result of non-occupational, environmental exposure. Asbestos was extensively used in many building materials, therefore large quantities of asbestos still remain in buildings that were built prior to the restriction of asbestos use that applies in many countries. The weathering and aging of such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respirology
Pulmonology (, , from Latin ''pulmō, -ōnis'' "lung" and the Ancient Greek, Greek suffix "study of"), pneumology (, built on Greek πνεύμων "lung") or pneumonology () is a specialty (medicine), medical specialty that deals with Respiratory disease, diseases involving the respiratory tract.ACP: Pulmonology: Internal Medicine Subspecialty . Acponline.org. Retrieved on 2011-09-30. It is also known as respirology, respiratory medicine, or chest medicine in some countries and areas. Pulmonology is considered a branch of internal medicine, and is related to intensive care medicine. Pulmonology often involves managing patients who need life support and mechanical ventilation. Pulmonologists are specially trained in diseases and conditions of the chest, pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visceral Pleura
The pleurae (: pleura) are the two flattened closed sacs filled with pleural fluid, each ensheathing each lung and lining their surrounding tissues, locally appearing as two opposing layers of serous membrane separating the lungs from the mediastinum, the inside surfaces of the surrounding chest walls and the diaphragm. Although wrapped onto itself resulting in an apparent double layer, each lung is surrounded by a single, continuous pleural membrane. The portion of the pleura that covers the surface of each lung is often called the visceral pleura. This can lead to some confusion, as the lung is not the only visceral organ covered by the pleura. The pleura typically dips between the lobes of the lung as ''fissures'', and is formed by the invagination of lung buds into each thoracic sac during embryonic development. The portion of the pleura seen as the outer layer covers the chest wall, the diaphragm and the mediastinum and is often also misleadingly called the parietal pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
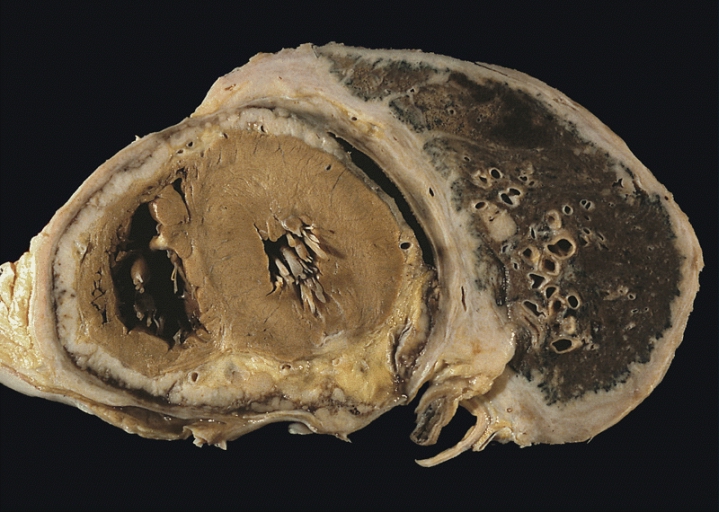
Malignant Mesothelioma
Mesothelioma is a type of cancer that develops from the thin layer of tissue that covers many of the internal organs (known as the mesothelium). The area most commonly affected is the lining of the lungs and chest wall. Less commonly the lining of the abdomen and rarely the sac surrounding the heart, or the sac surrounding each testis may be affected. Signs and symptoms of mesothelioma may include shortness of breath due to fluid around the lung, a swollen abdomen, chest wall pain, cough, feeling tired, and weight loss. These symptoms typically come on slowly. More than 80% of mesothelioma cases are caused by exposure to asbestos. The greater the exposure, the greater the risk. As of 2013, about 125 million people worldwide have been exposed to asbestos at work. High rates of disease occur in people who mine asbestos, produce products from asbestos, work with asbestos products, live with asbestos workers, or work in buildings containing asbestos. Asbestos exposure and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyspnea
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that consists of qualitatively distinct sensations that vary in intensity", and recommends evaluating dyspnea by assessing the intensity of its distinct sensations, the degree of distress and discomfort involved, and its burden or impact on the patient's activities of daily living. Distinct sensations include effort/work to breathe, chest tightness or pain, and "air hunger" (the feeling of not enough oxygen). The tripod position is often assumed to be a sign. Dyspnea is a normal symptom of heavy physical exertion but becomes pathological if it occurs in unexpected situations, when resting or during light exertion. In 85% of cases it is due to asthma, pneumonia, reflux/LPR, cardiac ischemia, COVID-19, interstitial lung disease, congestive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic (medicine)
A chronic condition (also known as chronic disease or chronic illness) is a health condition or disease that is persistent or otherwise long-lasting in its effects or a disease that comes with time. The term ''chronic'' is often applied when the course of the disease lasts for more than three months. Common chronic diseases include diabetes, functional gastrointestinal disorder, eczema, arthritis, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, autoimmune diseases, genetic disorders and some viral diseases such as hepatitis C and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. An illness which is lifelong because it ends in death is a terminal illness. It is possible and not unexpected for an illness to change in definition from terminal to chronic as medicine progresses. Diabetes and HIV for example were once terminal yet are now considered chronic, due to the availability of insulin for diabetics and daily drug treatment for individuals with HIV, which allow these individuals to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asbestosis
Asbestosis is long-term inflammation and pulmonary fibrosis, scarring of the human lung, lungs due to asbestos fibers. Symptoms may include shortness of breath, cough, wheezing, and chest pain, chest tightness. Complications may include lung cancer, mesothelioma, and pulmonary heart disease. Asbestosis is caused by breathing in asbestos fibers. It requires a relatively large exposure over a long period of time, which typically only occurs in those who directly work with asbestos. All types of asbestos fibers are associated with an increased risk. It is generally recommended that currently existing and undamaged asbestos be left undisturbed. Diagnosis is based upon a history of exposure together with medical imaging. Asbestosis is a type of interstitial pulmonary fibrosis. There is no specific treatment. Recommendations may include influenza vaccination, pneumococcal vaccination, oxygen therapy, and stopping smoking. Asbestosis affected about 157,000 people and resulted in 3,600 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exudative
An exudate is a fluid released by an organism through pores or a wound, a process known as exuding or exudation. ''Exudate'' is derived from ''exude'' 'to ooze' from Latin 'to (ooze out) sweat' (' 'out' and ' 'to sweat'). Medicine An exudate is any fluid that filters from the circulatory system into lesions or areas of inflammation. It can be a pus-like or clear fluid. When an injury occurs, leaving skin exposed, it leaks out of the blood vessels and into nearby tissues. The fluid is composed of serum, fibrin, and leukocytes. Exudate may ooze from cuts or from areas of infection or inflammation. Types * Purulent or suppurative exudate consists of plasma with both active and dead neutrophils, fibrinogen, and necrotic parenchymal cells. This kind of exudate is consistent with more severe infections, and is commonly referred to as pus. * Fibrinous exudate is composed mainly of fibrinogen and fibrin. It is characteristic of rheumatic carditis, but is seen in all severe injuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Labour Organization
The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is one of the first and oldest List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agencies of the UN. The ILO has Member states of the International Labour Organization, 187 member states: 186 out of 193 Member states of the United Nations, UN member states plus the Cook Islands. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, with around 40 field offices around the world, and employs some 3,381 staff across 107 nations, of whom 1,698 work in technical cooperation programmes and projects. The ILO's standards are aimed at ensuring accessible, productive, and sustainable Work (human activity), work worldwide in conditions of freedom, equity, security and dignity. They are set forth in List of International Labour Organization Conventions, 189 convent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung Parenchyma
file:emphysema, bullous, subpleural and honeycomb fibrosis (4563270966).jpg, upright=1.6, Lung parenchyma showing damage due to large subpleural Focal lung pneumatosis, bullae. Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ such as the brain or lungs, or a structure such as a tumour. In zoology, it is the tissue that fills the interior of flatworms. In botany, it is some layers in the cross-section of the leaf. Etymology The term ''parenchyma'' is Neo-Latin from the Ancient Greek word meaning 'visceral flesh', and from meaning 'to pour in' from 'beside' + 'in' + 'to pour'. Originally, Erasistratus and other anatomists used it for certain human tissues. Later, it was also applied to plant tissues by Nehemiah Grew. Structure The parenchyma is the ''functional'' parts of an organ (anatomy), organ, or of a structure such as a tumour in the body. This is in contrast to the stroma (animal tissue), stroma, which refers to the ''structural'' tis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Costophrenic Angles
The costodiaphragmatic recess, also called the costophrenic recess or phrenicocostal sinus, costodiaphragmatic-recess Retrieved May 2011 Imaging In anatomy, the costophrenic angles are the places where the diaphragm (''-phrenic'') meets the ribs (''costo-''). Each costophrenic angle can normally be seen as on chest x-ray as a sharply-pointed, downward indentation (dark) between each hemi-diaphragm (white) and the adjacent chest wall (white). A small portion of each lung normally reaches into the costophrenic angle. The normal angle usually measures thirty degrees. Pleural effusion With pleural effusion, fluid often builds up in the costophrenic angle (due to gravity). This can push the lung upwards, resulting in "blunting" of the costophrenic angle. The posterior angle is the deepest. Obtuse angulation is sign of disease. Chest x-ray is the first test done to confirm an excess of pleural fluid. The lateral upright chest x-ray should be examined when a pleural effusion is su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CT Scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry (medical), gantry to measure X-ray Attenuation#Radiography, attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce Tomography, tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is Contraindication, contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 Nanometre, nanometers to 10 Picometre, picometers, corresponding to frequency, frequencies in the range of 30 Hertz, petahertz to 30 Hertz, exahertz ( to ) and photon energies in the range of 100 electronvolt, eV to 100 keV, respectively. X-rays were discovered in 1895 in science, 1895 by the German scientist Wilhelm Röntgen, Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . X-rays can penetrate many solid substances such as construction materials and living tissue, so X-ray radiography is widely used in medical diagnostics (e.g., checking for Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |