|
Armesocarb
Armesocarb (developmental code name MLR-1019), also known as (''R'')-mesocarb or L-mesocarb, is a selective atypical dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DRI). It is currently under development for the treatment of Parkinson's disease and sleep disorders. It is the active (''R'')-enantiomer of the formerly clinically used stimulant-like drug mesocarb (MLR-1017; brand name Sydnocarb). Pharmacology Mesocarb is known to be a highly selective DRI. However, in 2021, it was discovered that mesocarb is not a conventional DRI but acts as a dopamine transporter (DAT) allosteric modulator or non-competitive inhibitor. In accordance with its nature as an atypical DAT blocker, the drug exhibits atypical effects compared to conventional DRIs. For example, mesocarb shows greater antiparkinsonian activity in animals compared to other DRIs. Mesocarb has wakefulness-promoting effects in animals. Armesocarb, as the active enantiomer of mesocarb, shows greater therapeutic potency than the racemic fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Russian Drugs
This page is a list of Russian drugs, or drugs that were developed in Russia, the former Soviet Union, and/or post-Soviet countries. Many Russian drugs are indicated for enhancing physical, mental, and/or cognitive performance, including drugs described as nootropics or cognitive enhancers, drugs combatting fatigue, so-called adaptogens or actoprotectors, and others. There have been concerns about Russian drugs in the Western world owing to allegedly lower standards of medical evidence in Russia compared to the West, for instance in the case of the Russian COVID vaccine Sputnik V. Some Russian drugs have been attempted to be repurposed and developed by pharmaceutical companies for use in the West, such as phenylpiracetam (fonturacetam), (''R'')-phenylpiracetam (MRZ-9547), Noopept (omberacetam), and armesocarb (the active enantiomer of mesocarb). List of Russian drugs * Aceclidine (Glaucostat, Glaunorm, Glaudin) – parasympathomimetic miotic * Acetomepregenol (ACM; mepre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopamine Reuptake Inhibitor
A dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DRI) is a class of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor of the monoamine neurotransmitter dopamine by blocking the action of the dopamine transporter (DAT). Reuptake inhibition is achieved when extracellular dopamine not absorbed by the postsynaptic neuron is blocked from re-entering the presynaptic neuron. This results in increased extracellular concentrations of dopamine and increase in dopaminergic neurotransmission. DRIs are used in the treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy for their psychostimulant effects, and in the treatment of obesity and binge eating disorder for their appetite suppressant effects. They are sometimes used as antidepressants in the treatment of mood disorders, but their use as antidepressants is limited given that strong DRIs have a high abuse potential and legal restrictions on their use. Lack of dopamine reuptake and the increase in extracellular levels of dopamine have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preclinical Research
In drug development, preclinical development, also termed preclinical studies or nonclinical studies, is a stage of research that begins before clinical trials (testing in humans) and during which important feasibility, iterative testing and drug safety data are collected, typically in laboratory animals. The main goals of preclinical studies are to determine a starting, safe dose for first-in-human study and assess potential toxicity of the product, which typically include new medical devices, prescription drugs, and diagnostics. Companies use stylized statistics to illustrate the risks in preclinical research, such as that on average, only one in every 5,000 compounds that enters drug discovery to the stage of preclinical development becomes an approved drug. Types of preclinical research Each class of product may undergo different types of preclinical research. For instance, drugs may undergo pharmacodynamics (what the drug does to the body) (PD), pharmacokinetics (wha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stimulants
Stimulants (also often referred to as psychostimulants or colloquially as uppers) is an overarching term that covers many drugs including those that increase activity of the central nervous system and the body, drugs that are pleasurable and invigorating, or drugs that have sympathomimetic effects. Stimulants are widely used throughout the world as prescription medicines as well as without a prescription (either legally or illicitly) as performance-enhancing or recreational drugs. Among narcotics, stimulants produce a noticeable crash or '' comedown'' at the end of their effects. The most frequently prescribed stimulants as of 2013 were lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse), methylphenidate (Ritalin), and amphetamine (Adderall). It was estimated in 2015 that the percentage of the world population that had used cocaine during a year was 0.4%. For the category "amphetamines and prescription stimulants" (with "amphetamines" including amphetamine and methamphetamine) the value was 0.7%, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxadiazoles
Oxadiazoles are a class of heterocyclic aromatic chemical compound of the azole family; with the molecular formula C2H2N2O. There are four isomers of oxadiazole: File:1,2,3-oxadiazole.svg, 1,2,3-oxadiazole File:1,2,4-oxadiazole.svg, 1,2,4-oxadiazole File:1,2,5-oxadiazole.svg, 1,2,5-oxadiazole(furazan) File:1,3,4-oxadiazole.svg, 1,3,4-oxadiazole 1,2,4-Oxadiazole, 1,2,5-oxadiazole, and 1,3,4-oxadiazole are all known and appear in a variety of pharmaceutical drugs including raltegravir, butalamine, fasiplon, oxolamine, and pleconaril. The 1,2,3-isomer is unstable and ring-opens to form the diazoketone tautomer; however, it does exist within the unusual sydnone motif. In 2018, a compound called bis(1,2,4-oxadiazole)bis(methylene) dinitrate which might have a 1.5 times the power of TNT was developed at the United States Army Research Laboratory (ARL) working with the Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos National Laboratory (often shortened as Los Alamos and LA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imines
In organic chemistry, an imine ( or ) is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond (). The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bonds. Imines are common in synthetic and naturally occurring compounds and they participate in many reactions. Structure For ketimines and aldimines, respectively, the five core atoms (C2C=NX and C(H)C=NX, X = H or C) are coplanar. Planarity results from the sp2-hybridization of the mutually double-bonded carbon and the nitrogen atoms. The C=N distance is 1.29-1.31 Å for nonconjugated imines and 1.35 Å for conjugated imines. By contrast, C-N distances in amines and nitriles are 1.47 and 1.16 Å, respectively. Rotation about the C=N bond is slow. Using NMR spectroscopy, both E- and Z-isomers of aldimines have been detected. Owing to steric effects, the E isomer is favored. Nomenclature and classification The term "imine" was coined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Drugs
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a particular factor is manipulated. Experiments vary greatly in goal and scale but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results. There also exist natural experimental studies. A child may carry out basic experiments to understand how things fall to the ground, while teams of scientists may take years of systematic investigation to advance their understanding of a phenomenon. Experiments and other types of hands-on activities are very important to student learning in the science classroom. Experiments can raise test scores and help a student become more engaged and interested in the material they are learning, especially when used over time. Experiments can vary from personal and informal natural comparisons ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enantiopure Drugs
An enantiopure drug is a pharmaceutical that is available in one specific enantiomeric form. Most biological molecules (proteins, sugars, etc.) are present in only one of many chiral forms, so different enantiomers of a chiral drug molecule bind differently (or not at all) to target receptors. Chirality can be observed when the geometric properties of an object is not superimposable with its mirror image. Two forms of a molecule are formed (both mirror images) from a chiral carbon, these two forms are called enantiomers. One enantiomer of a drug may have a desired beneficial effect while the other may cause serious and undesired side effects, or sometimes even beneficial but entirely different effects. The desired enantiomer is known as an eutomer while the undesired enantiomer is known as the distomer. When equal amounts of both enantiomers are found in a mixture, the mixture is known as a racemic mixture. If a mixture for a drug does not have a 1:1 ratio of its enantiomers it is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopamine Reuptake Inhibitors
A dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DRI) is a class of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor of the monoamine neurotransmitter dopamine by blocking the action of the dopamine transporter (DAT). Reuptake inhibition is achieved when extracellular dopamine not absorbed by the postsynaptic neuron is blocked from re-entering the presynaptic neuron. This results in increased extracellular concentrations of dopamine and increase in dopaminergic neurotransmission. DRIs are used in the treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy for their psychostimulant effects, and in the treatment of obesity and binge eating disorder for their appetite suppressant effects. They are sometimes used as antidepressants in the treatment of mood disorders, but their use as antidepressants is limited given that strong DRIs have a high abuse potential and legal restrictions on their use. Lack of dopamine reuptake and the increase in extracellular levels of dopamine have b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
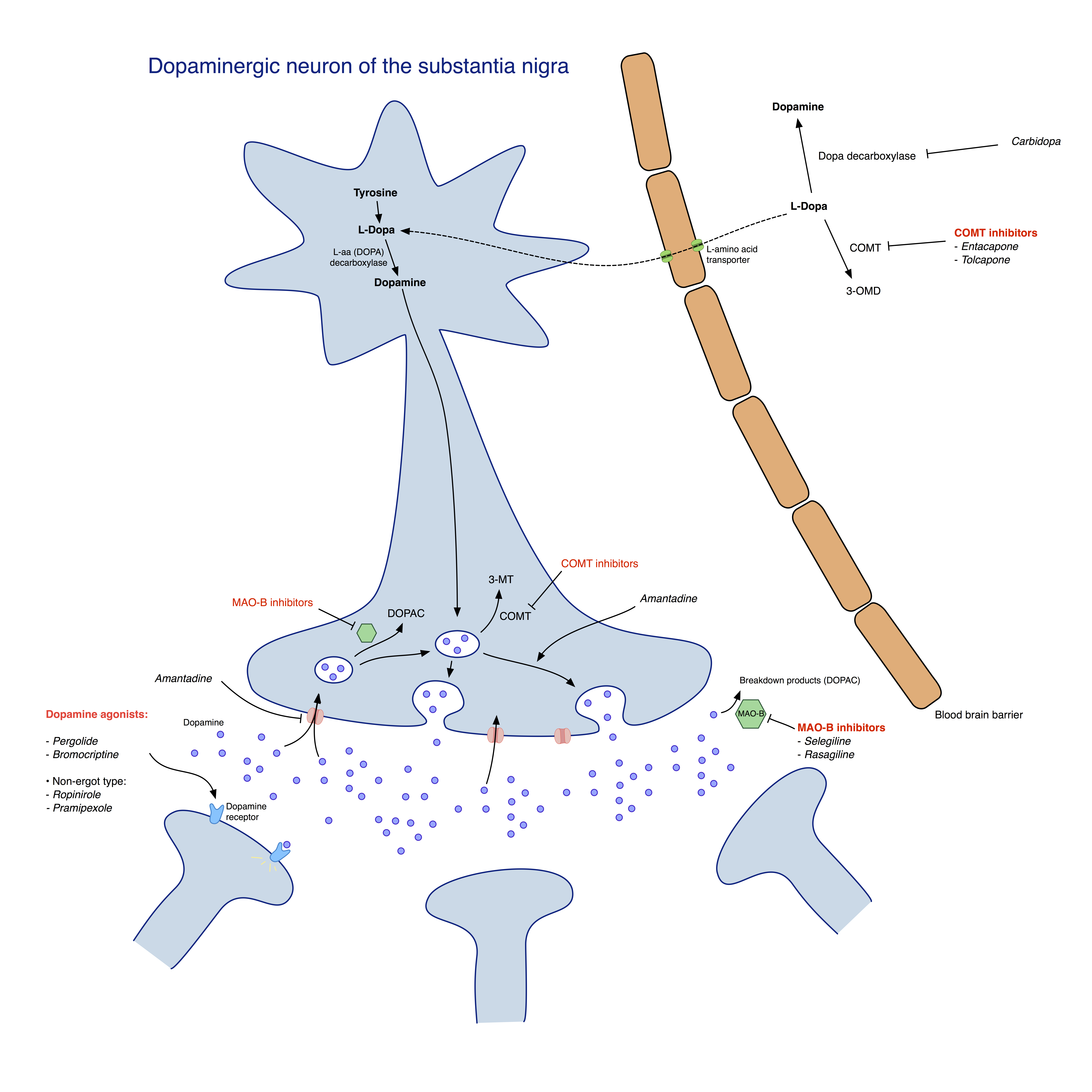
Antiparkinsonian Agents
In the management of Parkinson's disease, due to the chronic nature of Parkinson's disease (PD), a broad-based program is needed that includes patient and family education, support-group services, general wellness maintenance, exercise, and nutrition. At present, no cure for the disease is known, but medications or surgery can provide relief from the symptoms. While many medications treat Parkinson's, none actually reverses the effects of the disease. Furthermore, the gold-standard treatment varies with the disease state. People with Parkinson's, therefore, often must take a variety of medications to manage the disease's symptoms. Several medications currently in development seek to better address motor fluctuations and nonmotor symptoms of PD. However, none is yet on the market with specific approval to treat Parkinson's. Medication The main families of drugs useful for treating motor symptoms are levodopa, dopamine agonists, and MAO-B inhibitors. The most commonly used treatme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antidyskinetic Agents
Dyskinesia refers to a category of movement disorders that are characterized by involuntary muscle movements, including movements similar to tics or chorea and diminished voluntary movements. Dyskinesia can be anything from a slight tremor of the hands to an uncontrollable movement of the upper body or lower extremities. Discoordination can also occur internally especially with the respiratory muscles and it often goes unrecognized. Dyskinesia is a symptom of several medical disorders that are distinguished by their underlying cause. Types Medication-induced dyskinesias Acute dystonia is a sustained muscle contraction that sometimes appears soon after administration of antipsychotic medications. Any muscle in the body may be affected, including the jaw, tongue, throat, arms, or legs. When the throat muscles are involved, this type of dystonia is called an acute laryngospasm and is a medical emergency because it can impair breathing. Older antipsychotics such as Haloperidol or F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anilides
Anilides (or phenylamides) are a class of chemical compounds, which are amide derivatives of aniline. Preparation Aniline reacts with acyl chloride In organic chemistry, an acyl chloride (or acid chloride) is an organic compound with the functional group . Their formula is usually written , where R is a side chain. They are reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids (). A specific example ...s or carboxylic anhydrides to give anilides. For example, reaction of aniline with acetyl chloride provides acetanilide (CH3-CO-NH-C6H5). At high temperatures, aniline and carboxylic acids react to give anilides. Uses * Herbicides * Fungicides - Oxycarboxin, Carboxin References External links * {{organic-chemistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |