|
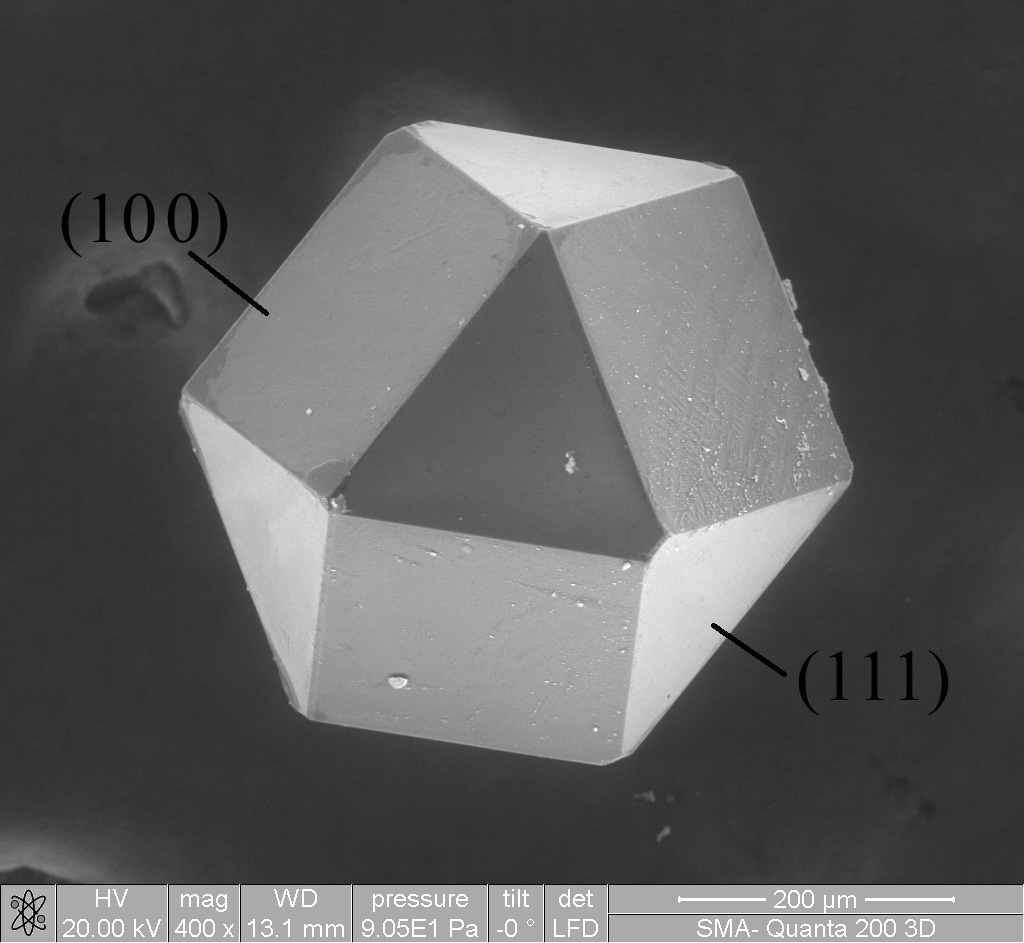
Armstrong Process
The Armstrong process is used to refine titanium. Its output is particle-sized dust which can be sprayed into pattern-molds.W.H.P. Bill, C.A. Blue, J.O. Kiggans, and J.D.K. Rivard, Powder Metallurgy and Solid State Processing of Armstrong Titanium and Titanium Alloy Powders, ITA Annual Conference 2007 It was patented in 1999. The output of this process has a "coral-like morphology", which differs from the traditional outputs like "spherical gas-atomized powder, mechanically crushed angular particles, or the titanium sponge morphology created during the Kroll process." History The Armstrong process was patented in 1999. In 2016 a paper by MacDonald et al. told that the Armstrong powder was produced directly from the reduction of Titanium tetrachloride "in a continuous liquid loop", and cost only "11-24 USD/kg", or roughly an order of magnitude higher than the price of steel. Description The reducing agent for the Armstrong process is sodium, which is liquefied and introduced in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium
Titanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in sea water, aqua regia, and chlorine. Titanium was discovered in Cornwall, Great Britain, by William Gregor in 1791 and was named by Martin Heinrich Klaproth after the Titans of Greek mythology. The element occurs within a number of minerals, principally rutile and ilmenite, which are widely distributed in the Earth's crust and lithosphere; it is found in almost all living things, as well as bodies of water, rocks, and soils. The metal is extracted from its principal mineral ores by the Kroll and Hunter processes. The most common compound, titanium dioxide (TiO2), is a popular photocatalyst and is used in the manufacture of white pigments. Other compounds include titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4), a component of smoke screens and cata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coral
Corals are colonial marine invertebrates within the subphylum Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact Colony (biology), colonies of many identical individual polyp (zoology), polyps. Coral species include the important Coral reef, reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and secrete calcium carbonate to form a hard skeleton. A coral "group" is a colony of very many cloning, genetically identical polyps. Each polyp is a sac-like animal typically only a few millimeters in diameter and a few centimeters in height. A set of tentacles surround a central mouth opening. Each polyp excretes an exoskeleton near the base. Over many generations, the colony thus creates a skeleton characteristic of the species which can measure up to several meters in size. Individual colonies grow by asexual reproduction of polyps. Corals also breed sexually by spawning: polyps of the same species release gametes simultaneously overnight, often around a full moon. Fertilized eggs form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology
Morphology, from the Greek and meaning "study of shape", may refer to: Disciplines *Morphology (archaeology), study of the shapes or forms of artifacts *Morphology (astronomy), study of the shape of astronomical objects such as nebulae, galaxies, or other extended objects *Morphology (biology), the study of the form or shape of an organism or part thereof *Morphology (folkloristics), the structure of narratives such as folk tales *Morphology (linguistics), the study of the structure and content of word forms * Morphology (sociology), the analysis of the typical social form taken by human relations and practices * Mathematical morphology, a theoretical model based on lattice theory, used for digital image processing * River morphology, the field of science dealing with changes of river platform * Urban morphology, study of the form, structure, formation and transformation of human settlements *Geomorphology, the study of landforms * Morphology (architecture and engineering), research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium Sponge
Titanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in sea water, aqua regia, and chlorine. Titanium was discovered in Cornwall, Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, by William Gregor in 1791 and was named by Martin Heinrich Klaproth after the Titan (mythology), Titans of Greek mythology. The element occurs within a number of minerals, principally rutile and ilmenite, which are widely distributed in the Earth's crust and lithosphere; it is found in almost all living things, as well as bodies of water, rocks, and soils. The metal is extracted from its principal mineral ores by the Kroll process, Kroll and Hunter process, Hunter processes. The most common compound, titanium dioxide (TiO2), is a popular photocatalysis, photocatalyst and is used in the manufacture of white pigments. Other compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kroll Process
The Kroll process is a pyrometallurgical industrial process used to produce metallic titanium from titanium tetrachloride. As of 2001 William Justin Kroll's process replaced the Hunter process for almost all commercial production. Process In the Kroll process, titanium tetrachloride is reduced by liquid magnesium to give titanium metal: : + 2 ->[825~^\mathrm] + 2 The reduction is conducted at 800–850 °C in a stainless steel retort. Complications result from partial reduction of the TiCl4, giving to the lower chlorides Titanium(II) chloride, TiCl2 and Titanium(III) chloride, TiCl3. The magnesium chloride, MgCl2 can be further refined back to magnesium. Appurtenant processes The resulting porous metallic titanium sponge is purified by Tank leaching, leaching or vacuum distillation. The sponge is crushed, and pressed before it is melted in a consumable electrode vacuum Electric arc furnace, arc furnace, "backfilled with pure gettered argon of a pressure high enough to avoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium Tetrachloride
Titanium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is an important intermediate in the production of titanium metal and the pigment titanium dioxide. is a volatile liquid. Upon contact with humid air, it forms thick clouds of titanium dioxide () and hydrochloric acid, a reaction that was formerly exploited for use in smoke machines. It is sometimes referred to as "tickle" or "tickle 4", as a phonetic representation of the symbols of its molecular formula (). Properties and structure is a dense, colourless liquid, although crude samples may be yellow or even red-brown. It is one of the rare transition metal halides that is a liquid at room temperature, being another example. This property reflects the fact that molecules of weakly self-associate. Most metal chlorides are polymers, wherein the chloride atoms bridge between the metals. Its melting point is similar to that of . has a "closed" electronic shell, with the same number of electrons as the nobl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. The free metal does not occur in nature and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the Abundance of elements in Earth's crust, sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl). Many salts of sodium are highly water-soluble: sodium ions have been Leaching (chemistry), leached by the action of water from the Earth, Earth's minerals over eons, and thus sodium and chlorine are the most common dissolved elements by weight in the oceans. Sodium was first isolated by Humphry Davy in 1807 by the electrolysis of sodium hydroxide. Among many other useful sodium compounds, sodium hydroxide (lye) is used in Soap, soap manufac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium Tetrachloride
Titanium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is an important intermediate in the production of titanium metal and the pigment titanium dioxide. is a volatile liquid. Upon contact with humid air, it forms thick clouds of titanium dioxide () and hydrochloric acid, a reaction that was formerly exploited for use in smoke machines. It is sometimes referred to as "tickle" or "tickle 4", as a phonetic representation of the symbols of its molecular formula (). Properties and structure is a dense, colourless liquid, although crude samples may be yellow or even red-brown. It is one of the rare transition metal halides that is a liquid at room temperature, being another example. This property reflects the fact that molecules of weakly self-associate. Most metal chlorides are polymers, wherein the chloride atoms bridge between the metals. Its melting point is similar to that of . has a "closed" electronic shell, with the same number of electrons as the nobl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Processes
Industrial processes are procedures involving chemical, physical, electrical, or mechanical steps to aid in the manufacturing of an item or items, usually carried out on a very large scale. Industrial processes are the key components of heavy industry. Chemical processes by main basic material Certain chemical process yield important basic materials for society, e.g., (cement, steel, aluminum, and fertilizer). However, these chemical reactions contribute to climate change by emitting carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, through chemical reactions, as well as through the combustion of fossil fuels to generate the high temperatures needed to reach the activation energies of the chemical reactions. Cement (the paste within concrete) * Calcination – Limestone, which is largely composed of fossilized calcium carbonate (CaCO3), breaks down at high temperatures into useable calcium oxide (CaO) and carbon dioxide gas (), which gets released as a by-product. This chemical reaction, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallurgical Processes
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys. Metallurgy encompasses both the science and the technology of metals, including the production of metals and the engineering of metal components used in products for both consumers and manufacturers. Metallurgy is distinct from the craft of metalworking. Metalworking relies on metallurgy in a similar manner to how medicine relies on medical science for technical advancement. A specialist practitioner of metallurgy is known as a metallurgist. The science of metallurgy is further subdivided into two broad categories: chemical metallurgy and physical metallurgy. Chemical metallurgy is chiefly concerned with the reduction and oxidation of metals, and the chemical performance of metals. Subjects of study in chemical metallurgy include mineral processing, the extraction of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium Processes
Titanium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in sea water, aqua regia, and chlorine. Titanium was discovered in Cornwall, Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, by William Gregor in 1791 and was named by Martin Heinrich Klaproth after the Titan (mythology), Titans of Greek mythology. The element occurs within a number of minerals, principally rutile and ilmenite, which are widely distributed in the Earth's crust and lithosphere; it is found in almost all living things, as well as bodies of water, rocks, and soils. The metal is extracted from its principal mineral ores by the Kroll process, Kroll and Hunter process, Hunter processes. The most common compound, titanium dioxide (TiO2), is a popular photocatalysis, photocatalyst and is used in the manufacture of white pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Materials Science
Materials science is an interdisciplinary field of researching and discovering materials. Materials engineering is an engineering field of finding uses for materials in other fields and industries. The intellectual origins of materials science stem from the Age of Enlightenment, when researchers began to use analytical thinking from chemistry, physics, and engineering to understand ancient, phenomenological observations in metallurgy and mineralogy. Materials science still incorporates elements of physics, chemistry, and engineering. As such, the field was long considered by academic institutions as a sub-field of these related fields. Beginning in the 1940s, materials science began to be more widely recognized as a specific and distinct field of science and engineering, and major technical universities around the world created dedicated schools for its study. Materials scientists emphasize understanding how the history of a material (''processing'') influences its struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |