|
Arlit Hostage Crisis
Arlit is an industrial town and capital of the Arlit Department of the Agadez Region of northern-central Niger, built between the Sahara Desert and the eastern edge of the Aïr Mountains. It is 200 kilometers south by road from the border with Algeria. As of 2012, the commune had a total population of 79,725 people. Uranium industry Founded in 1969 following the discovery of uranium, it has grown around the mining industry, developed by the French government. Two large uranium mines, at Arlit and nearby Akouta, are exploited by open top strip mining. One open-pit mine was built in 1971 by the National Mining Company of Niger, SOMAIR. The second open-pit mine, as well as a third underground mine, was built by the French Compagnie Minière d'Akouta (or COMINAK). All the ore from both is now processed and transported by a French company Orano Cycle, a holding of the Orano group, itself a state-owned operation of the French ''Commissariat à l'énergie atomique'' (CEA). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 205 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, two United Nations General Assembly observers#Current non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and ten other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and one UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (15 states, of which there are six UN member states, one UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and eight de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (two states, both in associated state, free association with New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium Mining
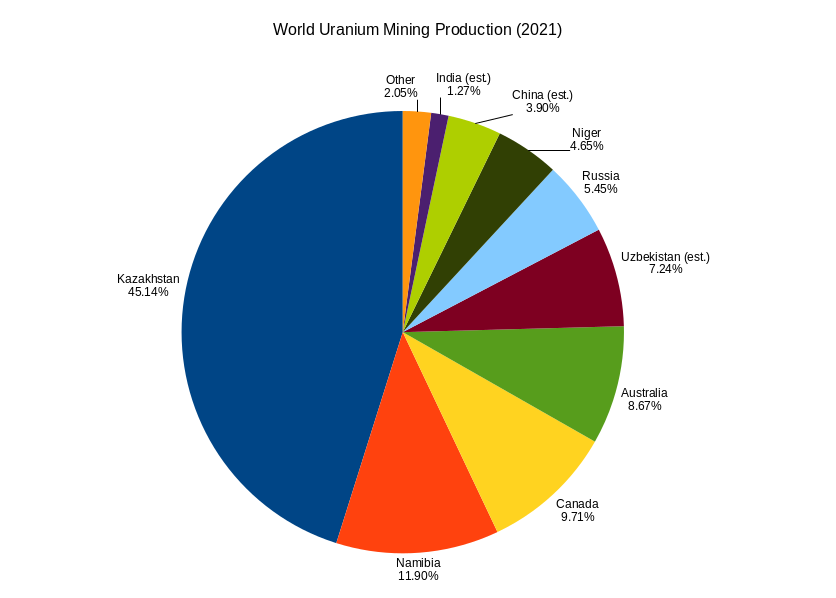
Uranium mining is the process of extraction of uranium ore from the earth. Over 50,000 tons of uranium were produced in 2019. Kazakhstan, Canada, and Australia were the top three uranium producers, respectively, and together account for 68% of world production. Other countries producing more than 1,000 tons per year included Namibia, Niger, Russia, Uzbekistan and China. Nearly all of the world's mined uranium is used to power nuclear power plants. Historically uranium was also used in applications such as uranium glass or ferrouranium but those applications have declined due to the radioactivity and toxicity of uranium and are nowadays mostly supplied with a plentiful cheap supply of depleted uranium which is also used in Armour-piercing ammunition, uranium ammunition. In addition to being cheaper, depleted uranium is also less radioactive due to a lower content of short-lived and than natural uranium. Uranium is mined by in-situ leaching (57% of world production) or by convent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Disease
In economics, Dutch disease is the apparent causal relationship between the increase in the economic development of a specific sector (for example natural resources) and a decline in other sectors (like the manufacturing sector or agriculture). The term was coined in 1977 by ''The Economist'' to describe the decline of the manufacturing sector in the Netherlands after the discovery of the large Groningen natural gas field in 1959. The presumed mechanism is that while revenues increase in a growing sector (or inflows of foreign aid), the given economy's currency becomes stronger (" appreciates") compared to foreign currencies (manifested in the exchange rate). This results in the country's other exports becoming more expensive for other countries to buy, while imports become cheaper, altogether rendering those sectors less competitive. While it most often refers to natural resource discovery, it can also refer to "any development that results in a large inflow of foreign cur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuareg Rebellion (1990–1995)
From 1990 to 1995, a rebellion by various Tuareg groups took place in Niger and Mali, with the aim of achieving autonomy or forming their own nation-state. The insurgency occurred in a period following the regional famine of the 1980s and subsequent refugee crisis, and a time of generalised political repression and crisis in both nations. The conflict is one in a series of Tuareg-based insurgencies in the colonial and post-colonial history of these nations. In Niger, it is also referred to as the Second or Third Tuareg Rebellion, a reference to the pre-independence rebellions of Ag Mohammed Wau Teguidda Kaocen of the Aïr Mountains in 1914 (Kaocen Revolt) and the rising of Firhoun of Ikazkazan in 1911, who reappeared in Mali in 1916. In fact, the nomadic Tuareg confederations have come into sporadic conflict with the sedentary communities of the region ever since they migrated from the Maghreb into the Sahel region between the 7th and 14th centuries CE. Some (but not all) Tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanty Town
A shanty town, squatter area, squatter settlement, or squatter camp is a settlement of improvised buildings known as shanties or shacks, typically made of materials such as mud and wood, or from cheap building materials such as corrugated iron sheets. A typical shanty town is squatted and, at least initially, lacks adequate infrastructure, including proper sanitation, safe water supply, electricity and street drainage. Over time, shanty towns may develop their infrastructure and even change into middle class neighbourhoods. They can be small informal settlements or they can house millions of people. First used in North America to designate a shack, the term ''shanty'' is likely derived from French ''chantier'' (construction site and associated low-level workers' quarters), or alternatively from Scottish Gaelic ''sean'' () meaning 'old' and ''taigh'' () meaning 'house old. Globally, some of the largest shanty towns are Ciudad Neza in Mexico, Orangi in Pakistan and Dharavi i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In-Gall
In-Gall (var. In Gall, I-n-Gall, In-Gal, Ingal, Ingall) is a department, commune and town in the Agadez Region of northeast Niger, with a year-round population of less than 500. Known for its oasis and salt flats, In-Gall is the gathering point for the Cure Salee festival of Tuareg and Wodaabe pastoralists to celebrate the end of the rainy season each September. During the festival, In-Gall's population grows to several thousand nomads, officials, and tourists. As of 2011, the commune had a total population of 47,170 people. In-Gall had been a stop on the main roads between the capital of Niger, Niamey (600 km to the southwest), and the mining town of Arlit (200 km to the northeast, 150 km from the Algerian border) or the provincial capital Agadez (100 km to the east). In the 1970s, the main road was repaved to transport uranium from the French-owned mines in Arlit, but the new road bypassed In-Gall, ending its use as a waystation. Since then, its popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bénin
Benin, officially the Republic of Benin, is a country in West Africa. It was formerly known as Dahomey. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north-west, and Niger to the north-east. The majority of its population lives on the southern coastline of the Bight of Benin, part of the Gulf of Guinea in the northernmost tropical portion of the Atlantic Ocean. The capital is Porto-Novo, and the seat of government is in Cotonou, the most populous city and economic capital. Benin covers an area of , and its population in was estimated to be approximately million. It is a tropical country with an economy heavily dependent on agriculture and is an exporter of palm oil and cotton. From the 17th to the 19th century, political entities in the area included the Kingdom of Dahomey, the city-state of Porto Novo, and other states to the north. This region was referred to as the Slave Coast of West Africa from the early 17th century due to the high number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotonou
Cotonou (; ) is the largest city in Benin. Its official population count was 679,012 inhabitants in 2012; however, over two million people live in the larger urban area. The urban area continues to expand, notably toward the west. The city lies in the southeast of the country, between the Atlantic Ocean and Lake Nokoué. Cotonou is the seat of government in Benin, although Porto-Novo is the official capital. History The name "Cotonou" means "by the river of death" in the Fon language.Butler, Stuart (2019) ''Bradt Travel Guide - Benin'', pgs. 74-91 At the beginning of the 19th century, Cotonou (then spelled "Kutonou") was a small fishing village, and is thought to have been formally founded by King Ghezo of Dahomey in 1830. It grew as a centre for the History of slavery, slave trade, and later palm oil and cotton. In 1851 the French Second Republic made a treaty with King Ghezo that allowed them to establish a trading post at Cotonou. During the reign of King Glele (1858–89), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Canard Enchaîné
(; English: "The Chained Duck" or "The Chained Paper", as is French slang meaning "newspaper") is a satirical weekly newspaper in France. Its headquarters is in Paris. Founded in 1915 during World War I, it features investigative journalism and leaks from sources inside the French government, the French political world and the French business world, as well as many jokes and cartoons. ''Le Canard enchaîné'' does not accept any advertisements and is privately owned, mostly by its own employees. Presentation Early history The name is a reference to Radical Georges Clemenceau's newspaper ''L'homme libre'' (‘The Free Man’), which was forced to close by government censorship and reacted upon its reopening by changing its name to ''L'homme enchaîné'' ("The Chained-up Man"); ''Le Canard enchaîné'' means ‘The chained-up duck’ but ''canard'' (duck) is also French slang for ‘newspaper’; it was also a reference to French journals published by soldiers during World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
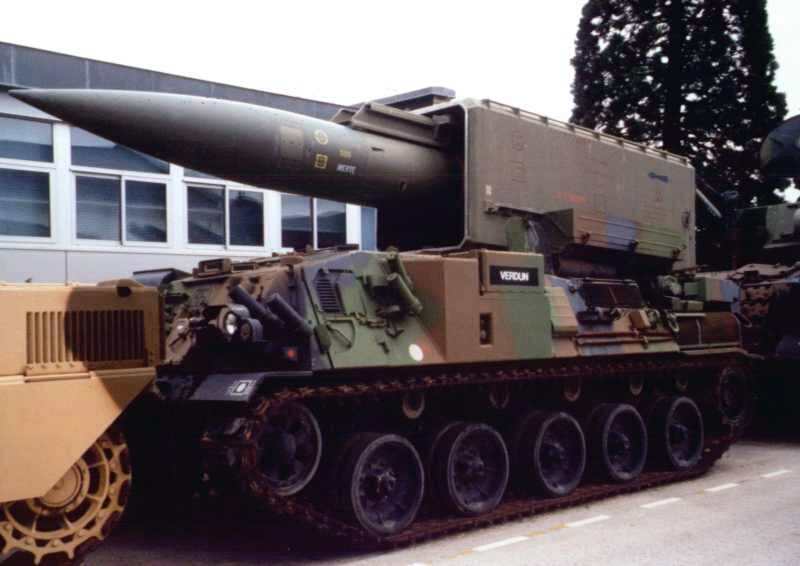
France And Nuclear Weapons
The ''Force de dissuasion'' (), known as the ''Force de frappe'' ('Strike Force') prior to 1961,Gunston, Bill. Bombers of the West. New York: Charles Scribner's and Sons; 1973. p104 is the French nuclear deterrence force. The ''Force de dissuasion'' used to be a triad of air-, sea- and land-based nuclear weapons intended for ''dissuasion'', the French term for deterrence. Following the end of the Cold War, France decommissioned all its land-based nuclear missiles, thus the ''Force de dissuasion'' today only incorporates an air- and sea-based arsenal. The French Nuclear Force, part of the French military, is the fourth largest nuclear-weapons force in the world, after the nuclear triads of the United States, the Russian Federation and the People's Republic of China. On 27 January 1996, France conducted its last nuclear test in the South Pacific and then signed the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT) in September 1996. In March 2008, French President Nicolas Sarkozy c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |