|
Arques-la-Bataille
Arques-la-Bataille () is a Communes of France, commune in the Seine-Maritime Departments of France, department in the Normandy (administrative region), Normandy region in north-western France. The zoologist Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville (1777–1850) was born in Arques. Geography Arques is situated near the confluence of the rivers Eaulne, Varenne (Arques), Varenne and Béthune (river), Béthune, with the forest of Arques to the north-east. It lies southeast of Dieppe, Seine-Maritime, Dieppe at the junction of the D23, D154, and D56 roads. Population Main sights The centre houses a castle dominating the town, which was built in the 11th century by William of Talou; his nephew, William I of England, William the Conqueror, regarding it as a menace to his own power, besieged and occupied it. After frequently changing hands, it came into the possession of the English, who were expelled in 1449 after an occupation of thirty years. In 1589, its cannon decided the Battle of Arqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Arques
The Battle of Arques occurred on 15–29 September 1589 between the French royal forces of King Henry IV of France and troops of the Catholic League commanded by Charles of Lorraine, Duke of Mayenne, during the eighth and final war (1585–1598) of the French Wars of Religion. It was a victory for Henry IV. Background At the death of Henry III of France, the Huguenot Henry of Navarre became by birthright the successor to the French throne (as Henry IV). Although he quickly declared his intention to "maintain and preserve the Catholic, apostolic and roman religion" of the country (), the major French cities sided with the Catholic League and its leader, the Duke of Mayenne (younger brother to the deceased Henry I, Duke of Guise). At that time, the royal army was in a shambles and Henry IV could only count on barely 20,000 men to conquer a rebellious country. In order to accomplish this task, he divided his troops into three commands: Henri I d'Orléans, Duke of Longueville ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri Marie Ducrotay De Blainville
Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville (; 12 September 1777 – 1 May 1850) was a French zoologist and anatomist. Life Blainville was born at Arques-la-Bataille, Arques, near Dieppe, Seine-Maritime, Dieppe. As a young man, he went to Paris to study art, but ultimately devoted himself to natural history. He attracted the attention of Georges Cuvier, for whom he occasionally substituted as lecturer at the Collège de France and at the Athenaeum Club, London. In 1812, he was aided by Cuvier in acquiring the position of assistant professor of anatomy and zoology in the Faculty of Sciences at Paris. Eventually, relations between the two men soured, a situation that ended in open enmity. In 1819, Blainville was elected a member of the American Philosophical Society in Philadelphia. In 1825, he was admitted a member of the French Academy of Sciences; and in 1830, he was appointed to succeed Jean-Baptiste Lamarck in the chair of natural history at the museum. Two years later, on the death of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
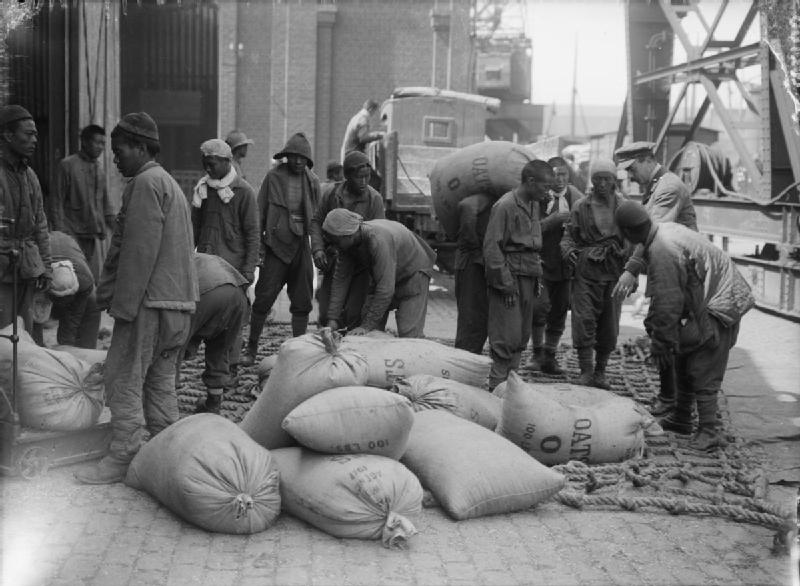
Chinese Labour Corps
The Chinese Labour Corps (CLC; ; ) was a labour corps recruited by the British government in the First World War to free troops for front line duty by performing support work and manual labour. The French government also recruited a significant number of Chinese labourers, and although those labourers working for the French were recruited separately and not part of the CLC, the term is often used to encompass both groups. In all, some 140,000 men served for both British and French forces before the war ended and most of the men were repatriated to China between 1918 and 1920. Origins In 1916, Field Marshal Sir Douglas Haig requested that 21,000 labourers be recruited to fill the manpower shortage caused by casualties during the First World War. Recruiting labourers from other countries was not something unusual at that time. Other than the Chinese, labour corps were serving in France from Egypt, Fiji, India, Malta, Mauritius, Seychelles, and the British West Indies, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varenne (Arques)
The Varenne () is a river of Normandy, France, in length, flowing through the department of Seine-Maritime. It is a tributary of the river Arques. The river is the ultimate source of the surname and given name Warren, via William de Warenne of Bellencombre castle, his hereditary seat. de Warenne was a companion of William the Conqueror and made first Earl of Surrey in 1088 as reward for his service during the Norman Conquest. Geography The river's source is just northwest of Buchy near to Montérolier, Its valley separates the pays de Caux on the west bank from the pays de Bray to the east. Of the three rivers that form the Arques, the Varenne is the shortest but paradoxically has the largest catchment area and highest speed (3.5 m/s). The only significant tributary is the Herring Creek (8 km in length) which joins on the left bank at Rosay. Its course takes it past the communes of Saint-Martin-Osmonville, Saint-Saëns, through the forest of Eawy and on to B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communauté D'agglomération De La Région Dieppoise
The Communauté d'agglomération de la région Dieppoise, also known as Dieppe Maritime is the ''communauté d'agglomération'', an intercommunal structure, centred on the city of Dieppe. It is located in the Seine-Maritime department, in the Normandy region, northern France. It was created on 31 December 2002.CA de la Région Dieppoise (N° SIREN : 247600786) BANATIC, accessed 17 October 2024. Its area is 129.0 km2. Its population was 46,223 in 2018, of which 28,561 in Dieppe proper.Comparateur de territoire INSEE, accessed 6 April 2022. Comp ...
|
William Of Talou
William of Talou, Count of Talou (Arques-la-Bataille, Arques) (before 1035–1086) was a powerful member of the Norman ducal family who exerted his influence during the early reign of William the Conqueror Duke of Normandy. Background William was the son of Richard II of Normandy, duke Richard II of Normandy by Papia of Envermeu.David C. Douglas, ''William the Conqueror'' (University of California Press, Berkeley, Los Angeles, 1964), p. 38 His brother was Mauger Archbishop of Rouen, Mauger, who became archbishop of Rouen in or shortly after 1037. In 1035, following the death of Robert I of Normandy on a pilgrimage to Jerusalem, William of Talou challenged his nephew's right to succeed his father, basing his own claim on a legitimate descent from Richard II. But the young Duke William had the backing of his powerful great-uncle, Robert I Archbishop of Rouen, Robert II, the archbishop of Rouen. When Archbishop Robert died in 1037 there was a power vacuum and all of Normandy fell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleanor's House
"Eleanor's House" is a short story by Willa Cather. It was first published in ''McClure's'' in October 1907. Plot summary Harold Forscythe and his new wife Ethel are visiting the Westfields, who live in Arques-la-Bataille. Harold admits to Harriet that he is still in mourning over his late wife. Later, he goes away as he does customarily. Ethel decides to join him at Fortuney near Pontoise, where he used to live with his late wife. Harriet will go with her. When they get there, the couple have a fight. Later however, Harriet tells her husband she is buying Harold's house in Fortuney - he is leaving for America with his wife, who is pregnant. Characters *Mrs Harriet Westfield. She went to a convent in Paris with Eleanor in her youth. *Mr Robert Westfield *Harold Forscythe *Ethel, Harold's new wife. *Eleanor Sanford, Harold's late wife. References to other works *Harriet mentions Antoine François Prévost's ''Manon Lescaut'', and Alfred de Musset Alfred Louis Charles de Musse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Béthune (river)
The Béthune () is a river of Normandy, France, in length, flowing through the department of Seine-Maritime and it is a tributary of the Arques (river), Arques. However, Sandre, the regulators of France's national Water Information System, consider the Béthune to be the upper part of the Arques. Geography The river's source is at the village of Gaillefontaine near to Forges-les-Eaux. Its valley is wholly within the pays de Bray. Its course takes it past the communes of Neufchâtel-en-Bray, Mesnières-en-Bray, Bures-en-Bray, Osmoy-Saint-Valery, Saint-Vaast-d'Équiqueville, Dampierre-Saint-Nicolas, Saint-Aubin-le-Cauf and finally Arques-la-Bataille where it joins the rivers Eaulne and Varenne (Arques), Varenne to form the Arques (river), Arques. Like other rivers in the region, the Béthune is classified as a first class river, offering anglers the chance to catch salmon and trout. See also *Schéma directeur d'aménagement et de gestion des eaux, French water management sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eaulne
The river Eaulne () is one of the rivers that flow from the plateau of the eastern Pays de Caux in the Seine-Maritime ''département'' of Normandy in northern France. It is long. The Eaulne's source is at Mortemer. It then flows northwestwards through Sainte-Beuve-en-Rivière, Saint-Germain-sur-Eaulne, Londinières, Douvrend, Envermeu, turning westward at Bellengreville and on to Ancourt, Martin-Église and joins the river Arques at Arques-la-Bataille Arques-la-Bataille () is a Communes of France, commune in the Seine-Maritime Departments of France, department in the Normandy (administrative region), Normandy region in north-western France. The zoologist Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville (177 .... See also * French water management scheme References Rivers of France Rivers of Normandy Rivers of Seine-Maritime {{France-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
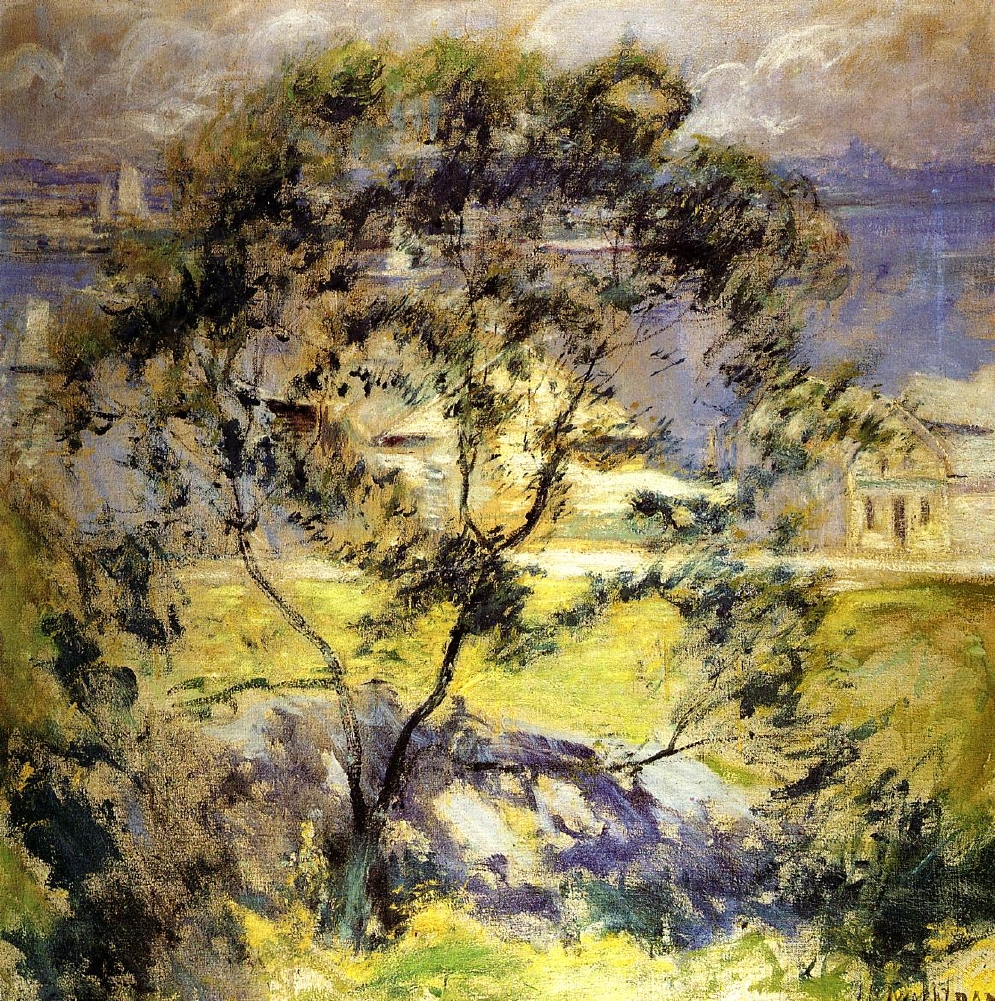
John Henry Twachtman
John Henry Twachtman (August 4, 1853 – August 8, 1902) was an American painter best known for his impressionist landscapes, though his painting style varied widely through his career. Art historians consider Twachtman's style of American Impressionism to be among the more personal and experimental of his generation. He was a member of "The Ten," a loosely-allied group of American artists dissatisfied with professional art organizations, who banded together in 1898 to exhibit their works as a stylistically unified group. Studies Twachtman was born in Cincinnati, Ohio and received his first art training there, including studying under Frank Duveneck. Like many other gifted and driven artists of his generation, including Henry Ossawa Tanner and Diego Rivera, he sought his training in Europe. He enrolled in the Academy of Fine Arts in Munich in 1875 and visited Venice with Duveneck and William Merritt Chase in 1878. His landscapes from this time exhibit the loosely brushed, shad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of The Seine-Maritime Department
The following is a list of the 707 communes of the French department of Seine-Maritime. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2025):Périmètre des groupements en 2025 BANATIC. Accessed 28 May 2025. * Métropole Rouen Normandie *Communauté urbaine Le Havre Seine Métropole
Le Havre Seine Métropole is the ''communauté urbaine'', an Communes of France#Intercommunality, intercommunal structure, centred on the Communes of France, city of Le Havre. It is located in the Seine-Maritime departments of Fra ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and surpass the ideas and achievements of classical antiquity. Associated with great social change in most fields and disciplines, including Renaissance art, art, Renaissance architecture, architecture, politics, Renaissance literature, literature, Renaissance exploration, exploration and Science in the Renaissance, science, the Renaissance was first centered in the Republic of Florence, then spread to the Italian Renaissance, rest of Italy and later throughout Europe. The term ''rinascita'' ("rebirth") first appeared in ''Lives of the Artists'' () by Giorgio Vasari, while the corresponding French word was adopted into English as the term for this period during the 1830s. The Renaissance's intellectual basis was founded in its version of Renaiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |