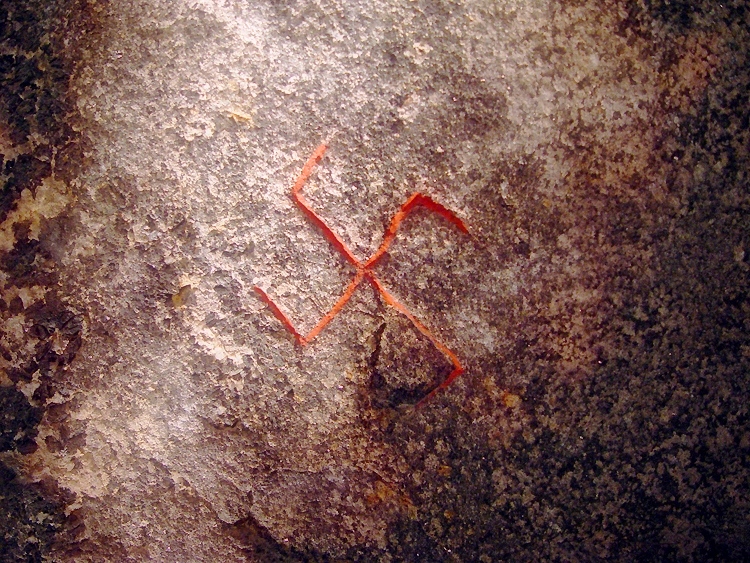|
Arkaim
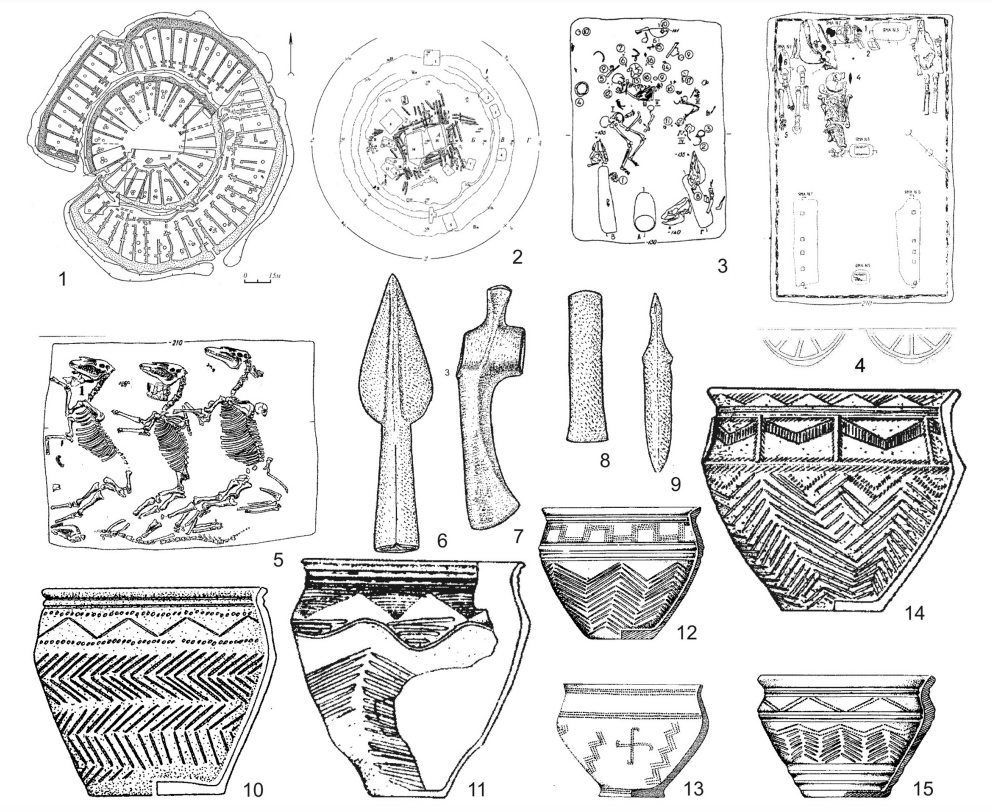
Arkaim () is a fortified archaeological site, dated to 2150-1650 BCE, belonging to the Sintashta culture, situated in the steppe of the Southern Urals, north-northwest of the village of Amursky and east-southeast of the village of Alexandrovsky in the Chelyabinsk Oblast of Russia, just north of the border with Kazakhstan. It was discovered in 1987 by a team of archaeologists which later came under the leadership of Gennady Zdanovich. The realization of its importance unprecedentedly forestalled the planned flooding of the area for a reservoir. The construction of Arkaim is attributed to the early Proto-Indo-Iranian-speakers of the Sintashta culture, which some scholars believe represents the proto-Indo-Iranians before their split into different groups and migration to Central Asia and from there to the Iranian plateau, Indian subcontinent and other parts of Eurasia. Discovery and salvage of the site In the summer of 1987 a team of archaeologists headed by Gennady Zdanovich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
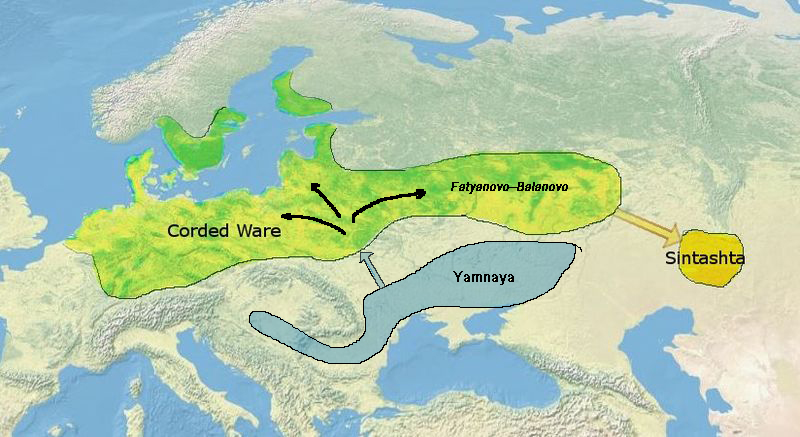
Sintashta Culture
The Sintashta culture is a Middle Bronze Age archaeological culture of the Southern Urals, dated to the period 2200–1900 BCE. It is the first phase of the Sintashta–Petrovka complex, –1750 BCE. The culture is named after the Sintashta archaeological site, in Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, and spreads through Orenburg Oblast, Bashkortostan, and Northern Kazakhstan. Widely regarded as the origin of the Indo-Iranian languages, whose speakers originally referred to themselves as the ''Aryan''s'','' the Sintashta culture is thought to represent an eastward migration of peoples from the Corded Ware culture. The earliest known chariots have been found in Sintashta burials, and the culture is considered a strong candidate for the origin of the technology, which spread throughout the Old World and played an important role in ancient warfare. Sintashta settlements are also remarkable for the intensity of copper mining and bronze metallurgy carried out there, which is unusual f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gennady Zdanovich
Gennadii Borisovich Zdanovich (; 4 October 1938 – 19 November 2020) was a Russian archaeologist based at the historical site of Arkaim, Chelyabinsk, Russia. Zdanovich led the excavation campaign at Arkaim in the Southern Urals. In the archaeology of the Sintashta culture The Sintashta culture is a Middle Bronze Age archaeological culture of the Southern Urals, dated to the period 2200–1900 BCE. It is the first phase of the Sintashta–Petrovka complex, –1750 BCE. The culture is named after the Sintashta ..., he introduced the term "the Country of Towns".Andrey Bersenev, Andrey Epimakhov and Dmitry ZdanovichSINTASHTA BOW OF THE BRONZE AGE OF THE SOUTH TRANS-URALS, RUSSIA in: "Bronze Age Warfare: Manufacture and Use of Weaponry", 2011, He was a proponent of an approach which seeks to unify archaeological and ecological approaches to the environment. Zdanovich died on 19 November 2020. References 2020 deaths 1938 births 20th-century Russian archaeologists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders of Russia, land borders with fourteen countries. Russia is the List of European countries by population, most populous country in Europe and the List of countries and dependencies by population, ninth-most populous country in the world. It is a Urbanization by sovereign state, highly urbanised country, with sixteen of its urban areas having more than 1 million inhabitants. Moscow, the List of metropolitan areas in Europe, most populous metropolitan area in Europe, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, while Saint Petersburg is its second-largest city and Society and culture in Saint Petersburg, cultural centre. Human settlement on the territory of modern Russia dates back to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Iranians
The Indo-Iranian peoples, also known as Ā́rya or Aryans from their self-designation, were a group of Indo-European speaking peoples who brought the Indo-Iranian languages to parts of Europe, Central Asia, and South Asia in waves from the first part of the 2nd millennium BC onwards. They eventually branched out into the Iranian peoples and Indo-Aryan peoples. Nomenclature The term '' Aryan'' has long been used to denote the ''Indo-Iranians'', because ''Ā́rya'' was the self-designation of the ancient speakers of the Indo-Iranian languages, specifically the Iranian and the Indo-Aryan peoples, collectively known as the Indo-Iranians. Despite this, some scholars use the term Indo-Iranian to refer to this group, though the term "Aryan" remains widely used by most scholars, such as Josef Wiesehofer, Will Durant, and Jaakko Häkkinen. Population geneticist Luigi Luca Cavalli-Sforza, in his 1994 book ''The History and Geography of Human Genes'', also uses the term Aryan to d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Country Of Towns
In the archaeology of Russia, the Country of Towns (, ''strana gorodov'') is a tentative term for a territory in the southern Trans-Urals where a number of middle Bronze Age (~2,000 BC) fortified settlements of the Sintashta culture were found in the 1970s and 1980s.Andrey Bersenev, Andrey Epimakhov and Dmitry ZdanovichSINTASHTA BOW OF THE BRONZE AGE OF THE SOUTH TRANS-URALS, RUSSIA in: "Bronze Age Warfare: Manufacture and Use of Weaponry", 2011, The best known site of the territory is Arkaim. Since the discovery of the Sintashta culture, aerial photography has revealed that there is a compactly grouped number of town-type settlements (over 20) in the northern steppe of the southern Trans-Urals, within an area bounded roughly 350~400 km north–south and 120~150 km east–west between Magnitorgorsk and Chelyabinsk in Orenburg Oblast, Chelyabinsk Oblast, Northern Kazakhstan and Bashkortostan. Therefore, in the 2000s, the principal investigator of this area, Gennady ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bredinsky District
Bredinsky District () is an administrative and municipal district (raion), one of the twenty-seven in Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia.Resolution #161 It is located in the south of the oblast. The area of the district is . Its administrative center An administrative centre is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune, is located. In countries with French as the administrative language, such as Belgiu ... is the rural locality (a settlement) of Bredy. Population: 33,039 ( 2002 Census); The population of Bredy accounts for 33.2% of the district's total population. References Notes Sources * {{Use mdy dates, date=December 2012 Districts of Chelyabinsk Oblast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chariot
A chariot is a type of vehicle similar to a cart, driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid Propulsion, motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 1950–1880 BC and are depicted on cylinder seals from Central Anatolia Region, Central Anatolia in Kültepe dated to c. 1900 BC. The critical invention that allowed the construction of light, horse-drawn chariots was the spoked wheel. The chariot was a fast, light, open, two-wheeled conveyance drawn by two or more Equidae, equids (usually horses) that were hitched side by side, and was little more than a floor with a waist-high guard at the front and sides. It was initially used for ancient warfare during the Bronze Age, Bronze and Iron Age, Iron Ages, but after its military capabilities had been superseded by Light cavalry, light and Heavy cavalry, heavy cavalries, chariots continued to be used for travel and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swastika
The swastika (卐 or 卍, ) is a symbol used in various Eurasian religions and cultures, as well as a few Indigenous peoples of Africa, African and Indigenous peoples of the Americas, American cultures. In the Western world, it is widely recognized as a symbol of the German Nazi Party who Cultural appropriation, appropriated it for their party insignia starting in the early 20th century. The appropriation continues with its use by Neo-Nazism, neo-Nazis around the world. The swastika was and continues to be used as a symbol of divinity and spirituality in Indian religions, including Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism. It generally takes the form of a cross, the arms of which are of equal length and perpendicular to the adjacent arms, each bent midway at a right angle. The word ''swastika'' comes from , meaning 'conducive to well-being'. In Hinduism, the right-facing symbol (clockwise) () is called , symbolizing ('sun'), prosperity and good luck, while the left-facing symbol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet Union, it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by area, extending across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and sharing Geography of the Soviet Union#Borders and neighbors, borders with twelve countries, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire, it was nominally organized as a federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR. In practice, Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, economy were Soviet-type economic planning, highly centralized. As a one-party state go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yama
Yama (), also known as Kāla and Dharmarāja, is the Hindu god of death and justice, responsible for the dispensation of law and punishment of sinners in his abode, Naraka. He is often identified with Dharmadeva, the personification of ''Dharma'', though the two deities have different origins and myths. In Vedic tradition, Yama was considered the first mortal who died and espied the way to the celestial abodes; as a result, he became the ruler of the departed. His role, characteristics, and abode have been expounded in texts such as the ''Upanishads'', the ''Ramayana'', the ''Mahabharata'', and the ''Puranas''. Yama is described as the twin of the goddess Yami, and the son of the god Surya (sun) (in earlier traditions Vivasvat) and Sanjna. He judges the souls of the dead and, depending on their deeds, assigns them to the realm of the Pitris (forefathers), Naraka (hell), or to be reborn on the earth. Yama is one of the Lokapalas (guardians of the realms), appointed as the pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avesta
The Avesta (, Book Pahlavi: (), Persian language, Persian: ()) is the text corpus of Zoroastrian literature, religious literature of Zoroastrianism. All its texts are composed in the Avestan language and written in the Avestan alphabet. Modern Edition (book), editions of the Avesta are based on the various manuscript traditions that have survived in Zoroastrianism in India, India and Zoroastrianism in Iran, Iran. The individual texts of the Avesta were originally Oral tradition, oral compositions. They were composed over a long period of several centuries during the Avestan period, Old Iranian period (possibly ranging from 15th century BCE – 4th century BCE). The written transmission began during the Sassanian empire, Sassanian period, with the creation of the Avestan alphabet. The resulting texts were then compiled into a comprehensive edition of the Sasanian Avesta, Avesta in 21 volumes. This edition was lost sometime after the 10th century CE and only a small part survi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vedas
FIle:Atharva-Veda samhita page 471 illustration.png, upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the ''Atharvaveda''. The Vedas ( or ; ), sometimes collectively called the Veda, are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the oldest layer of Sanskrit literature and the oldest Hindu texts, scriptures of Hinduism. There are four Vedas: the Rigveda, the Yajurveda, the Samaveda and the Atharvaveda. Each Veda has four subdivisions – the Samhitas (mantras and benedictions), the Brahmanas (commentaries on and explanation of rituals, ceremonies and sacrifices – Yajñas), the Aranyakas (text on rituals, ceremonies, sacrifices and symbolic-sacrifices), and the Upanishads (texts discussing meditation, philosophy and spiritual knowledge).Gavin Flood (1996), ''An Introduction to Hinduism'', Cambridge University Press, , pp. 35–39A Bhattacharya (2006), ''Hindu Dharma: Introduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |