|
Arnold Harberger
Arnold Carl Harberger (born July 27, 1924) is an American economist. His approach to the teaching and practice of economics is to emphasize the use of analytical tools that are directly applicable to real-world issues. His influence on academic economics is reflected in part by the widespread use of the term " Harberger triangle" to refer to the standard graphical depiction of the efficiency cost of distortions of competitive equilibrium. Life Harberger completed his B.A. in economics at Johns Hopkins University, and his M.A. in international relations in 1947 and his Ph.D. in economics in 1950 at the University of Chicago. After teaching at Johns Hopkins, Harberger returned to the University of Chicago to teach full-time from 1953 to 1982, and part-time from 1984 to 1991. Since 1984, he has been a professor at the University of California, Los Angeles, serving as professor emeritus since 2014. He married Chilean Anita Valjalo in 1958. The two remained together until her death ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newark, New Jersey
Newark ( , ) is the List of municipalities in New Jersey, most populous City (New Jersey), city in the U.S. state of New Jersey, the county seat of Essex County, New Jersey, Essex County, and a principal city of the New York metropolitan area.Table1. New Jersey Counties and Most Populous Cities and Townships: 2020 and 2010 Censuses , New Jersey Department of Labor and Workforce Development. Accessed December 1, 2022.New Jersey County Map , New Jersey Department of State. Accessed December 27, 2022. As of the 2020 U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin America
Latin America is the cultural region of the Americas where Romance languages are predominantly spoken, primarily Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese. Latin America is defined according to cultural identity, not geography, and as such it includes countries in both North and South America. Most countries south of the United States tend to be included: Mexico and the countries of Central America, South America and the Caribbean. Commonly, it refers to Hispanic America plus Brazil. Related terms are the narrower Hispanic America, which exclusively refers to Spanish-speaking nations, and the broader Ibero-America, which includes all Iberic countries in the Americas and occasionally European countries like Spain, Portugal and Andorra. Despite being in the same geographical region, English- and Dutch language, Dutch-speaking countries and territories are excluded (Suriname, Guyana, the Falkland Islands, Jamaica, Trinidad and Tobago, Belize, etc.), and French- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordon Tullock
Gordon Tullock (; February 13, 1922 – November 3, 2014) was an American professor of law and economics at the George Mason University School of Law. He is best known for his work on public choice theory, the application of economic thinking to political issues. He was one of the founding figures in his field. Early life and education Tullock was born February 13, 1922, in Rockford, Illinois, where he attended and graduated from Rockford Central High School. Tullock attended the University of Chicago where, after a break for military service during World War II, he received a J.D. in 1947. He later completed Chinese language instruction at Yale and Cornell universities. Career Following a brief period in private practice, he joined the Foreign Service in fall 1947, and was posted to Tianjin, China and later to Hong Kong and Korea. In 1956, he resigned from the Foreign Service. While he originally intended to pursue a career as a foreign trader in the Far East, his work on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harold Hotelling
Harold Hotelling (; September 29, 1895 – December 26, 1973) was an American mathematical statistician and an influential economic theorist, known for Hotelling's law, Hotelling's lemma, and Hotelling's rule in economics, as well as Hotelling's T-squared distribution in statistics. He also developed and named the principal component analysis method widely used in finance, statistics and computer science. He was associate professor of mathematics at Stanford University from 1927 until 1931, a member of the faculty of Columbia University from 1931 until 1946, and a professor of Mathematical Statistics at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill from 1946 until his death. A street in Chapel Hill bears his name. In 1972, he received the North Carolina Award for contributions to science. Statistics Hotelling is known to statisticians because of Hotelling's T-squared distribution which is a generalization of the Student's t-distribution in multivariate setting, and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
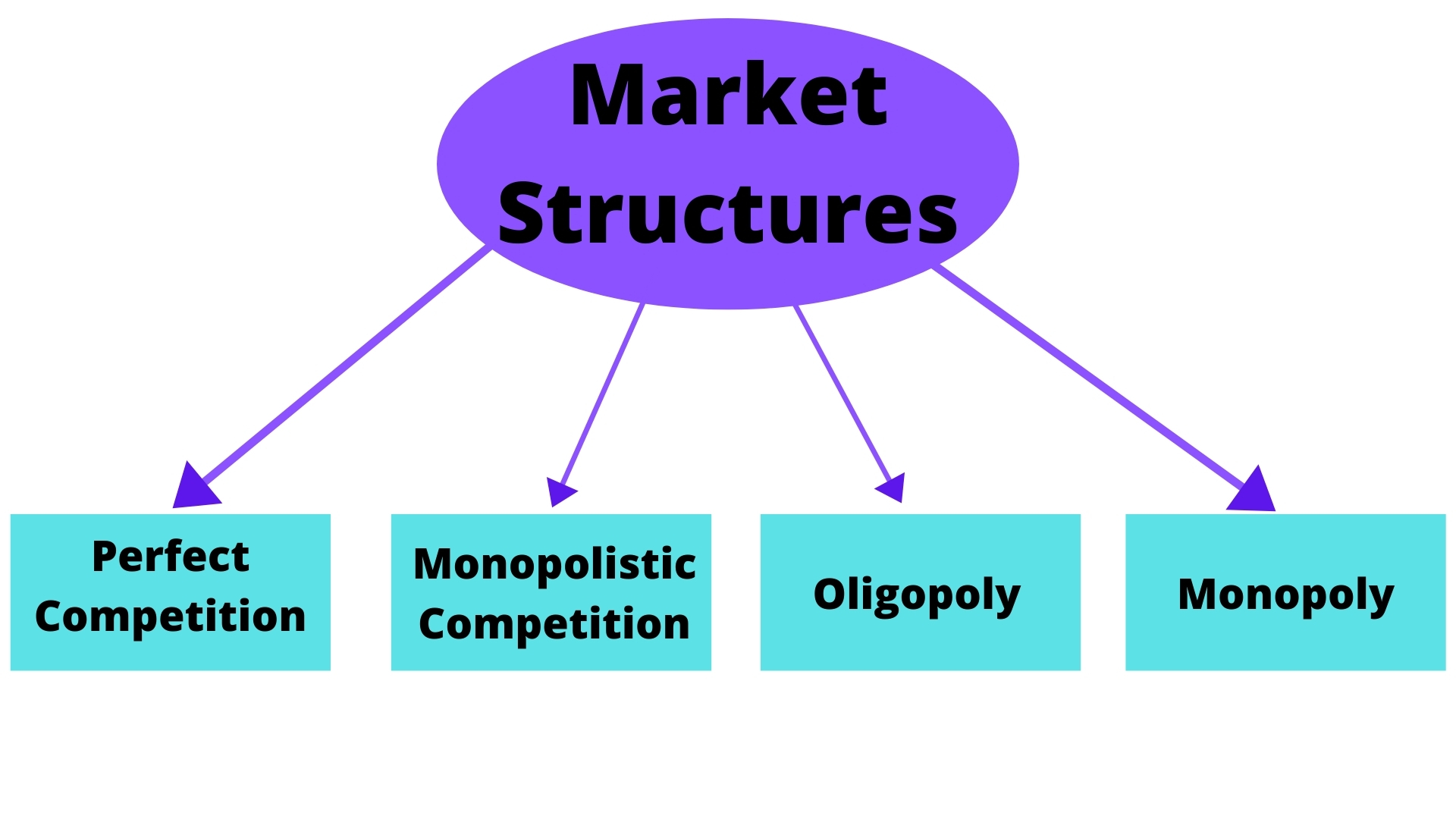
Market Power
In economics, market power refers to the ability of a theory of the firm, firm to influence the price at which it sells a product or service by manipulating either the supply or demand of the product or service to increase economic profit. In other words, market power occurs if a firm does not face a perfectly elastic demand curve and can set its price (P) above marginal cost (MC) without losing revenue. This indicates that the magnitude of market power is associated with the gap between P and MC at a firm's profit maximising level of output. The size of the gap, which encapsulates the firm's level of market dominance, is determined by the residual demand curve's form. A steeper reverse demand indicates higher earnings and more dominance in the market. Such propensities contradict Perfect competition, perfectly competitive markets, where market participants have no market power, P = MC and firms earn zero economic profit. Market participants in perfectly competitive markets are cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monopoly
A monopoly (from Greek language, Greek and ) is a market in which one person or company is the only supplier of a particular good or service. A monopoly is characterized by a lack of economic Competition (economics), competition to produce a particular thing, a lack of viable substitute goods, and the possibility of a high monopoly price well above the seller's marginal cost that leads to a high monopoly profit. The verb ''monopolise'' or ''monopolize'' refers to the ''process'' by which a company gains the ability to raise prices or exclude competitors. In economics, a monopoly is a single seller. In law, a monopoly is a business entity that has significant market power, that is, the power to charge Monopoly price, overly high prices, which is associated with unfair price raises. Although monopolies may be big businesses, size is not a characteristic of a monopoly. A small business may still have the power to raise prices in a small industry (or market). A monopoly may als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efficiency Loss
Efficiency is the often measurable ability to avoid making mistakes or wasting materials, energy, efforts, money, and time while performing a task. In a more general sense, it is the ability to do things well, successfully, and without waste. In more mathematical or scientific terms, it signifies the level of performance that uses the least amount of inputs to achieve the highest amount of output. It often specifically comprises the capability of a specific application of effort to produce a specific outcome with a minimum amount or quantity of waste, expense, or unnecessary effort.Sickles, R., and Zelenyuk, V. (2019).Measurement of Productivity and Efficiency: Theory and Practice. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. . Efficiency refers to very different inputs and outputs in different fields and industries. In 2019, the European Commission said: "Resource efficiency means using the Earth's limited resources in a sustainable procent manner while minimising impacts on the envi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franco Modigliani
Franco Modigliani (; ; 18 June 1918 – 25 September 2003) was an Italian-American economist and the recipient of the 1985 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economics. He was a professor at University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign, Carnegie Mellon University, and MIT Sloan School of Management. Early life and education Modigliani was born on 18 June 1918 in Rome to the Jewish family of a pediatrician father and a voluntary social worker mother."Franco Modigliani" by Daniel B. Klein and Ryan Daza, inThe Ideological Migration of the Economics Laureates, '' Econ Journal Watch'', 10(3), September 2013, pp. 472–293 He entered university at the age of seventeen, enrolling in the faculty of Law at the Sapienza University of Rome.Parisi, Daniela (2005) "Five Italian Articles Written by the Young Franco Modigliani (1937–1938)", ''Rivista Internazional di Scienze Sociali'', 113(4), pp. 555–557 (in language) In his second year at Sapienza, his submission to a nationwide contest in econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenneth Arrow
Kenneth Joseph Arrow (August 23, 1921 – February 21, 2017) was an American economist, mathematician and political theorist. He received the John Bates Clark Medal in 1957, and the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1972, along with John Hicks. In economics, Arrow was a major figure in postwar neoclassical economic theory. Four of his students (Roger Myerson, Eric Maskin, John Harsanyi, and Michael Spence) went on to become Nobel laureates themselves. His contributions to social choice theory, notably his " impossibility theorem", and his work on general equilibrium analysis are significant. His work in many other areas of economics, including endogenous growth theory and the economics of information, was also foundational. Education and early career Arrow was born on August 23, 1921, in New York City. Arrow's mother, Lilian (Greenberg), was from Iași, Romania, and his father, Harry Arrow, was from nearby Podu Iloaiei. The family was of Romanian-Jewish desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centenarian
A centenarian is a person who has reached the age of 100. Because life expectancies at birth worldwide are well below 100, the term is invariably associated with longevity. The United Nations estimated that there were 316,600 living centenarians worldwide in 2012, and 573,000 in 2020, almost quadruple the 2000 estimate of 151,000. As world population and life expectancy continue to increase, the number of centenarians is expected to increase substantially in the 21st century. According to the Office of National Statistics in the United Kingdom, one-third of babies born in the country in 2013 are expected to live to 100. According to a 1998 United Nations demographic survey, Japan is expected to have 272,000 centenarians by 2050; other sources suggest that the number could be closer to 1 million. The incidence of centenarians in Japan was one per 3,522 people in 2008. In Japan, the population of centenarians is highly skewed towards females. Japan in fiscal year 2016 had 57,52 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
América Economía
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a single continent, the Americas or America is the 2nd largest continent by area after Asia, and is the 3rd largest continent by population. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. Along with their Lists of islands of the Americas, associated islands, the Americas cover 8% of Earth's total surface area and 28.4% of its land area. The topography is dominated by the American Cordillera, a long chain of mountains that runs the length of the west coast. The flatter eastern side of the Americas is dominated by large river basins, such as the Amazon basin, Amazon, St. Lawrence River–Great Lakes, Mississippi River System, Mississippi, and Río de la Plata Basin, La Plata basins. Since the Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milton Friedman
Milton Friedman (; July 31, 1912 – November 16, 2006) was an American economist and statistician who received the 1976 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his research on consumption analysis, monetary history and theory and the complexity of stabilization policy. With George Stigler, Friedman was among the intellectual leaders of the Chicago school of economics, a neoclassical school of economic thought associated with the faculty at the University of Chicago that rejected Keynesianism in favor of monetarism before shifting their focus to new classical macroeconomics in the mid-1970s. Several students, young professors and academics who were recruited or mentored by Friedman at Chicago went on to become leading economists, including Gary Becker, Robert Fogel, and Robert Lucas Jr. Friedman's challenges to what he called "naive Keynesian theory" began with his interpretation of consumption, which tracks how consumers spend. He introduced a theory w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |