|
Artemis I
Artemis I, formerly Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), was an uncrewed Lunar orbit, Moon-orbiting mission that was launched in November 2022. As the first major spaceflight of NASA's Artemis program, Artemis I marked the agency's return to lunar exploration after the conclusion of the Apollo program five decades earlier. It was the first integrated flight test of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, and its main objective was to test the Orion spacecraft, especially its heat shield, in preparation for subsequent Artemis missions. These missions seek to reestablish a human presence on the Moon and demonstrate technologies and business approaches needed for future scientific studies, including exploration of Mars. The Orion spacecraft for Artemis I was Stacking (rocketry), stacked on October 20, 2021, and on August 17, 2022, the fully stacked vehicle was rolled out for launch after a series of delays caused by difficulties in pre-flight test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artemis II
Artemis II is a planned mission under the NASA-led Artemis program, set to be the second launch of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and the first crewed flight of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft. Scheduled to launch in early 2026, the mission will carry four astronauts on a free-return trajectory around the Moon and back to Earth. It will be the first crewed mission to venture beyond low Earth orbit and travel to the Moon since Apollo 17 in 1972. Initially designated as Exploration Mission-2 (EM-2), the mission was originally planned to retrieve samples from a captured asteroid as part of the now-canceled Asteroid Redirect Mission. It was later renamed following the establishment of the Artemis program. History Mission planning and launcher selection (2017–2021) In 2017, Exploration Mission-2 was a projected single-launch mission of a Space Launch System (SLS) Block 1B rocket with an Exploration Upper Stage, lunar Block 1 Orion spacecraft, and a payload i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
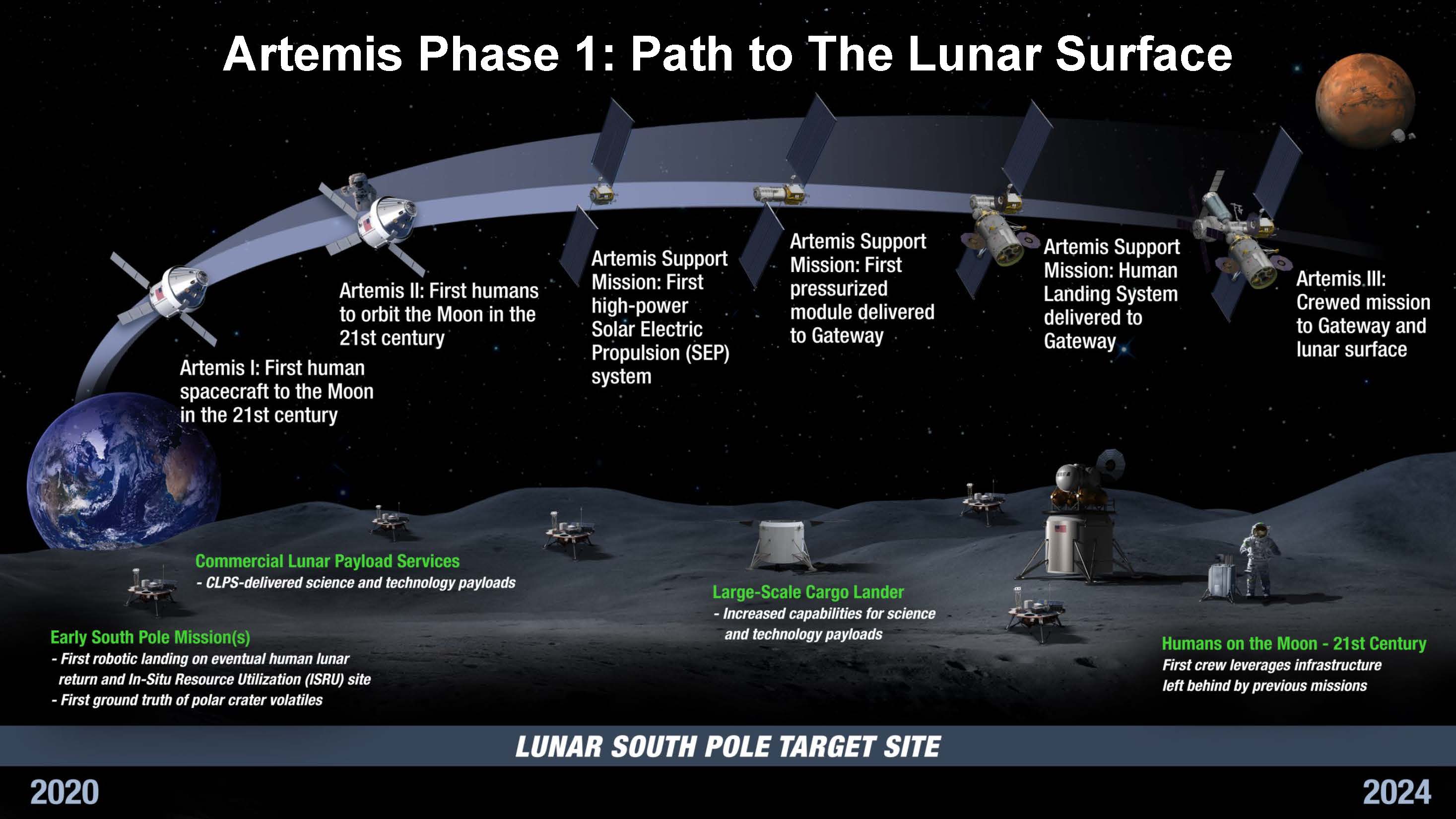
Artemis Program
The Artemis program is a Exploration of the Moon, Moon exploration program led by the United States' National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), formally established in 2017 via Space Policy Directive 1. The program's stated long-term goal is to establish a Moonbase, permanent base on the Moon to facilitate Human mission to Mars, human missions to Mars. It is intended to reestablish a human presence on the Moon for the first time since the Apollo 17 mission in 1972 and continue the direct exploration of Mars begun with data from the Mariner 9 probe in the same year. Two principal elements of the Artemis program are derived from the now-cancelled Constellation program: the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft (with the European Service Module, ESM instead of a US-built service module) and the Space Launch System's Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Booster#Five-segment booster, solid rocket boosters (originally developed for the Ares V). Other elements of the program, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orion (spacecraft)
Orion (Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle or Orion MPCV) is a partially reusable crewed spacecraft used in NASA's Artemis program. The spacecraft consists of a Crew Module (CM) space capsule designed by Lockheed Martin that is paired with a European Service Module (ESM) manufactured by Airbus Defence and Space. Capable of supporting a crew of four beyond low Earth orbit, Orion can last up to 21 days undocked and up to six months docked. It is equipped with solar panels, an automated docking system, and glass cockpit interfaces. Orion is launched atop a Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, with a tower launch escape system. Orion was conceived in the early 2000s by Lockheed Martin as a proposal for the Crew Exploration Vehicle (CEV) to be used in NASA's Constellation program and was selected by NASA in 2006. Following the cancellation of the Constellation program in 2010, Orion was extensively redesigned for use in NASA's Journey to Mars initiative; later named Moon to Mars. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baja California
Baja California, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California, is a state in Mexico. It is the northwesternmost of the 32 federal entities of Mexico. Before becoming a state in 1952, the area was known as the North Territory of Baja California (). It has an area of (3.57% of the land mass of Mexico) and comprises the northern half of the Baja California peninsula, north of the 28th parallel, plus oceanic Guadalupe Island. The mainland portion of the state is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean; on the east by Sonora, the United States on the north and on the south by Baja California Sur. The state has an estimated population of 3,769,020 as of 2020, significantly higher than the sparsely populated Baja California Sur to the south, and similar to San Diego County, California, and Imperial County, California, to its north. Over 75% of the population lives in Mexicali (the state's capital city), Ensenada, or Tijuana (the state's largest city). Other impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geocentric Orbit
A geocentric orbit, Earth-centered orbit, or Earth orbit involves any object orbiting Earth, such as the Moon or artificial satellites. In 1997, NASA estimated there were approximately 2,465 artificial satellite payloads orbiting Earth and 6,216 pieces of space debris as tracked by the Goddard Space Flight Center. More than 16,291 objects previously launched have undergone orbital decay and entered Earth's atmosphere. A spacecraft enters orbit when its centripetal acceleration due to gravity is less than or equal to the centrifugal acceleration due to the horizontal component of its velocity. For a low Earth orbit, this velocity is about ; by contrast, the fastest crewed airplane speed ever achieved (excluding speeds achieved by deorbiting spacecraft) was in 1967 by the North American X-15. The energy required to reach Earth orbital velocity at an altitude of is about 36 MJ/kg, which is six times the energy needed merely to climb to the corresponding altitude. Spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stacking (rocketry)
A multistage rocket or step rocket is a launch vehicle that uses two or more rocket ''stages'', each of which contains its own engines and propellant. A ''tandem'' or ''serial'' stage is mounted on top of another stage; a ''parallel'' stage is attached alongside another stage. The result is effectively two or more rockets stacked on top of or attached next to each other. Two-stage rockets are quite common, but rockets with as many as five separate stages have been successfully launched. By jettisoning stages when they run out of propellant, the mass of the remaining rocket is decreased. Each successive stage can also be optimized for its specific operating conditions, such as decreased atmospheric pressure at higher altitudes. This ''staging'' allows the thrust of the remaining stages to more easily accelerate the rocket to its final velocity and height. In serial or tandem staging schemes, the first stage is at the bottom and is usually the largest, the second stage and subse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exploration Of Mars
The planet Mars has been explored remotely by spacecraft. Uncrewed spacecraft, Probes sent from Earth, beginning in the late 20th century, have yielded a large increase in knowledge about the Martian system, focused primarily on understanding Geology of Mars, its geology and Planetary habitability, habitability potential. Engineering Interplanetary spaceflight, interplanetary journeys is complicated and the exploration of Mars has experienced a high failure rate, especially the early attempts. Roughly sixty percent of all spacecraft destined for Mars failed before completing their missions, with some failing before their observations could begin. Some missions have been met with unexpected success, such as the twin Mars Exploration Rovers, ''Spirit (rover), Spirit'' and ''Opportunity (rover), Opportunity'', which operated for years beyond their specification. Current status There are two functional rovers on the surface of Mars, the Curiosity (rover), ''Curiosity'' and Persever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Shield
In engineering, a heat shield is a component designed to protect an object or a human operator from being burnt or overheated by dissipating, reflecting, and/or absorbing heat. The term is most often used in reference to exhaust heat management and to systems for dissipating frictional heat. Heat shields are used most commonly in the automotive and aerospace industries. Principles of operation Heat shields protect structures from extreme temperatures and thermal gradients by two primary mechanisms. Thermal insulation and radiative cooling, respectively isolate the underlying structure from high external surface temperatures, while emitting heat outwards through thermal radiation. To achieve good functionality the three attributes required of a heat shield are low thermal conductivity (high thermal resistance), high emissivity, and good thermal stability (refractoriness). Porous ceramics with high emissivity coatings (HECs) are often employed to address these three characteristic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exploration Flight Test-1
Exploration Flight Test-1 or EFT-1 (previously known as Orion Flight Test 1 or OFT-1) was a technology demonstration mission and the first flight test of the crew module portion of the Orion spacecraft. Without a crew, it was launched on 5 December 2014 at 12:05 UTC (7:05 am EST, local time at the launch site) by a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37B at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The mission was a four-hour, two-orbit test of the Orion crew module featuring a high apogee on the second orbit and concluding with a high-energy reentry at around . This mission design corresponds to the Apollo 2/3 missions of 1966, which validated the Apollo flight control system and heat shield at re-entry conditions planned for the return from lunar missions. Objectives EFT-1 tested various systems of the crew module portion of the Orion spacecraft, including separation events, avionics, heat shielding, parachutes, and recovery operations pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
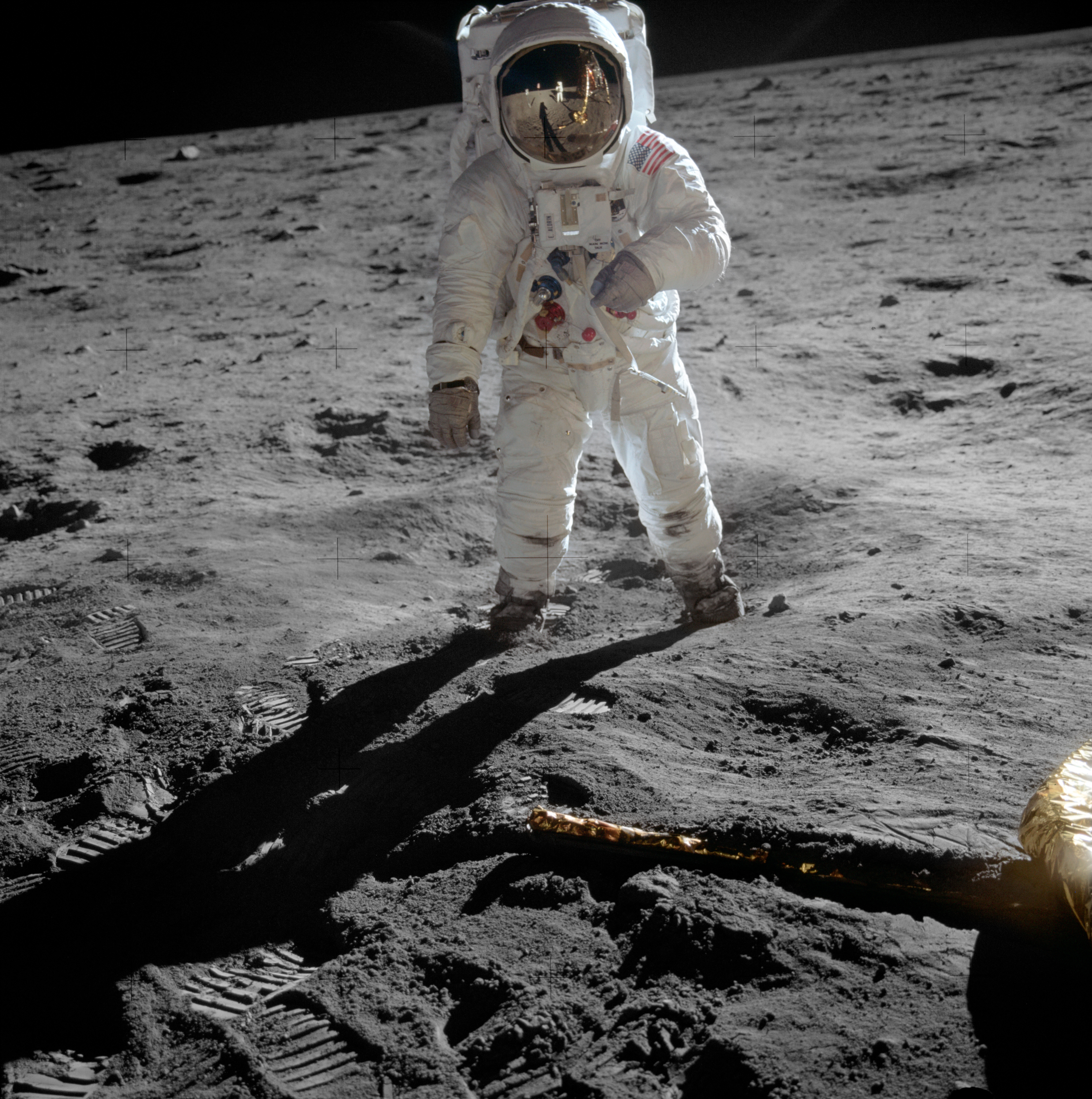
Apollo Program
The Apollo program, also known as Project Apollo, was the United States human spaceflight program led by NASA, which Moon landing, landed the first humans on the Moon in 1969. Apollo followed Project Mercury that put the first Americans in space. It was conceived in 1960 as a three-person spacecraft during President Presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower, Dwight D. Eisenhower's administration. Apollo was later dedicated to President John F. Kennedy's national goal for the 1960s of "landing a man on the Moon and returning him safely to the Earth" in an address to United States Congress, Congress on May 25, 1961. It was the third American human spaceflight program to fly, preceded by Project Gemini conceived in 1961 to extend spaceflight capability in support of Apollo. Kennedy's goal was accomplished on the Apollo 11 mission when astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin landed their Apollo Lunar Module (LM) on July 20, 1969, and walked on the lunar surface, while Michael Collins ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascent Abort-2
Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) was a test of the launch escape system (LAS) of NASA's Orion spacecraft. The test followed Orion's Pad Abort-1 test in 2010 and Exploration Flight Test-1 in 2014 in which the capsule first flew in space. It preceded an uncrewed flight of Orion around the Moon as the Artemis 1 mission, and paves the way for human use of Orion in subsequent missions of the Artemis program. The test flight lifted off from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on 2 July 2019 at 11:00 UTC (07:00 EDT, local time at the launch site). The flight was successful, and the launch abort system performed as designed. Mission highlights An Orion test article, aerodynamically similar to but lacking the full features of the space-tested capsule, was launched from Cape Canaveral SLC-46 by the purpose-built Orion Abort Test Booster (ATB). The booster was a repurposed Peacekeeper missile first stage (SR118) procured from the United States Air Forc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orion Program
Orion (Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle or Orion MPCV) is a Reusable spacecraft, partially reusable crewed spacecraft used in NASA's Artemis program. The spacecraft consists of a Crew Module (CM) space capsule designed by Lockheed Martin that is paired with a European Service Module (ESM) manufactured by Airbus Defence and Space. Capable of supporting a crew of four beyond low Earth orbit, Orion can last up to 21 days undocked and up to six months docked. It is equipped with Solar panels on spacecraft, solar panels, an NASA Docking System, automated docking system, and glass cockpit interfaces. Orion is launched atop a Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, with a tower launch escape system. Orion was conceived in the early 2000s by Lockheed Martin as a proposal for the Crew Exploration Vehicle (CEV) to be used in NASA's Constellation program and was selected by NASA in 2006. Following the cancellation of the Constellation program in 2010, Orion was extensively redesigned for use i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |