|
Asan Barrage
The Asan Barrage is a barrage (dam), barrage in the Uttarakhand-Himachal Pradesh border region in Doon Valley (Dehradun district), northern India, situated at the confluence of the Eastern Yamuna Canal and the Asan River and about from Dakpathar, and 28 km. northwest of Dehradun in Uttarakhand. The barrage is 287.5m long and has water throughout the year which is fed from the river Asan and the discharge channel of the river Yamuna. Since 2020 it has been declared as Uttarakhand's first Ramsar site. Directly behind the barrage on its eastern flank, water reenters the Eastern Yamuna Canal on the west side of the Yamuna, Yamuna River. At a distance of from the barrage on the canal, water reaches the 30 MW Kulhal Power Plant at . The power plant contains three 10 MW Kaplan turbine-generators and has a design hydraulic head of . Once discharged from the power station, the water is conducted by the canal to the 72 MW Khara Power Station at in Uttar Pradesh. The Khara Power Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dakpathar
Dakpathar, also spelled Dakpatthar and Dak Pather is a small hill town situated in Dehradun district of Uttarakhand, India. It is on the left bank of the Yamuna River and northwest of the city of Dehradun Dehradun (), also known as Dehra Doon, is the winter capital and the List of cities in Uttarakhand by population, most populous city of the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is the administrative headquarters of the eponymous Dehradun district, d .... Dakpathar lies about above sea level at the foothills of Shivalik range. It is the location of the Dakpathar Barrage, which forms a reservoir along the town that is popular for recreation. The Dam itself is long and is a combination of river Yamuna and river tons at khodri. It serves to divert water into the East Yamuna Canal for hydroelectric power production at the Dhakrani and Dhalipur Power Plants. References {{Dehradun district Cities and towns in Dehradun district ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tons River
The Tons (टौंस नदी) is the largest tributary of the Yamuna. It flows through Garhwal region in Uttarakhand, touching Himachal Pradesh. The Tons thrust is named after this river. With its source in the high Bandarpunch mountain, it is one of the most major perennial Indian Himalayan rivers. In fact, it carries more water than the Yamuna itself, which it meets below Kalsi near Dehradun, Uttarakhand. Tons Valley Tons Valley lies in Jaunsar Bawar region, as it emerges from the Himalayas has haridwar on its eastern bank. The cantonment town of Chakrata is situated between, the Tons and Yamuna rivers. Tributaries The Pabbar River is a tributary of the Tons River connecting to it from the west. It is also the westernmost river that drains east to the Ganges. The Sutlej River is the next watershed over and is the easternmost river that drains west into the Indus. The Asan River is another tributary of the Tons that is often named (incorrectly) after this great r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dehradun Canals
Dehradun canals refers to the heritage network of canals that was once spread across Dehradun in Uttarakhand, India, with the earliest, Rajpur Canal, dating back to early 17th century. After the city became the state capital in 2000, rapid and unchecked road-widening schemes led to the covering, or in some cases demolition, of most of the historic canals. One of the last remaining canals was covered in 2007. Despite public protests and advisories from environmentalists about the ecological benefit of the canals, they were covered to make room for ever-increasing traffic. Many environmental groups have campaigned for the revival of the historic network, citing its aesthetic value and positive effects on the city's urban environment and microclimate. Currently, the Government of Uttarakhand has not announced any plans of reviving or restoring the canal network. History The construction of the first canal, Rajpur Canal, in the early 17th century has been attributed to Rani Karnava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dakpathar Barrage
The Dakpathar Barrage is a concrete barrage across the Yamuna River adjacent to Dakpathar in Uttarakhand, India. In a run-of-the-river scheme, the barrage serves to divert water into the East Yamuna Canal for hydroelectric power production at the Dhakrani and Dhalipur Power Plants. The foundation stone for the dam was laid on 23 May 1949 by India's Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru. The barrage is controlled by 25 floodgates and has a length of . The entrance to the canal is directly behind the dam on its left bank. After traveling , water reaches the Dhakrani Power Plant at and is utilized for power production. The 33.75 MW power plant contains three 11.25 MW Kaplan turbine-generators and has a design hydraulic head of . About after Dhakrani the canal reaches the 51 MW Dhalipur Power Plant at . This power plant contains three 17 MW Francis turbine-generators and has a design head of . Both power plants were commissioned in 1965 and have a design discharge of . Water dischar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' (, , from wikt:ऋच्, ऋच्, "praise" and wikt:वेद, वेद, "knowledge") is an ancient Indian Miscellany, collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts (''śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one Shakha of the many survive today, namely the Shakala Shakha, Śakalya Shakha. Much of the contents contained in the remaining Shakhas are now lost or are not available in the public forum. The ''Rigveda'' is the oldest known Vedic Sanskrit text. Its early layers are among the oldest extant texts in any Indo-European language. Most scholars believe that the sounds and texts of the ''Rigveda'' have been orally transmitted with precision since the 2nd millennium BCE, through Indian mathematics#Styles of memorisation, methods of memorisation of exceptional complexity, rigour and fidelity, though the dates are not confirmed and remain contentious till concrete evidence surfaces. Philolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
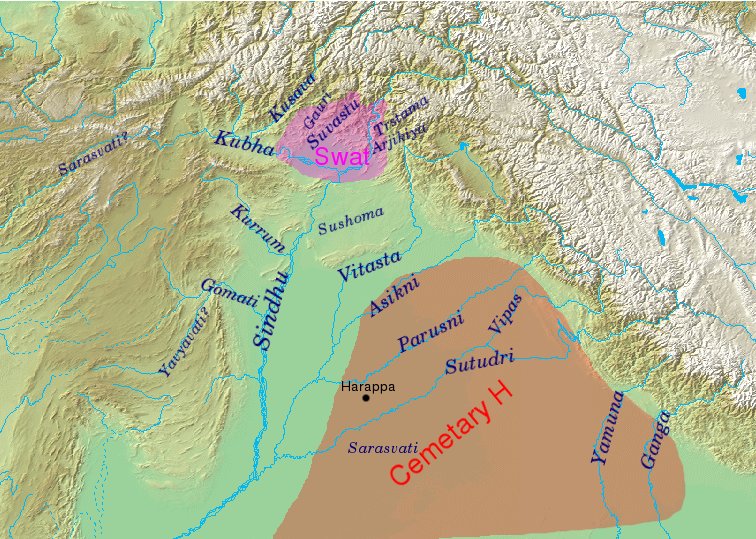
Asmanvati
The Rigveda refers to a number of rivers located in the northwestern Indian subcontinent, from Gandhara to Kurukshetra. Rigvedic geography Identification of Rigvedic hydronyms has engaged multiple historians; it is the single most important way of establishing the geography and chronology of the early Vedic period. Rivers with certain identifications stretch from eastern Afghanistan to the western Gangetic plain, clustering in the Punjab. The Rigveda mentions the ''sapta-sindhavaḥ'' (, seven rivers), along with other rivers: ''Sapta-sindhavaḥ'' is cognate with Avestan ''hapta həndu'', and is interpreted as referring to Punjab. The region's name comes from پنج, ''panj'', 'five' and آب, ''āb'', 'water' thus " five waters", a Persian calque of the Indo-Aryan ''Pancha-nada'' meaning "five rivers". The same names were often imposed on different rivers as the Vedic culture migrated eastward from around Afghanistan (where they stayed for a considerable time) to the subc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paonta Sahib
Paonta Sahib is an industrial town of Himachal Pradesh in India. It is located in the south of Sirmaur district, on National Highway 72 (New NH 7). Paonta Sahib is an important place of worship for Sikhs, hosting a large Gurdwara named Gurudwara Paonta Sahib, on the banks of the river Yamuna. The river is the boundary between the states of Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand. History The town was founded by Sikh Guru Shri Guru Gobind Singh Ji. The Gurudwara Paonta Sahib has linkages to the tenth Sikh Guru, Shri Guru Gobind Singh Ji and the Sikh leader Banda Singh Bahadur. Its original name was Paontika. In Hindi language, ''Paon'' means "feet" and ''tika'' means "became stable". It is believed that Shri Guru Gobind Singh Ji and his horse stopped at this place, and he decided to stay here. He lived here for four and a half years, having never stayed so long at any other place in his entire life. He wrote many Sikh religious books during the stay and moved to Anandpur Sahib to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saharanpur District
Saharanpur district is the northernmost of the districts of Uttar Pradesh state, India. Bordering the states of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand, and close to the foothills of Shivalik range, it lies in the northern part of the Doab region. The district headquarters are in Saharanpur, which is also the headquarters of Saharanpur Division. Other principal towns are Sarsawa, Behat, Deoband, Gangoh and Rampur Maniharan. Geography Saharanpur is located at , about south-southeast from Chandigarh and north-northeast from Delhi and 61 Km. South of Dehradun and about 70 Km. South East from the town of Paonta Sahib, Himachal Pradesh. It has an average elevation of . It is bordered by Yamunanagar and Karnal districts of Haryana to the west, Sirmaur district of Himachal Pradesh to the northwest, Dehradun district of Uttarakhand to the north, Haridwar district of Uttarakhand to the east and Muzaffarnagar and Shamli districts to the south. It is the northernmost di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sivalik Hills
The Sivalik Hills, also known as Churia Hills, are a mountain range of the outer Himalayas. The literal translation of "Sivalik" is 'tresses of Shiva'. The hills are known for their numerous fossils, and are also home to the Soanian Middle Paleolithic archaeological culture. Geography The Sivalik Hills are a mountain range of the outer Himalayas that stretches over about from the Indus River eastwards close to the Brahmaputra River, spanning the northern parts of the Indian subcontinent. It is wide with an average elevation of . Between the Teesta and Raidāk Rivers in Assam is a gap of about . They are well known for their Neogene and Pleistocene aged vertebrate fossils. Geology Geologically, the Sivalik Hills belong to the Tertiary deposits of the outer Himalayas. They are chiefly composed of sandstone and conglomerate rock formations, which are the solidified detritus of the Himalayas to their north; they are poorly consolidated. The sedimentary rocks comprising the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vikasnagar
Vikasnagar is a city and a municipality in Dehradun district in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. Vikas Nagar is also a tehsil in Dehradun district It is also known as Pachawadoon (Western Doon) and is the second financial and economic hub of Dehradun district, after the city of Dehradun. Vikasnagar was earlier known for its tea gardens, exporting tea to other countries. But now due to years of constant neglect and lack of skilled labor, it has lost its reputation. Vikasnagar is also famous for Basmati rice and fruits like litchi and Dussehri mangoes. Vikasnagar, along with Herbertpur, is the chief marketplace area for the people of Jaunsar-Bawar. Etymology Vikasnagar was formerly known as Chauhadpur Nardidih. After independence, several hydroelectric power projects were laid in the region because of which the region witnessed a spurt in growth and development activities. Hence the name was changed to Vikasnagar from Chauhadpur by the then Union Cabinet Minister for Rehabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shiva
Shiva (; , ), also known as Mahadeva (; , , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, [mɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐh]) and Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the God in Hinduism, Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions within Hinduism. Shiva is known as ''The Destroyer'' within the Trimurti, the Hinduism, Hindu trinity which also includes Brahma and Vishnu. In the Shaivite tradition, Shiva is the Supreme Lord who creates, protects and transforms the universe. In the goddess-oriented Shaktism, Shakta tradition, the Supreme Goddess (Devi) is regarded as the energy and creative power (Shakti) and the equal complementary partner of Shiva. Shiva is one of the five equivalent deities in Panchayatana puja of the Smarta Tradition, Smarta tradition of Hinduism. Shiva has many aspects, benevolent as well as fearsome. In benevolent aspects, he is depicted as an Omniscience, omniscient yogi who lives an Asceticism#Hinduism, ascetic life on Kailasa as well as a house ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapkeshwar Mahadev
Tapkeshwar Temple, also known as Tapkeshwar Mahadev Temple, is a temple in Dehradun dedicated to Shiva. The temple is on the bank of the Tons River, built on top of a natural cave, which holds the temple's main shivalinga. History The Tapkeshwar Temple is believed to be 6,000 years old. It has a natural shivalinga in the cave, which became a place of reverence for the local people. It is also believed that this was used as a residence by Dronacharya, the teacher of the Pandavas and Kauravas in the Hindu epic Mahabharata; the cave is called Drona Cave after him. Dronacharya's wife Kalyani was unable to breastfeed their newborn son Ashwatthama. As Dronacharya was unable to afford a cow or cow's milk, Ashwatthama prayed to Shiva, who then fed him milk dripping from the shivalinga in the cave. Operations The temple is popular as both a tourist destination and a pilgrimage site in Dehradun. Pilgrims bathe in the nearby sulphur-water springs before entering the temple. Drona C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |