|
Areobindus Dagalaifus Areobindus
Flavius Areobindus Dagalaifus Areobindus (; 479–512) was an Eastern Roman general and politician. The scion of a distinguished line, he led troops in the Anastasian War, and served as consul in 506. During an urban riot in 512, Areobindus evaded a mob which wanted to force a change of government by proclaiming him emperor. He died soon after.Kazhdan (1991), p. 162 Origins and family Areobindus was born into an extremely distinguished family, which combined Roman and barbarian heritage: his father was Dagalaifus ( – after 461), consul in 461, who in turn was the son of Areobindus, consul in 434, both of Gothic origin. His mother was Godisthea (born ), daughter of Ardabur, general and consul in 447, and granddaughter of Aspar, the powerful Alan general and consul in 434.Martindale (1980), p. 143 Shortly after 478, Areobindus married Anicia Juliana (after 461 – 527/528), daughter of the Western Roman emperor Olybrius and his wife Placidia. Together they had a son, Olybrius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Areobindus Presides Over The Games MNMA Cluny 13135 N02 , Byzantine general
{{hndis ...
Areobindus, also Ariobindas or Areovindas may refer to: * Areobindus (consul 434) (died 449), consul in 434 * Areobindus Dagalaiphus Areobindus, grandson of the previous, consul in 506 * Areobindus (died 546) Areobindus (died 546) was an official and military commander of the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire. He served as a senator in Constantinople and briefly as ''magister militum'' in Africa in 545/6. Areobindus was sent to Africa by Emperor Justi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olybrius (consul 491)
Flavius Olybrius ( Greek: Ολύβριος ''fl''. 491-after 532) was an aristocrat of the Eastern Roman Empire and a consul for the year 491. He is sometimes referred to as "Olybrius Junior" in the sources, probably referencing his young age. Olybrius was through his mother Anicia Juliana a descendant of the conjoined Valentinianic and Theodosian dynasties, and the grandson of the emperor Olybrius () and the great-grandson of Western Roman Emperor Valentinian III (). He was also a potential ''augustus'' on the death of the Eastern Roman Emperor Zeno () of the Leonid dynasty. Life Olybrius was the son of Areobindus Dagalaifus Areobindus, magister militum from 503 to 504 and consul in 506, and of Anicia Juliana, the daughter of the Western Roman Emperor Olybrius and wife Placidia, who was the daughter of the Western Roman Emperor Valentinian III and wife Licinia Eudoxia. Alan Cameron explains, "It may be that, alone among the consuls here discussed, Olybrius was actu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arzanene
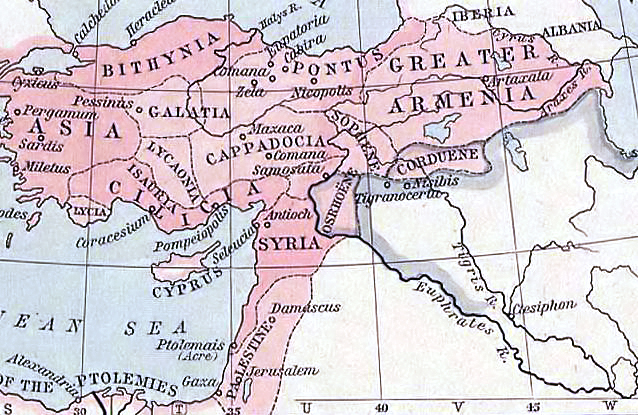
Arzanene () or Aghdznik () was a historical region in the southwest of the ancient kingdom of Armenia. It was ruled by one of the four (''bidakhsh'', ) of Armenia, the highest ranking nobles below the king who ruled over the kingdom's border regions. Its probable capital was the fortress-city of Arzen. The region briefly became home to the capital of Armenia during the reign of Tigranes the Great, who built his namesake city Tigranocerta there. Arzanene was placed under the direct suzerainty of the Roman Empire after the Peace of Nisibis in 298. It was briefly brought back under Armenian control c. 371 but was soon lost again following the partition of Armenia in 387. Name It is generally agreed the Greco-Roman name of Arzanene is derived from the city of Arzan ( or in Armenian), which was probably the capital of the province. The name is identified with the ''Alzi'' or ''Alše'' mentioned in Neo-Assyrian and Urartian inscriptions and is of non-Armenian origin. Geog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edessa, Mesopotamia
Edessa (; ) was an ancient city ('' polis'') in Upper Mesopotamia, in what is now Urfa or Şanlıurfa, Turkey. It was founded during the Hellenistic period by Macedonian general and self proclaimed king Seleucus I Nicator (), founder of the Seleucid Empire. He named it after an ancient Macedonian capital. The Greek name (''Édessa'') means "tower in the water". It later became capital of the Kingdom of Osroene, and continued as capital of the Roman province of Osroene. In Late Antiquity, it became a prominent center of Christian learning and seat of the Catechetical School of Edessa. During the Crusades, it was the capital of the County of Edessa. The city was situated on the banks of the Daysan River (; ; ), a tributary of the Khabur, and was defended by Şanlıurfa Castle, the high central citadel. Ancient Edessa is the predecessor of modern Urfa (; ; ; ), in Şanlıurfa Province, Turkey. Modern names of the city are likely derived from Urhay or Orhay (), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantia (Osrhoene)
Constantia or Konstantia () was a town of some importance in the province Osrhoene in Mesopotamia, on the road between Nisibis and Carrhae, at no great distance from Edessa. It was, after his departure from Nisibis, the residence of the '' dux Mesopotamiae'' until the foundation of Dara. There is considerable variation in different authors in the way in which the name of this town is written and the names under which it is known, including: Constantia or Konstantia (Κωνσταντία), Constantina or Konstantina (Κωνσταντίνα), Antoninopolis, Nicephorium or Nikephorion (Νικηφόριον), Maximianopolis (Μαξιμιανούπολις), Constantinopolis in Osrhoene, Tella and Antiochia Arabis, Antiochia in Mesopotamia ( – ''Antiocheia tes Mesopotamias'') and Antiochia in Arabia ( – ''Antiocheia e Arabike''). According to Pliny it was founded by Seleucus I Nicator after the death of Alexander the Great. According to the Byzantine historian John Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world. Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years. In the 9th century BCE, the Assyrians made written references to Arabs as inhabitants of the Levant, Mesopotamia, and Arabia. Throughout the Ancient Near East, Arabs established influential civilizations starting from 3000 BCE onwards, such as Dilmun, Gerrha, and Magan (civilization), Magan, playing a vital role in trade between Mesopotamia, and the History of the Mediterranean region, Mediterranean. Other prominent tribes include Midian, ʿĀd, and Thamud mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, Bible and Quran. Later, in 900 BCE, the Qedarites enjoyed close relations with the nearby Canaan#Canaanites, Canaanite and Aramaeans, Aramaean states, and their territory extended from Lower Egypt to the Southern Levant. From 1200 BCE to 110 BCE, powerful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hephthalite
The Hephthalites (), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit and Prakrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during the 5th to 8th centuries CE, part of the larger group of Eastern Iranian Huns. They formed an empire, the Imperial Hephthalites, and were militarily important from 450 CE, when they defeated the Kidarites, to 560 CE, when combined forces from the First Turkic Khaganate and the Sasanian Empire defeated them. After 560 CE, they established "principalities" in the area of Tokharistan, under the suzerainty of the Western Turks (in the areas north of the Oxus) and of the Sasanian Empire (in the areas south of the Oxus), before the Tokhara Yabghus took over in 625. The Imperial Hephthalites, based in Bactria, expanded eastwards to the Tarim Basin, westwards to Sogdia and southwards through Afghanistan, but they never went beyond the Hindu-Kush, which was occupied by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Singara
Singara (, ''tà Síngara''; Syriac: ܫܝܓܪ) was a strongly fortified post at the northern extremity of Mesopotamia, which for a while, as it appears from coins minted there, was occupied by the Romans as an advanced colony against the Persians. It was the camp of ''legio'' I ''Parthica''. Location Its position south-east of Nisibis was indifferently defined by ancient writers, with Stephanus of Byzantium calling it a city of Arabia "near Edessa" and Ptolemy placing it on the Tigris. There is no doubt, however, that it and its adjacent mountain (, ''ò Síngaras óros'') were the predecessors of the modern Sinjar and Mount Sinjar in modern Iraq's Nineveh Plains. History It was first taken by the Romans during Trajan's eastern campaigns, when general Lusius Quietus captured the city without a fight in the winter of 114. Although it was abandoned following the Roman withdrawal from Mesopotamia in 117, the city became once again part of the Roman Empire with the Parthian c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kavadh I
Kavad I ( ; 473 – 13 September 531) was the Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 488 to 531, with a two or three-year interruption. A son of Peroz I (), he was crowned by the nobles to replace his deposed and unpopular uncle Balash (). Inheriting a declining empire where the authority and status of the Sasanian kings had largely ended, Kavad tried to reorganize his empire by introducing many reforms whose implementation was completed by his son and successor, Khosrow I. They were made possible by Kavad's use of the Mazdakite preacher Mazdak, leading to a social revolution that weakened the authority of the nobility and the clergy. Because of this, and the execution of the powerful king-maker Sukhra, Kavad was deposed and imprisoned in the Castle of Oblivion. He was replaced by his brother Jamasp. However, with the aid of his sister and an officer named Siyawush, Kavad and some of his followers fled east to the territory of the Hephthalite king, who provided him with an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nisibis
Nusaybin () is a municipality and Districts of Turkey, district of Mardin Province, Turkey. Its area is 1,079 km2, and its population is 115,586 (2022). The city is populated by Kurds of different tribal affiliation. Nusaybin is separated from the larger Kurds, Kurdish-majority city of Qamishli by the Syria–Turkey border. The city is at the foot of the Mount Izla escarpment at the southern edge of the Tur Abdin hills, standing on the banks of the Jaghjagh River (), the ancient Mygdonius (). The city existed in the Assyrian Empire and is recorded in Akkadian language, Akkadian inscriptions as ''Naṣibīna''. Having been part of the Achaemenid Empire, in the Hellenistic period the settlement was re-founded as a ''polis'' named "Antioch on the Mygdonius" by the Seleucid dynasty after the conquests of Alexander the Great. A part of first the Roman Republic and then the Roman Empire, the city (; ) was mainly Syriac language, Syriac-speaking, and control of it was contested be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dara (Mesopotamia)
Dara or Daras (Turkish language, Turkish: Dara Antik Kenti; Kurmanji, Kurdish: Darê; ; ) was an important East Roman Empire, East Roman fortress city in northern Mesopotamia on the border with the Sassanid Empire. Because of its great strategic importance, it featured prominently in the Roman-Persian Wars, Roman-Persian conflicts (in Battle of Dara, 530, 540, 544, Siege of Dara (573), 573, and 604). The former archbishopric remains a multiple Catholic titular see. Today, the village of Dara, Artuklu, Dara, in the Mardin Province occupies its location. History Foundation by Anastasius During the Anastasian War in 502–506, the Roman armies fared poorly against the Sassanid Empire, Sassanid Persians. According to the ''Syriac Chronicle'' of Zacharias Rhetor, Zacharias of Mytilene, the Roman generals blamed their difficulties on the lack of a strong base in the area, as opposed to the Persians, who held the great city of Nusaybin, Nisibis (which until its cession in 363 had ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amida (Roman City)
Amida can mean : Places and jurisdictions * Amida (Mesopotamia), now Diyarbakır, an ancient city in Asian Turkey; it is (nominal) seat of: ** The Chaldean Catholic Archeparchy of Amida ** The Latin titular Metropolitan see of Amida of the Romans ** The Armenian Catholic titular see Amida of the Armenians ** The Syrian Catholic (Antiochian Rite) titular Metropolitan see Amida of the Syriacs * Mount Amida, mountain in Saeki-ku, Hiroshima, Japan Other * Amitābha Buddha, in Japanese * ''Amida'' (beetle), a beetle genus * ''Amida'', a ladder climbing puzzle video game * Amida, is Swiss watchmaker founded in 1925 in Grenchen. See also * Amitabha (other) * Amidah, the central prayer of Jewish worship * Amidakuji, a way of drawing lots * Aëtius of Amida Aëtius of Amida (; ; Latin: ''Aëtius Amidenus''; fl. mid-5th century to mid-6th century) was a Byzantine Greek physician and medical writer, particularly distinguished by the extent of his erudition. His birt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |