|
Arene Substitution Patterns
Arene substitution patterns are part of organic chemistry IUPAC nomenclature and pinpoint the position of substituents other than hydrogen in relation to each other on an aromatic hydrocarbon. ''Ortho'', ''meta'', and ''para'' substitution * In ''ortho''-substitution, two substituents occupy positions next to each other, which may be numbered 1 and 2. In the diagram, these positions are marked R and ''ortho''. * In ''meta''-substitution, the substituents occupy positions 1 and 3 (corresponding to R and ''meta'' in the diagram). * In ''para''-substitution, the substituents occupy the opposite ends (positions 1 and 4, corresponding to R and ''para'' in the diagram). The toluidines serve as an example for these three types of substitution. Synthesis Electron donating groups, for example amino, hydroxyl, alkyl, and phenyl groups tend to be ''ortho''/''para''-directors, and electron withdrawing groups such as nitro, nitrile, and ketone groups, tend to be ''meta''-directors. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromatic Compound
Aromatic compounds or arenes are organic compounds "with a chemistry typified by benzene" and "cyclically conjugated." The word "aromatic" originates from the past grouping of molecules based on odor, before their general chemical properties were understood. The current definition of aromatic compounds does not have any relation to their odor. Aromatic compounds are now defined as cyclic compounds satisfying Hückel's rule. Aromatic compounds have the following general properties: * Typically unreactive * Often non polar and hydrophobic * High carbon-hydrogen ratio * Burn with a strong sooty yellow flame, due to high C:H ratio * Undergo electrophilic substitution reactions and nucleophilic aromatic substitutions Arenes are typically split into two categories - benzoids, that contain a benzene derivative and follow the benzene ring model, and non-benzoids that contain other aromatic cyclic derivatives. Aromatic compounds are commonly used in organic synthesis and are involved in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recrystallization (chemistry)
Recrystallization is a broad class of List of purification methods in chemistry , chemical purification techniques characterized by the dissolution of an impure sample in a solvent or solvent mixture, followed by some change in conditions that encourages the formation of pure isolate as solid crystals. Recrystallization as a purification technique is driven by spontaneous process , spontaneous processes of molecular self-assembly , self-assembly that leverage the highly ordered (i.e. low-entropy) and periodic characteristics of a crystal's molecular structure to produce purification. Basic principles The driving force of this purification emerges from the difference in molecular interactions between the isolate and the impurities: if a molecule of the desired isolate interacts with any isolate crystal present, it is likely the molecule Deposition (chemistry) , deposits on the crystal's ordered surface and contributes to the crystal's growth; if a molecule of the impurity inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
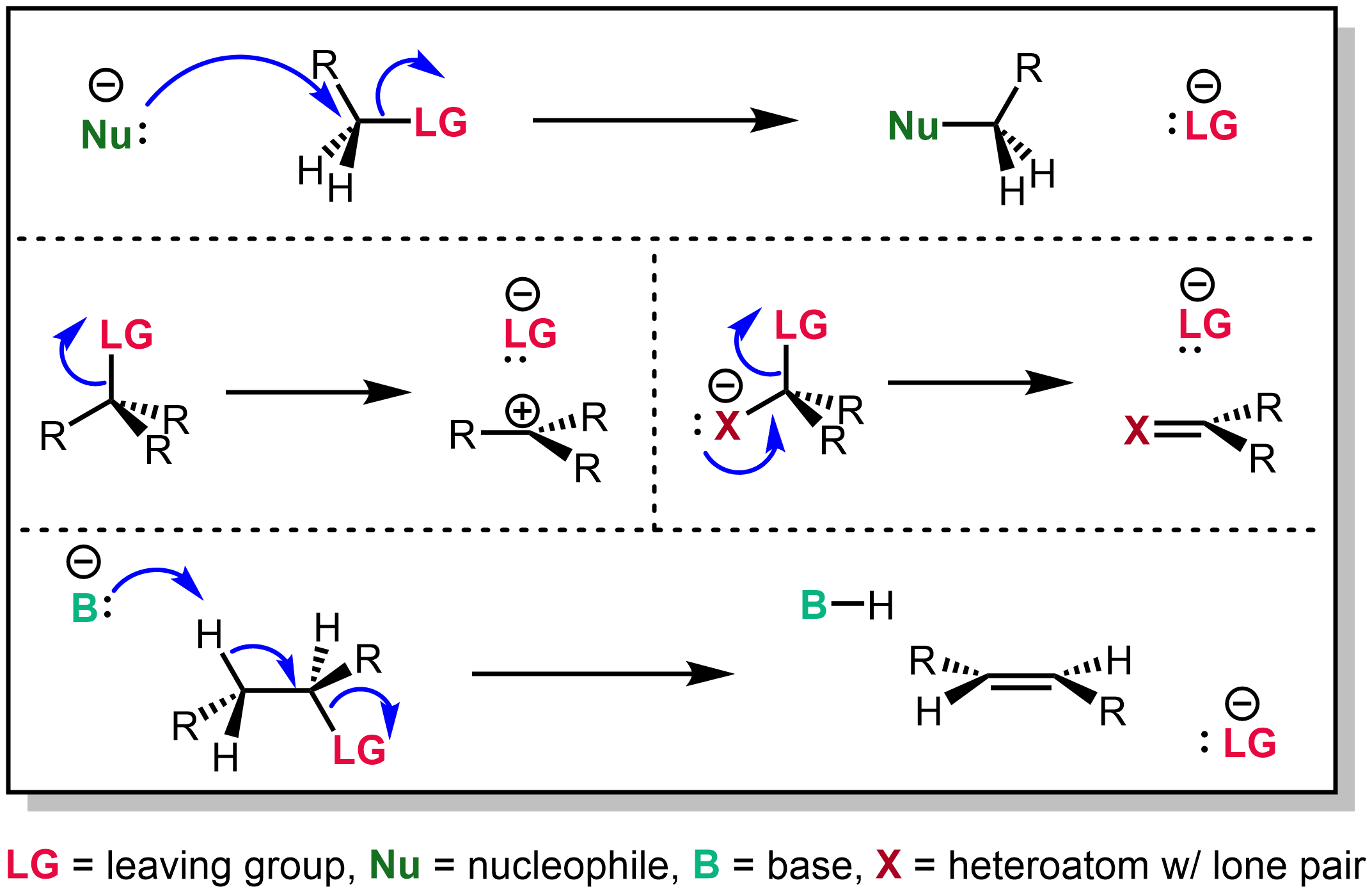
Leaving Group
In organic chemistry, a leaving group typically means a Chemical species, molecular fragment that departs with an electron, electron pair during a reaction step with heterolysis (chemistry), heterolytic bond cleavage. In this usage, a ''leaving group'' is a less formal but more commonly used synonym of the term ''nucleofuge''; although IUPAC gives the term a broader definition. A species' ability to serve as a leaving group can affect whether a reaction is viable, as well as what mechanism the reaction takes. Leaving group ability depends strongly on context, but often correlates with ability to stabilize additional electron density from bond heterolysis. Common anionic leaving groups are , and halides and sulfonate esters such as tosylate (). Water (), alcohols (), and amines () are common neutral leaving groups, although they often require activating catalysts. Some moieties, such as hydride (H−) serve as leaving groups only extremely rarely. Nomenclature IUPAC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naphthalene
Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula . It is the simplest polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and is a white Crystal, crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 Parts-per notation, ppm by mass. As an Aromaticity, aromatic hydrocarbon, naphthalene's structure consists of a fused pair of benzene rings. It is the main ingredient of traditional mothballs. History In the early 1820s, two separate reports described a white solid with a pungent odor derived from the distillation of coal tar. In 1821, John Kidd (chemist), John Kidd cited these two disclosures and then described many of this substance's properties and the means of its production. He proposed the name ''naphthaline'', as it had been derived from a kind of naphtha (a broad term encompassing any volatile, flammable liquid hydrocarbon mixture, including coal tar). Naphthalene's chemical formula was determined by Michael Faraday in 1826. The structure of two f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acridine
Acridine is an organic compound and a nitrogen heterocycle with the formula C13H9N. Acridines are substituted derivatives of the parent ring. It is a planar molecule that is structurally related to anthracene with one of the central CH groups replaced by nitrogen. Like the related molecules pyridine and quinoline, acridine is mildly basic. It is an almost colorless solid, which crystallizes in needles. There are few commercial applications of acridines; at one time acridine dyes were popular, but they are now relegated to niche applications, such as with acridine orange. The name is a reference to the acrid odour and acrid skin-irritating effect of the compound. Isolation and syntheses Carl Gräbe and Heinrich Caro first isolated acridine in 1870 from coal tar. Acridine is separated from coal tar by extracting with dilute sulfuric acid. Addition of potassium dichromate to this solution precipitates acridine bichromate. The bichromate is decomposed using ammonia. Acridi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calixarene
A calixarene is a macrocycle or cyclic oligomer based on a methylene-linked phenols. With hydrophobic cavities that can hold smaller molecules or ions, calixarenes belong to the class of cavitands known in host–guest chemistry. Nomenclature Calixarene nomenclature is straightforward and involves counting the number of repeating units in the ring and including it in the name. A calix rene has 4 units in the ring and a calix rene has 6. A substituent in the meso position Rb is added to the name with a prefix C- as in C-methylcalix rene The word calixarene is derived from the Greek calix or chalice because this type of molecule resembles a vase (or cup) and from the word arene that refers to the aromatic building block. Synthesis Calixarenes are generally produced by condensation of two components: an electron-rich aromatic compound, classically a 4-substituted phenol, and an aldehyde, classically formaldehyde. *The scope for the aromatic component is broad diverse. The ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzyl
In organic chemistry, benzyl is the substituent or molecular fragment possessing the structure . Benzyl features a benzene ring () attached to a methylene group (). Nomenclature In IUPAC nomenclature, the prefix benzyl refers to a substituent, for example benzyl chloride or benzyl benzoate. Benzyl is not to be confused with phenyl with the formula . The term benzylic is used to describe the position of the first carbon bonded to a benzene or other aromatic ring. For example, is referred to as a "benzylic" carbocation. The benzyl free radical has the formula . The benzyl cation or phenylcarbenium ion is the carbocation with formula ; the benzyl anion or phenylmethanide ion is the carbanion with the formula . None of these species can be formed in significant amounts in the solution phase under normal conditions, but they are useful referents for discussion of reaction mechanisms and may exist as reactive intermediates. Abbreviations Benzyl is most commonly abbreviated Bn. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbocation
Carbocation is a general term for ions with a positively charged carbon atom. In the present-day definition given by the IUPAC, a carbocation is any even-electron cation with significant partial positive charge on a carbon atom. They are further classified in two main categories according to the coordination number of the charged carbon: three in the carbenium ions and five in the carbonium ions. Among the simplest carbocations are the methenium (a carbenium ion), methanium (a carbonium ion), acylium ions , and Vinyl cation, vinyl cations. Until the early 1970s, carbocations were called ''carbonium ions''. This nomenclature was proposed by George Andrew Olah, G. A. Olah. Carbonium ions, as originally defined by Olah, are characterized by a Three-center two-electron bond, three-center two-electron delocalized bonding scheme and are essentially synonymous with so-called 'non-classical carbocations', which are carbocations that contain bridging C–C or C–H σ-bonds. However ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopropyl
In organic chemistry, a propyl group is a three-carbon alkyl substituent with chemical formula for the linear form. This substituent form is obtained by removing one hydrogen atom attached to the terminal carbon of propane. A propyl substituent is often represented in organic chemistry with the symbol Pr (not to be confused with the element praseodymium). An isomeric form of propyl is obtained by moving the point of attachment from a terminal carbon atom to the central carbon atom, named isopropyl or 1-methylethyl. To maintain four substituents on each carbon atom, one hydrogen atom has to be moved from the middle carbon atom to the carbon atom which served as attachment point in the ''n''-propyl variant, written as . Linear propyl is sometimes termed normal and hence written with a prefix ''n''- (i.e., ''n-''propyl), as the absence of the prefix ''n''- does not indicate which attachment point is chosen, i.e. absence of prefix does not automatically exclude the possibility of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tert-Butyl
In organic chemistry, butyl is a four-carbon alkyl radical or substituent group with general chemical formula , derived from either of the two isomers (''n''-butane and isobutane) of butane. The isomer ''n''-butane can connect in two ways, giving rise to two "-butyl" groups: * If it connects at one of the two terminal carbon atoms, it is normal butyl or ''n''-butyl: (preferred IUPAC name: butyl) * If it connects at one of the non-terminal (internal) carbon atoms, it is secondary butyl or ''sec''-butyl: (preferred IUPAC name: butan-2-yl) The second isomer of butane, isobutane, can also connect in two ways, giving rise to two additional groups: * If it connects at one of the three terminal carbons, it is isobutyl: (preferred IUPAC name: 2-methylpropyl) * If it connects at the central carbon, it is tertiary butyl, ''tert''-butyl or ''t''-butyl: (preferred IUPAC name: ''tert''-butyl) Nomenclature According to IUPAC nomenclature, "isobutyl", "''sec''-butyl", and "''tert'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimethylsilyl
A trimethylsilyl group (abbreviated TMS) is a functional group in organic chemistry. This group consists of three methyl groups bonded to a silicon atom [−Si(CH3)3], which is in turn bonded to the rest of a molecule. This structural group is characterized by Chemically inert, chemical inertness and a large molecular volume, which makes it useful in a number of applications. A trimethylsilyl group bonded to a methyl group forms tetramethylsilane, which is abbreviated as TMS as well. Compounds with trimethylsilyl groups are not normally found in nature. Chemists sometimes use a trimethylsilylating reagent to derivatize rather non-volatile compounds such as certain Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols, phenols, or carboxylic acids by substituting a trimethylsilyl group for a hydrogen in the hydroxyl groups on the compounds. This way Silyl ether, trimethylsiloxy groups [−O-Si(CH3)3] are formed on the molecule. A couple of examples of trimethylsilylating agents include trimethyls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
Electrophilic aromatic substitution (SEAr) is an organic reaction in which an atom that is attached to an aromatic ring, aromatic system (usually hydrogen) is replaced by an electrophile. Some of the most important electrophilic aromatic substitutions are aromatic nitration, aromatic halogenation, aromatic sulfonation, alkylation Friedel–Crafts reaction and acylation Friedel–Crafts reaction. Illustrative reactions The most widely practised example of this reaction is the ethylation of benzene. :: Approximately 24,700,000 tons were produced in 1999. (After dehydrogenation and polymerization, the commodity plastic polystyrene is produced.) In this process, acids are used as catalyst to generate the incipient carbocation. Many other electrophilic reactions of benzene are conducted, although on a much smaller scale; they are valuable routes to key intermediates. The nitration of benzene is achieved via the action of the nitronium ion as the electrophile. The Aromatic sulfonation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |