|
ArtemiFlow
ArtemiFlow is a biotechnology company, founded in 2012 by Peter Seeberger. The company produces and sells pharmaceutical drugs containing the active ingredient artemisinin and its derivatives to fight malaria, Cancer (medicine), cancer and other diseases. As of 2025, Adam Maust is the CEO of ArtemiFlow. Science and development Seeberger developed a process to produce artemisinin in large quantities in a cost-effective and environmentally friendly way, especially to meet the needs of developing countries. This was an alternative to Sanofi, Sanofi's genetic engineering process. Initial difficulties were the large-scale implementation of the manufacturing process, the cultivation of annual mugwort in Vietnam and the financing of the Start-up company, start-up. According to the first CEO Dirk Pohlmann, the company was hoping for support from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. The latter supported competing products from the Sanofi company made from genetically modified yeast. Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirk Pohlmann
Dirk Pohlmann (born August 11, 1959) is a German journalist, author, Scriptwriter, screenwriter, director and producer of about 25 historical documentaries for German Public broadcasting, public media Arte, ARD (broadcaster), ARD and ZDF. He held positions of leadership in CargoLifter, CargoLifter World and ArtemiFlow. Since 2019, Dirk Pohlmann has served as the editor-in-chief of Free21, an Alternative media, alternative German Political Blog, political blog and print journal. He also makes contributions to the Australian News Programme TNT Radio. After 2004, Pohlmann's main focus has been on intelligence operations during the Cold War and after. Since 2016, after ending his cooperation with German public media, he has published only in alternative media. Life After his ''Abitur'', Pohlmann studied journalism, philosophy as well as law at Johannes Gutenberg University in Mainz. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotechnology
Biotechnology is a multidisciplinary field that involves the integration of natural sciences and Engineering Science, engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms and parts thereof for products and services. Specialists in the field are known as biotechnologists. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used by Károly Ereky in 1919 to refer to the production of products from raw materials with the aid of living organisms. The core principle of biotechnology involves harnessing biological systems and organisms, such as bacteria, yeast, and plants, to perform specific tasks or produce valuable substances. Biotechnology had a significant impact on many areas of society, from medicine to agriculture to environmental science. One of the key techniques used in biotechnology is genetic engineering, which allows scientists to modify the genetic makeup of organisms to achieve desired outcomes. This can involve inserting genes from one organism into another, and con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotechnology Companies By Country
Biotechnology is a multidisciplinary field that involves the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms and parts thereof for products and services. Specialists in the field are known as biotechnologists. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used by Károly Ereky in 1919 to refer to the production of products from raw materials with the aid of living organisms. The core principle of biotechnology involves harnessing biological systems and organisms, such as bacteria, yeast, and plants, to perform specific tasks or produce valuable substances. Biotechnology had a significant impact on many areas of society, from medicine to agriculture to environmental science. One of the key techniques used in biotechnology is genetic engineering, which allows scientists to modify the genetic makeup of organisms to achieve desired outcomes. This can involve inserting genes from one organism into another, and consequently, create n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic. The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fever, fatigue, cough, breathing difficulties, anosmia, loss of smell, and ageusia, loss of taste. Symptoms may begin one to fourteen days incubation period, after exposure to the virus. At least a third of people who are infected asymptomatic, do not develop noticeable symptoms. Of those who develop symptoms noticeable enough to be classified as patients, most (81%) develop mild to moderate symptoms (up to mild pneumonia), while 14% develop severe symptoms (dyspnea, hypoxia (medical), hypoxia, or more than 50% lung involvement on imaging), and 5% develop critical symptoms (respiratory failure, shock (circulatory), shock, or organ dysfunction, multiorgan dysfunction). Older people have a higher risk of developing severe symptoms. Some complicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Chemical Society
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a scientific society based in the United States that supports scientific inquiry in the field of chemistry. Founded in 1876 at New York University, the ACS currently has more than 155,000 members at all degree levels and in all fields of chemistry, chemical engineering, and related fields. It is one of the world's largest scientific societies by membership. The ACS is a 501(c) organization, 501(c)(3) non-profit organization and holds a congressional charter under Title 36 of the United States Code. Its headquarters are located in Washington, D.C., and it has a large concentration of staff in Columbus, Ohio. The ACS is a leading source of scientific information through its peer-reviewed scientific journals, national conferences, and the Chemical Abstracts Service. Its publications division produces over 80 Scientific journal, scholarly journals including the prestigious ''Journal of the American Chemical Society'', as well as the weekly tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artemisia Annua
''Artemisia annua'', also known as sweet wormwood, sweet annie, sweet sagewort, annual mugwort or annual wormwood, is a common type of wormwood native to temperate Asia, but naturalized in many countries including scattered parts of North America. The chemical compound artemisinin, which is isolated from ''A. annua'', is a medication used to treat malaria. Discovery of artemisinin and its antimalarial properties by the Chinese scientist Tu Youyou led to the award of the 2011 Lasker Prize and 2015 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Description ''Artemisia annua'' belongs to the plant family of ''Asteraceae'' and is an annual short-day plant. Its stem is erect and brownish or violet-brown. The plant itself is hairless and naturally grows from 30 to 100 cm tall, although in cultivation plants can reach a height of 200 cm. The leaves of ''A. annua'' have a length of 3–5 cm and are divided by deep cuts into two or three small leaflets. The intensive aromatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Kentucky
The University of Kentucky (UK, UKY, or U of K) is a Public University, public Land-grant University, land-grant research university in Lexington, Kentucky, United States. Founded in 1865 by John Bryan Bowman as the Agricultural and Mechanical College of Kentucky, the university is one of the state's two land-grant universities (the other being Kentucky State University). It is the institution with the highest enrollment in the state, with 35,952 students in the fall of 2024. The institution comprises 16 colleges, a graduate school, 93 undergraduate programs, 99 master's degrees, master programs, 66 Doctor of Philosophy, doctoral programs, and 4 professional programs. It is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". According to the National Science Foundation, Kentucky spent $476.5 million on research and development in 2022, ranking it 61st in the nation. The University of Kentuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bill And Melinda Gates Foundation
The Gates Foundation is an American private foundation founded by Bill Gates and Melinda French Gates. Based in Seattle, Washington, it was launched in 2000 and is reported to be List of wealthiest charitable foundations, the third largest charitable foundation in the world, holding $77.2 billion in assets as of December 31, 2024. The primary stated goals of the foundation are to enhance healthcare and reduce extreme poverty across the world, and to expand educational opportunities and access to information technology in the U.S. Key individuals of the foundation include Warren Buffett, chief executive officer Mark Suzman, and Michael Larson (businessman), Michael Larson. The scale of the foundation and the way it seeks to apply business techniques to giving makes it one of the leaders in venture philanthropy, though the foundation itself notes that the philanthropic role has limitations. In 2007, its founders were ranked as the second most generous philanthropists in the U.S., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
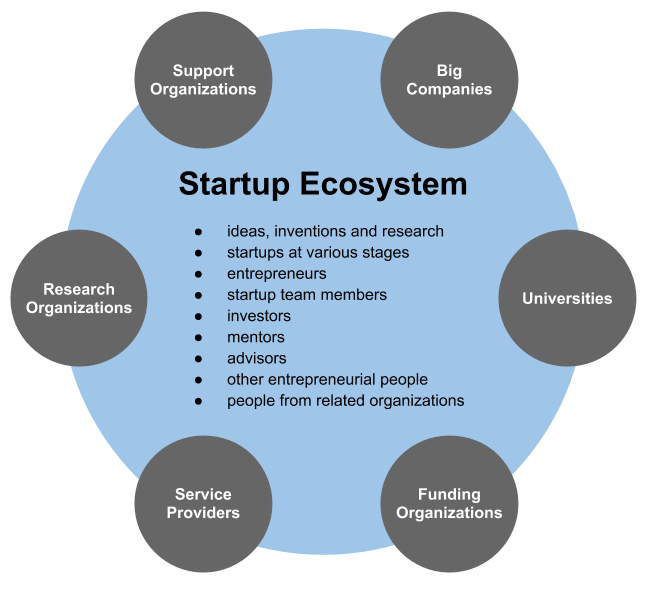
Start-up Company
A startup or start-up is a company or project undertaken by an entrepreneur to seek, develop, and validate a scalable business model. While entrepreneurship includes all new businesses including self-employment and businesses that do not intend to go public, startups are new businesses that intend to grow large beyond the solo-founder. During the beginning, startups face high uncertainty and have high rates of failure, but a minority of them do go on to become successful and influential, such as unicorns.Erin Griffith (2014)Why startups fail, according to their founders, Fortune.com, 25 September 2014; accessed 27 October 2017 Actions Startups typically begin by a founder (solo-founder) or co-founders who have a way to solve a problem. The founder of a startup will do the market validation by problem interview, solution interview, and building a minimum viable product (MVP), i.e. a prototype, to develop and validate their business models. The startup process can take a long perio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Seeberger
Peter H. Seeberger (born 1966, in Nuremberg) is a German chemist. Biography Seeberger studied chemistry at the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg. He completed his Ph.D. in biochemistry in 1995 as a Fulbright scholar at the University of Colorado at Boulder. After being a post-doctoral fellow at Sloan Kettering Institute for Cancer Research in New York, he became assistant professor at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1998, where he was promoted to Firmenich Associate Professor of Chemistry in 2002. Starting 2003 he was a professor of organic chemistry at the department of chemistry and applied biosciences at ETH Zurich as well as an affiliate professor at Burnham Institute in La Jolla, California. Since the summer of 2008 he is one of the directors of Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces in Golm, near Potsdam, where is the head of the department of biomolecular systems. Seeberger is a specialist in the area of glycomics. His awards include Klung W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Mugwort
''Artemisia annua'', also known as sweet wormwood, sweet annie, sweet sagewort, annual mugwort or annual wormwood, is a common type of wormwood native to temperate Asia, but naturalized in many countries including scattered parts of North America. The chemical compound artemisinin, which is isolated from ''A. annua'', is a medication used to treat malaria. Discovery of artemisinin and its antimalarial properties by the Chinese scientist Tu Youyou led to the award of the 2011 Lasker Prize and 2015 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Description ''Artemisia annua'' belongs to the plant family of ''Asteraceae'' and is an annual short-day plant. Its stem is erect and brownish or violet-brown. The plant itself is hairless and naturally grows from 30 to 100 cm tall, although in cultivation plants can reach a height of 200 cm. The leaves of ''A. annua'' have a length of 3–5 cm and are divided by deep cuts into two or three small leaflets. The intensive aromatic s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |