|
Arun Valley
The River Arun () is a river in the English county of West Sussex. At long, it is the longest river entirely in Sussex and one of the longest starting in Sussex after the River Medway, River Wey and River Mole. From the series of small streams that form its source in the area of St Leonard's Forest in the Weald, the Arun flows westwards through Horsham to Nowhurst where it is joined by the North River. Turning to the south, it is joined by its main tributary, the western River Rother, and continues through a gap in the South Downs to Arundel to join the English Channel at Littlehampton. It is one of the faster flowing rivers in England, and is tidal as far inland as Pallingham Quay, upstream from the sea at Littlehampton. The Arun gives its name to the Arun local government district of West Sussex. The first major improvements to the river were made between the 1540s and the 1570s, when Arundel became a port, and navigation up to Pallingham was improved, but barges had d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stopham
Stopham is a hamlet (place), hamlet and Civil parishes in England, civil parish in the Chichester (district), District of Chichester in West Sussex, England, about west of Pulborough on the A283 road. It is in the civil parish of Fittleworth. The parish has a land area of . The United Kingdom Census 2001, 2001 Census recorded 87 people living in 39 households, of whom 40 were economically active. Manor The Domesday Book of 1086 records a Manorialism, manor of Stopham or ''Stopeham''. Descendants of the same family, the Bartletts or Barttelots, who married the senior co-heir of the Stophams in 1379, have ensured that the same lineage, albeit with a different surname, has held the manor since the Norman Conquest of England. Since 1875 they have been Barttelot baronets, baronets. Part of the present manor house is dated 1485, but there was a house on the site before that. The house was given a new east front in the 16th century but was partly demolished in 1638. Its plan is E-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
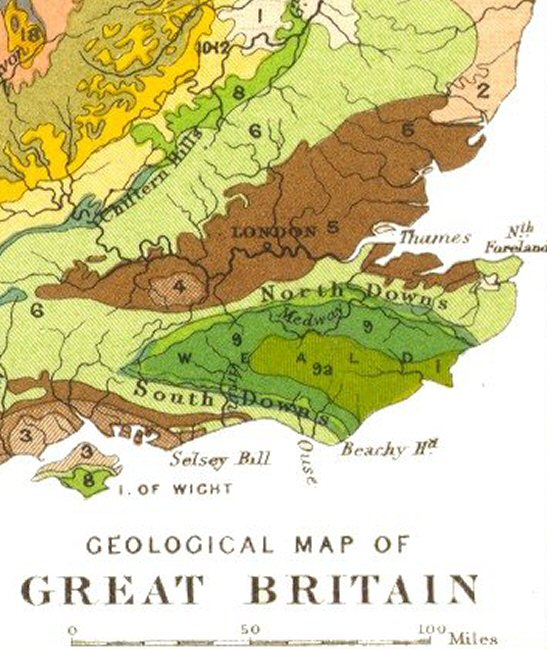
South Downs
The South Downs are a range of chalk hills in the south-eastern coastal counties of England that extends for about across the south-eastern coastal counties of England from the Itchen valley of Hampshire in the west to Beachy Head, in the Eastbourne Downland Estate, East Sussex, in the east. The Downs are bounded on the northern side by a steep escarpment, from whose crest there are extensive views northwards across the Weald. The South Downs National Park forms a much larger area than the chalk range of the South Downs, and includes large parts of the Weald. The national park is the UK's most visited, attracting an estimated 39 million visitor-days annually. The South Downs are characterised by rolling chalk downland with close-cropped turf and dry valleys, and are recognised as one of the most important chalk landscapes in England. The range is one of the four main areas of chalk downland in southern England. The South Downs are relatively less populated compared to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancing, West Sussex
Lancing is a large coastal village and civil parish in the Adur district of West Sussex, England, on the western edge of the Adur Valley. It occupies part of the narrow central section of the Sussex coastal plain between smaller Sompting to the west, larger Shoreham-by-Sea Shoreham-by-Sea (often shortened to Shoreham) is a coastal town and port in the Adur District, Adur district, in the county of West Sussex, England. In 2011 it had a population of 20,547. The town is bordered to its north by the South Downs, to ... to the east, and the parish of Coombes to the north. Excluding definitive suburbs it may have the largest undivided nucleated village, village cluster in Britain. However, its economy is commonly analysed as integral to the Brighton/Worthing/Littlehampton conurbation. Its settled area beneath the South Downs National Park covers , the majority of its land. The Lancing area is characterised by mid-rise coastal urban homes, farmland, and wildlife reserves of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Adur
The Adur () is a river in Sussex, England; it gives its name to the Adur district of West Sussex. The river, which is long, was once navigable for large vessels up as far as Steyning, where there was a large Saxon port, but by the 11th century the lower river became silted up and the port moved down to the deeper waters at the mouth of the river in Shoreham-by-Sea. Course of river The Adur begins as two separate branches, the western Adur and the eastern Adur, which meet west of Henfield. The western Adur rises at Slinfold, from where it flows around Coolham and then through Shipley, where Hammer Pond and Lancing Brook join it on the right bank. On the left bank, it is joined by the outflow of Knepphill Pond, which forms part of the Knepp Castle pleasure grounds laid out by John Nash in 1806–13. He designed the present castellated mansion known as Knepp Castle for Sir Charles Merrick Burrell, but the grounds include the remains of an 11th-century castle, known by the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Language (Celtic)
Common Brittonic (; ; ), also known as British, Common Brythonic, or Proto-Brittonic, is a Celtic languages, Celtic language historically spoken in Great Britain, Britain and Brittany from which evolved the later and modern Brittonic languages. It is a form of Insular Celtic languages, Insular Celtic, descended from Proto-Celtic language, Proto-Celtic, a theorized parent language that, by the first half of the first millennium BC, was Divergence (linguistics), diverging into separate dialects or languages. Pictish language, Pictish is linked, most probably as a sister language or a descendant branch. Evidence from early and modern Welsh shows that Common Brittonic was significantly influenced by Latin during the Roman Britain, Roman period, especially in terms related to the Latin Church, church and Western Christianity, Christianity. By the sixth century AD, the languages of the Celtic Britons were rapidly diverging into Neo-Brittonic: Welsh language, Welsh, Cumbric, Cornish l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographia
The ''Geography'' (, , "Geographical Guidance"), also known by its Latin names as the ' and the ', is a gazetteer, an atlas, and a treatise on cartography, compiling the geographical knowledge of the 2nd-century Roman Empire. Originally written by Claudius Ptolemy in Greek at Alexandria around 150 AD, the work was a revision of a now-lost atlas by Marinus of Tyre using additional Roman and Persian gazetteers and new principles. Its translation – Kitab Surat al-Ard – into Arabic by Al-Khwarismi in the 9th century was highly influential on the geographical knowledge and cartographic traditions of the Islamic world. Alongside the works of Islamic scholars – and the commentary containing revised and more accurate data by Alfraganus – Ptolemy's work was subsequently highly influential on Medieval and Renaissance Europe. Manuscripts Versions of Ptolemy's work in antiquity were probably proper atlases with attached maps, although some scholars believe that the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzantine, Islamic science, Islamic, and Science in the Renaissance, Western European science. The first was his astronomical treatise now known as the ''Almagest'', originally entitled ' (, ', ). The second is the ''Geography (Ptolemy), Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian physics, Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ' (, 'On the Effects') but more commonly known as the ' (from the Koine Greek meaning 'four books'; ). The Catholic Church promoted his work, which included the only mathematically sound geocentric model of the Sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portsmouth And Arundel Canal
The Portsmouth and Arundel Canal was a canal in the south of England that ran between Portsmouth and Ford in the Arundel district. It was built in 1823 but was never a financial success and was abandoned in 1855; the company was wound up in 1888. The canal was part of a larger scheme for the construction of a secure inland canal route from London to Portsmouth, which allowed craft to move between the two without having to venture into the English Channel and possibly encounter enemy ships or natural disaster. It was built by the Portsmouth & Arundel Navigation company. The canal was made up of three sections: a pair of ship canals, one on Portsea Island and one to Chichester, and a barge canal that ran from Ford on the River Arun to Hunston where it joined the Chichester section of the canal Ford to Hunston Section This section of the canal connected the river Arun at Ford to the junction with the Chichester arm of the canal. It had two locks at Ford to allow the canal to dro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wey And Arun Canal
The Wey and Arun Canal is a partially open, canal in the southeast of England. It runs southwards from the River Wey at Gunsmouth in Shalford, Surrey to the River Arun at Wisborough Green, Pallingham, in West Sussex. The canal comprises parts of two separate undertakings – the northern part of the ''Arun Navigation'', opened in 1787 between Pallingham and Newbridge Wharf, and the ''Wey and Arun Junction Canal'', opened in 1816, which connected the Arun at Newbridge to the Wey and Godalming Navigations, Godalming Navigation near Shalford, south of Guildford. The Arun Navigation was built with three locks and one turf-sided flood lock. The Junction Canal was built with 23 canal lock, locks Passing through a rural landscape, there was little freight traffic to justify its continued existence – the canal was officially abandoned in 1871. Without maintenance, the canal gradually became derelict over much of its length. However, since 1970, restoration by The Wey & Arun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry FitzAlan, 19th Earl Of Arundel
Henry Fitzalan, 12th Earl of Arundel (23 April 151224 February 1580) was an English nobleman, who over his long life assumed a prominent place at the court of all the later Tudor sovereigns. Court career under Henry VIII He was the only son of William Fitzalan, 11th Earl of Arundel, and his second wife Anne Percy, daughter of Henry Percy, 4th Earl of Northumberland, and was named for Henry VIII, who personally stood as his godfather at his baptism. At 15, Henry Fitzalan became a page at the court of King Henry VIII, attending the king to Calais in 1532. When he came of age, in 1533, he was summoned to Parliament as Lord Maltravers, a subsidiary title of his father, who was still alive. He attended the trials of Anne Boleyn and her alleged lover Lord Rochford in May 1536. In 1540 he was appointed deputy of Calais. He remained there, improving the fortifications at his own expense, until his father's death in early 1544. He returned to England to assume the earldom, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flash Lock
A flash lock is a type of lock (water transport), lock for river or canal transport. Early locks were designed with a single gate, known as a flash lock or staunch lock. The earliest European references to what were clearly flash locks were in Roman times. Development In England the "gate" was similar to a temporary needle dam: a set of boards, called ''paddles'', supported against the current by upright timbers called ''rymers'' which normally kept the level of water above it to navigable levels. Boats moving downstream would wait above the lock until the paddles (and their rymers) were removed, which would allow a "flash" of water to pass through, carrying the boats with it. Boats moving upstream would be winched or towed through the lock with the paddles removed. Considerable skill was involved both in removing the paddles in a timely manner and navigating the boat through the lock. Flash locks of this type have been Science and technology of the Song dynasty#Civil enginee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |