|
Armīniya
Arminiya, also known as the Ostikanate of Arminiya (, ''Hayastani ostikanut'yun'') or the Emirate of Armenia (, ''imārat armīniya''), was a political and geographic designation given by the Muslim Arabs to the lands of Greater Armenia, Caucasian Iberia, and Caucasian Albania, following their conquest of these regions in the 7th century. Though the caliphs initially permitted an Armenian prince to represent the province of ''Arminiya'' in exchange for tribute and the Armenians' loyalty during times of war, Caliph Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan introduced direct Arab rule of the region, headed by an '' ostikan'' with his capital in Dvin. According to the historian Stephen H. Rapp in the third edition of the ''Encyclopaedia of Islam'': History Early period: the Arab conquest of Armenia The details of the early conquest of Armenia by the Arabs are uncertain, as the various Arabic sources conflict with the Greek and Armenian sources, both in chronology and in the details of the eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain. The rights and obligations of a vassal are called vassalage, while the rights and obligations of a suzerain are called suzerainty. The obligations of a vassal often included military support by knights in exchange for certain privileges, usually including land held as a tenant or fief. The term is also applied to similar arrangements in other feudal societies. In contrast, fealty (''fidelitas'') was sworn, unconditional loyalty to a monarch. European vassalage In fully developed vassalage, the lord and the vassal would take part in a commendation ceremony composed of two parts, the Homage (feudal), homage and the fealty, including the use of Christian sacraments to show its sacred importance. According to Eginhard's brief description, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
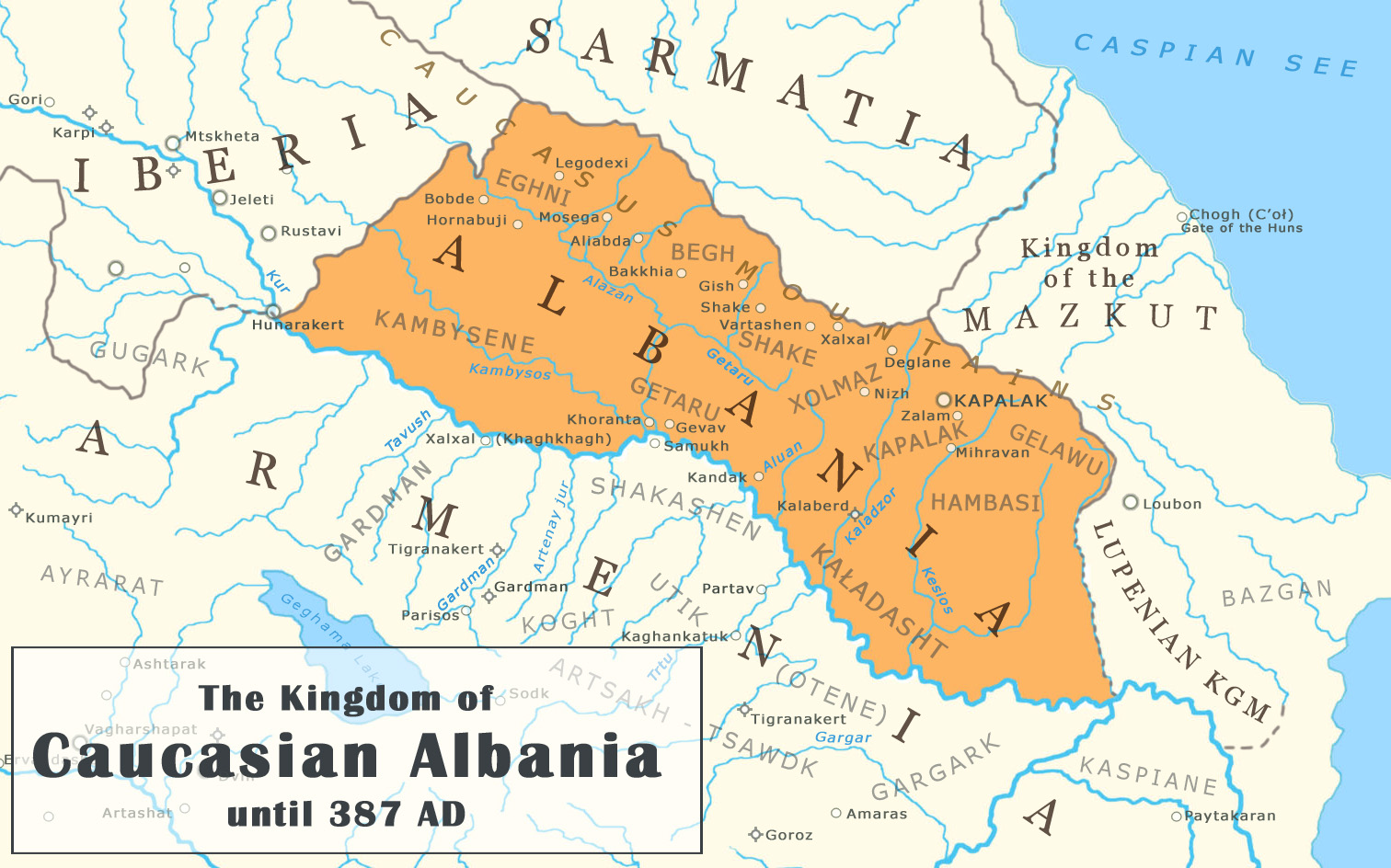
Caucasian Albania
Caucasian Albania is a modern exonym for a former state located in ancient times in the Caucasus, mostly in what is now Azerbaijan (where both of its capitals were located). The modern endonyms for the area are ''Aghwank'' and ''Aluank'', among the Udi people, who regard themselves as descended from the inhabitants of Caucasian Albania. However, its original endonym is unknown. The name Albania is derived from the Ancient Greek name and Latin , created from Greek sources that incorrectly translated the Armenian language. The prefix "Caucasian" is used to avoid confusion with Albania in the Balkans, which has no geographical or historical connections to Caucasian Albania. Little is known of the region's prehistory, including the origins of Caucasian Albania as a geographical and/or ethnolinguistic concept. In the 1st century BC and the 1st century AD, the area south of the Greater Caucasus and north of the Lesser Caucasus was divided between Caucasian Albania in the east, Kingd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslim Conquest Of Persia
As part of the early Muslim conquests, which were initiated by Muhammad in 622, the Rashidun Caliphate conquered the Sasanian Empire between 632 and 654. This event led to the decline of Zoroastrianism, which had been the official religion of Name of Iran, Persia (or Iran) since the time of the Achaemenid Empire. The persecution of Zoroastrians by the early Muslims during and after this conflict prompted many of them to flee eastward to Indian subcontinent, India, where they were Zoroastrianism in India, granted refuge by various kings. While Pre-Islamic Arabia, Arabia was experiencing the rise of Islam in the 7th century, Persia was struggling with unprecedented levels of political, social, economic, and military weakness; the Military of the Sasanian Empire, Sasanian army had greatly exhausted itself in the Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628. Following the execution of Sasanian shah Khosrow II in 628, Persia's internal political stability began deteriorating at a rapid pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Romanization (cultural), Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine the Great, Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I, Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslim Conquest Of The Levant
The Muslim conquest of the Levant (; ), or Arab conquest of Syria, was a 634–638 CE invasion of Byzantine Syria by the Rashidun Caliphate. A part of the wider Arab–Byzantine wars, the Levant was brought under Arab Muslim rule and developed into the provincial region of Bilad al-Sham. Clashes between the Arabs and Byzantines on the southern Levantine borders of the Byzantine Empire had occurred during the lifetime of Muhammad, with the Battle of Muʿtah in 629 CE. However, the actual conquest did not begin until 634, two years after Muhammad's death. It was led by the first two Rashidun caliphs who succeeded Muhammad: Abu Bakr and Umar ibn al-Khattab. During this time, Khalid ibn al-Walid was the most important leader of the Rashidun army. It was the first time since the collapse of the Neo-Babylonian Empire in 539 BCE that the region was ruled again by Semitic-speaking people, after centuries of Persian (Achaemenid Empire), and then Roman-Greek ( Macedonian Empire, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satrapy Of Armenia
The Satrapy of Armenia ( Old Persian: 𐎠𐎼𐎷𐎡𐎴 or 𐎠𐎼𐎷𐎡𐎴𐎹 ), a region controlled by the Orontid dynasty (570–201 BC), was one of the satrapies of the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BC that later became an independent kingdom. Its capitals were Tushpa and later Erebuni. History Orontid dynasty The Orontid dynasty, or known by their native name, Eruandid or Yervanduni, was an Iranian; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; hereditary dynasty that ruled the satrapy of Armenia, the successor state to the Iron Age kingdom of Urartu (Ararat). It is suggested that it held dynastic familial linkages to the ruling Achaemenid dynasty. Throughout their existence, the Orontids stressed their lineage from the Achaemenids to strengthen their political legitimacy. Members of the dynasty ruled Armenia intermittently during the period spanning from the 6th to at least the 2nd centuries BC, first as client kings or satraps of the Median and Achaemenid empires an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have conventionally been considered as a natural barrier between Europe and Asia, bisecting the Eurasian landmass. Mount Elbrus, Europe's highest mountain, is situated in the Western Caucasus area of Russia. On the southern side, the Lesser Caucasus includes the Javakheti Plateau and the Armenian highlands. The Caucasus is divided into the North Caucasus and South Caucasus, although the Western Caucasus also exists as a distinct geographic space within the North Caucasus. The Greater Caucasus mountain range in the north is mostly shared by Russia and Georgia as well as the northernmost parts of Azerbaijan. The Lesser Caucasus mountain range in the south is mostly located on the territory of sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the List of largest empires#Timeline of largest empires to date, largest empire by that point in history, spanning a total of . The empire spanned from the Balkans and ancient Egypt, Egypt in the west, most of West Asia, the majority of Central Asia to the northeast, and the Indus Basin, Indus Valley of South Asia to the southeast. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Medes, Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognised for its imposition of a succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power centered in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conquering the region of Parthia in Iran's northeast, then a satrapy (province) under Andragoras, who was rebelling against the Seleucid Empire. Mithridates I ( BC) greatly expanded the empire by seizing Media and Mesopotamia from the Seleucids. At its height, the Parthian Empire stretched from the northern reaches of the Euphrates, in what is now central-eastern Turkey, to present-day Afghanistan and western Pakistan. The empire, located on the Silk Road trade route between the Roman Empire in the Mediterranean Basin and the Han dynasty of China, became a center of trade and commerce. The Parthians largely adopted the art, architecture, religious beliefs, and regalia of their culturally heterogeneous empire, which encompassed Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranian peoples, Iranians"), was an List of monarchs of Iran, Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, the length of the Sasanian dynasty's reign over ancient Iran was second only to the directly preceding Arsacid dynasty of Parthia. Founded by Ardashir I, whose rise coincided with the decline of Arsacid influence in the face of both internal and external strife, the House of Sasan was highly determined to restore the legacy of the Achaemenid Empire by expanding and consolidating the Iranian nation's dominions. Most notably, after defeating Artabanus IV of Parthia during the Battle of Hormozdgan in 224, it began competing far more zealously with the neighbouring Roman Empire than the Arsacids had, thus sparking a new phase of the Roman–Iranian Wars. This effort by Ardashir's dynasty ultimately re-established Iran as a major power of late an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopaedia Of Islam
The ''Encyclopaedia of Islam'' (''EI'') is a reference work that facilitates the Islamic studies, academic study of Islam. It is published by Brill Publishers, Brill and provides information on various aspects of Islam and the Muslim world, Islamic world. It is considered to be the standard reference work in the field of Islamic studies. The first edition was published in 1913–1938, the second in 1954–2005, and the third was begun in 2007. Content According to Brill, the ''EI'' includes "articles on distinguished Muslims of every age and land, on tribes and dynasties, on the crafts and sciences, on political and religious institutions, on the geography, ethnography, flora and fauna of the various countries and on the history, topography and monuments of the major towns and cities. In its geographical and historical scope it encompasses the old Arabo-Islamic empire, the Islamic countries of Iran, Central Asia, the Indian sub-continent and Indonesia, the Ottoman Empire and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen H
Stephen or Steven is an English first name. It is particularly significant to Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is widely regarded as the first martyr (or " protomartyr") of the Christian Church. The name, in both the forms Stephen and Steven, is often shortened to Steve or Stevie. In English, the female version of the name is Stephanie. Many surnames are derived from the first name, including Stephens, Stevens, Stephenson, and Stevenson, all of which mean "Stephen's (son)". In modern times the name has sometimes been given with intentionally non-standard spelling, such as Stevan or Stevon. A common variant of the name used in English is Stephan ( ); related names that have found some currency or significance in English include Stefan (pronounced or in English), Esteban (often pronounced ), and the Shakespearean Stephano ( ). Origins The name "Stephen" (and its com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |