|
Armintomyidae
''Armintomys'' is an extinct genus of rodent from North America related to jerboas and jumping mice. It is the only genus in the family Armintomyidae. It lived during the early Eocene, and is the oldest known example of a hystricomorphous zygomasseteric dentition. In addition, Armintomys is also the oldest known rodent that had an incisor enamel transition from pauciserial to uniserial. Its remains have only been found in the Wind River Basin in Wyoming, and could be found there during the species' existence on Earth. It was previously assumed that Armintomys belonged to the Dipodoidea family, but has since been understood to have been part of an early radiation of dipodoid rodent Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and Mandible, lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal specie ...s, but was not directly ancestral to any later dip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Dawson (paleontologist)
Mary R. Dawson (February 27, 1931 – November 29, 2020) was a vertebrate paleontologist and curator emeritus at the Carnegie Museum of Natural History in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Education and career Dawson was raised in Michigan, received her undergraduate degree from Michigan State University, and received her Ph.D. from the University of Kansas. She was Curator of Vertebrate Paleontology at the Carnegie Museum of Natural History in Pittsburgh from 1972 until she retired in 2003, including serving as chair of the Earth Sciences Division from 1973 to 1997. Research Dawson's research has focused on the evolution of mammals, especially of Cenozoic rodents and lagomorphs. She has also maintained an active research program at Ellesmere Island and other sites in the high Arctic which showed that tropical and subtropical animals lived inside the Arctic Circle during the exceptionally warm climates of the Paleogene geological period. Through this work, she and her collaborat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and recover. As a species' potential Range (biology), range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxon, Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the Fossil, fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. Over five billion species are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryotes globally, possibly many times more if microorganisms are included. Notable extinct animal species include Dinosaur, non-avian dinosaurs, Machairodontinae, saber-toothed cats, and mammoths. Through evolution, species arise through the process of specia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and Mandible, lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are native to all major land masses except for Antarctica, and several oceanic islands, though they have subsequently been introduced to most of these land masses by human activity. Rodents are extremely diverse in their ecology and lifestyles and can be found in almost every terrestrial habitat, including human-made environments. Species can be arboreal, fossorial (burrowing), saltatorial/ricochetal (leaping on their hind legs), or semiaquatic. However, all rodents share several morphological features, including having only a single upper and lower pair of ever-growing incisors. Well-known rodents include Mouse, mice, rats, squirrels, prairie dogs, porcupines, beavers, Cavia, guinea pigs, and hamsters. Once included wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean. The region includes Middle America (Americas), Middle America (comprising the Caribbean, Central America, and Mexico) and Northern America. North America covers an area of about , representing approximately 16.5% of Earth's land area and 4.8% of its total surface area. It is the third-largest continent by size after Asia and Africa, and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, fourth-largest continent by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. , North America's population was estimated as over 592 million people in list of sovereign states and dependent territories in North America, 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
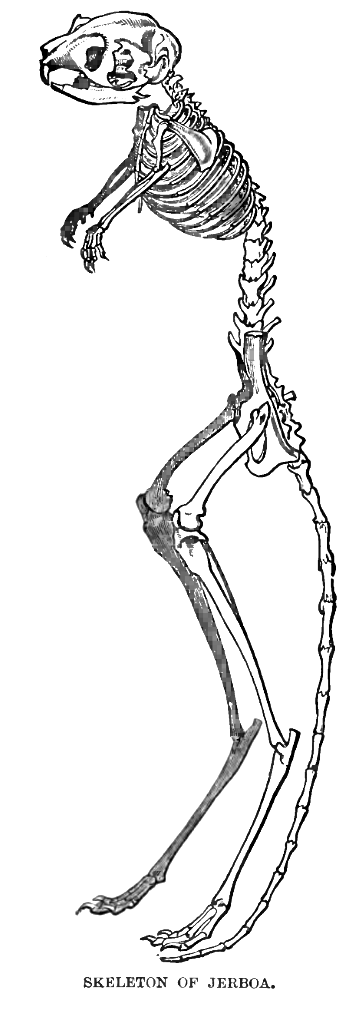
Jerboa
Jerboas () are the members of the family Dipodidae. They are hopping desert rodents found throughout North Africa and Asia. They tend to live in hot deserts. When chased, jerboas can run at up to . Some species are preyed on by little owls (''Athene noctua'') in central Asia. Most species of jerboas have excellent hearing that they use to avoid becoming the prey of nocturnal predators. The typical lifespan of a jerboa is around 2–3 years. Taxonomy Jerboas, as previously defined, were thought to be paraphyletic, with the jumping mice (Zapodidae) and birch mice (Sminthidae) also being classified in the family Dipodidae. However, phylogenetic analysis split all three as distinct families, leaving just the jerboas in Dipodidae and revealing them to be a monophyletic group. This animal has a body length (including the head) of between , with an additional of tail, which is always longer than the full body. Jerboa dental records reveal a slow increase in crown heights, which cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jumping Mouse
Zapodidae, the jumping mice, is a family of mouse-like rodents in North America and China. Although mouse-like in general appearance, these rodents are distinguished by their elongated hind limbs, and, typically, by the presence of four pairs of cheek-teeth in each jaw. There are five toes to all the feet, but the first in the fore-feet is rudimentary, and furnished with a flat nail. The tail makes up about 60% of its body length and is used to gain balance while jumping. The cheeks have pouches. The Sichuan jumping "yeti" mouse ('' Eozapus setchuanus'') from China can be identified by the ‘Y’ marking on its belly. Jumping mice live in wooded areas, grassy fields and alpine meadows. When disturbed, they can leap eight to ten feet at a time, diminishing to three to four as they widen the gap between them and any pursuer. They are nocturnal and generally live alone. Nests are often found in clefts of rocks, among timber, or in hollow trees. Typically, they will have two to thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''Ēṓs'', 'Eos, Dawn') and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch.See: *Letter from William Whewell to Charles Lyell dated 31 January 1831 in: * From p. 55: "The period next antecedent we shall call Eocene, from ήως, aurora, and χαινος, recens, because the extremely small proportion of living species contained in these strata, indicates what may be considered the first commencement, or ''dawn'', of the existing state of the animate creation." The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isoto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygomasseteric System
The zygomasseteric system (or zygomasseteric structure) refers to the anatomical arrangement of the masseter muscle and the zygomatic arch (cheek bone) in the skulls of Rodent, rodents. This system plays a crucial role in the diverse chewing mechanics observed across rodent species. The zygomatic arch is modified to accommodate the masseter muscle, a primary muscle responsible for jaw movement. The masseter muscle itself is often divided into superficial, lateral, and medial components, allowing for a wide range of jaw motion, particularly the anteroposterior or propalinal movement (front-to-back chewing motion) characteristic of rodents. Variations in the structure of the zygomatic arch and the masseter muscle's insertion points have led to the classification of rodents into four main zygomasseteric types: protrogomorphous, sciuromorphous, hystricomorphous, and myomorphous, reflecting adaptations to different dietary niches and chewing strategies. Protrogomorphy The members of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
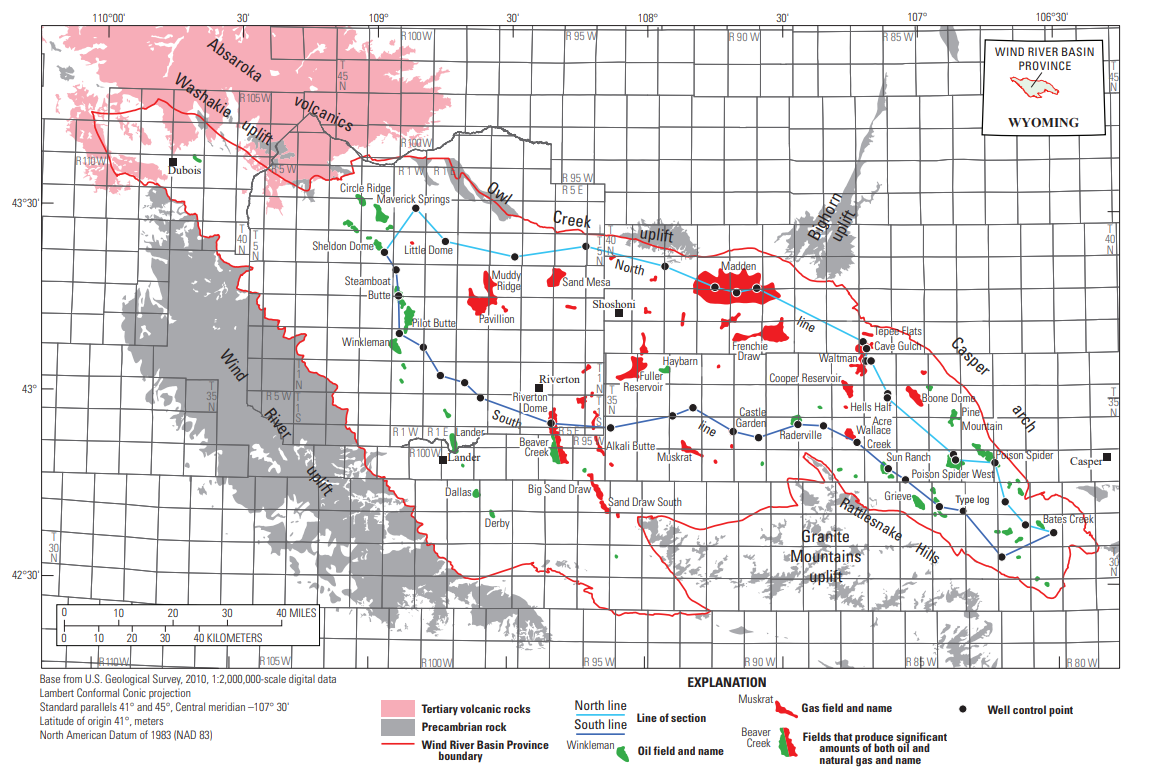
Wind River Basin
The Wind River Basin is a semi-arid intermontane foreland basin in central Wyoming, United States. It is bounded by Laramide orogeny, Laramide uplifts on all sides. On the west is the Wind River Range and on the North are the Absaroka Range and the Owl Creek Mountains. The Casper Arch separates the Wind River from the Powder River Basin to the east and the Sweetwater Uplift (Granite Mountains (Wyoming), Granite Range) lies to the south. The basin contains a sequence of of predominantly marine sediments deposited during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic Eras. During the Laramide over of Eocene lake, lacustrine and fluvial sediments were deposited within the basin. Following the Eocene an additional of sediments were deposited before, and as the basin was uplifted in the late Tertiary period, Tertiary. The geological formations within the basin are significant producers of petroleum and natural gas. The basin contains over 60 oil and gas fields mostly as structural traps within sevent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wyoming
Wyoming ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States, Western United States. It borders Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho to the west, Utah to the southwest, and Colorado to the south. With an estimated population of 587,618 as of 2024, Wyoming is the List of U.S. states and territories by population, least populous state despite being the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 10th largest by area, and it has the List of U.S. states by population density, second-lowest population density after Alaska. The List of capitals in the United States, state capital and List of municipalities in Wyoming, most populous city is Cheyenne, Wyoming, Cheyenne, which had a population of 65,132 in 2020. Wyoming's western half consists mostly of the ranges and rangelands of the Rocky Mountains; its eastern half consists of high-elevation prairie, and is referred to as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering Water distribution on Earth, 70.8% of Earth's crust. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most of which is located in the form of continental landmasses within Earth's land hemisphere. Most of Earth's land is at least somewhat humid and covered by vegetation, while large Ice sheet, sheets of ice at Polar regions of Earth, Earth's polar polar desert, deserts retain more water than Earth's groundwater, lakes, rivers, and Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water combined. Earth's crust consists of slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's outer core, Earth has a liquid outer core that generates a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipodoidea
Dipodoidea is a Superfamily (biology), superfamily of Rodent, rodents, also known as dipodoids, found across the Northern Hemisphere. This superfamily includes over 50 species among the 16 genera in 3 families. They include the Jerboa, jerboas (family Dipodidae), Jumping mouse, jumping mice (family Zapodidae), and Birch mouse, birch mice (family Sminthidae). Different species are found in grassland, Desert, deserts, and Forest, forests. They are all capable of saltation (jumping while in a bipedal stance), a feature that is most highly evolved in the desert-dwelling jerboas. Taxonomy Formerly, Dipodoidea contained only a single large family, Dipodidae, which contained Jerboa, jerboas, Zapodidae, jumping mice, and Birch mouse, birch mice as subfamilies. However, phylogenetic evidence found all three to be distinct families from one another, and thus they were split into three different families within Dipodoidea. Characteristics Dipodoids are small to medium-sized rodents, ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |