|
Architecture Of The Philippines
The architecture of the Philippines reflects the historical and cultural traditions in the country. Most prominent historic structures in the archipelago are influenced by Austronesian and American architectures. During three hundred thirty years of Spanish colonization, the Philippine architecture was dominated by the Spanish influences. The Augustinian friars, along with other religious orders, built many grand churches and cathedrals all over the Philippine Islands. During this period the traditional Filipino ''Bahay na bató'' (Filipino for "house of stone") style for the large houses emerged. These were large houses built of stone and wood combining Filipino, Spanish and Chinese style elements. After the Philippines was ceded to the United States as a consequence of the Spanish–American War in 1898, the architecture of the Philippines was influenced by American aesthetics. In this period, the plan for the modern City of Manila was designed, with many neoclassical arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural heritage around the world considered to be of outstanding value to humanity". To be selected, a World Heritage Site is nominated by its host country and determined by the UNESCO's World Heritage Committee to be a unique landmark which is geographically and historically identifiable, having a special cultural or physical significance, and to be under a sufficient system of legal protection. World Heritage Sites might be ancient ruins or historical structures, buildings, cities, deserts, forests, islands, lakes, monuments, mountains or wilderness areas, and others. A World Heritage Site may signify a remarkable accomplishment of humankind and serve as evidence of humanity's intellectual history on the planet, or it might be a place of grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marawi City
Marawi, officially the Islamic City of Marawi (Maranao language, Maranao: ''Bandar a Marawi''; ; Jawi script, Jawi ''(Batang Arab)'': ), is a Cities of the Philippines#Legal classification, component city and capital of the Provinces of the Philippines, province of Lanao del Sur, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 207,010 people. Marawi is located upon the shores of Lake Lanao. It is primarily inhabited by the Maranao people. The city is also called the "Summer Capital of the South" due to its higher elevation and cooler climate, a nickname it shares with Malaybalay. On May 23, 2017, the city suffered extensive damage during the Siege of Marawi as militants affiliated with the Islamic State invaded the city and engaged in a five-month urban warfare, until when Defense Secretary Delfin Lorenzana announced the ending of the battle in October. Etymology ''Dansalan'' (Marawi's prior name) derived from the Mëranaw word "dansal", which means rendez ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Datu
''Datu'' is a title which denotes the rulers (variously described in historical accounts as chiefs, sovereign princes, and monarchs) of numerous Indigenous peoples throughout the Philippine archipelago. The title is still used today, though not as much as early Philippine history. It is a cognate of ''datuk'', ''dato'', and ''ratu'' in several other Austronesian languages. Overview In early Philippine history, ''datus'' and a small group of their Cognatic kinship, close relatives formed the "apex stratum" of the traditional three-tier social hierarchy of lowland Philippine societies. Only a member of this birthright aristocracy (called ''maginoo'', ''nobleza'', ''maharlika'', or ''timagua'' by various early chroniclers) could become a ''datu''; members of this elite could hope to become a ''datu'' by demonstrating prowess in war or exceptional leadership. In large coastal polities such as those in Maynila (historical polity), Maynila, Tondo (historical polity), Tondo, Pangasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultan
Sultan (; ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be used as the title of certain rulers who claimed almost full sovereignty (i.e., not having dependence on any higher ruler) without claiming the overall caliphate, or to refer to a powerful governor of a province within the caliphate. The adjectival form of the word is "sultanic", and the state and territories ruled by a sultan, as well as his office, are referred to as a sultanate ( '. The term is distinct from king ( '), though both refer to a sovereign ruler. The use of "sultan" is restricted to Muslim countries, where the title carries religious significance, contrasting the more secular ''king'', which is used in both Muslim and non-Muslim countries. Brunei, Malaysia and Oman are the only sovereign states which retain the title "sultan" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
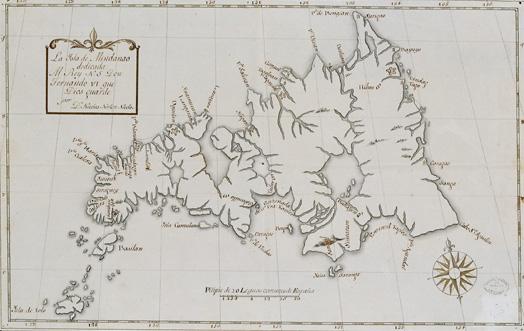
Mindanao
Mindanao ( ) is the List of islands of the Philippines, second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and List of islands by population, seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of the same name that also includes its adjacent islands, notably the Sulu Archipelago. According to the 2020 census, Mindanao had a population of 26,252,442, while the entire island group had an estimated population of 27,021,036. Mindanao is divided into six administrative regions: the Zamboanga Peninsula, Northern Mindanao, the Caraga region, the Davao Region, Davao region, Soccsksargen, and the autonomous region of Bangsamoro. According to the 2020 census, Davao City is the most populous city on the island, with 1,776,949 people, followed by Zamboanga City (pop. 977,234), Cagayan de Oro (pop. 728,402), General Santos (pop. 697,315), Butuan (pop. 372,910), Iligan (pop. 363,115) and Cotabato City (pop. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Lanao
Lake Lanao ( Maranao: ''Ranao'' or ''Ranaw'') is a large ancient lake in the province of Lanao del Sur, Philippines. With a surface area of , it is the largest lake in Mindanao, the deepest and second largest lake in the Philippines, and counted as one of the 15 ancient lakes in the world. Scholars have been pushing for the lake's inclusion in the UNESCO World Heritage List. The lake's native people call themselves the Maranao or Meranaw. Their name was derived from the name of the lake, meaning "the people living around the lake". History In 1965, Lake Lanao was renamed to ''Lake Sultan Alonto'' by Republic Act No. 4260, which was later repealed by Republic Act No. 6434 in 1972. The lake has great hydroelectric potential due to its 700 meter elevation, and as such, in 1950, the Philippines National Power Corporation (NAPOCOR) began the construction of a series of hydroelectric plants titled Agus I – Agus VII along the Agus River system, which generates 70% of the electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maranao People
The Maranao people (Maranao language, Maranao: ''Bangsa'' ''Mëranaw''; Filipino language, Filipino: ''mga'' ''Maranaw''), also spelled Meranaw, Maranaw, and Mëranaw, is a predominantly Muslim Filipino people, Filipino ethnic groups of the Philippines, ethnic group native to the region around Lanao Lake in the island of Mindanao. They are known for their artwork, weaving, wood, plastic and metal crafts and epic literature, the Darangen. They are ethnically and culturally closely related to the Iranun people and Maguindanao people, all three groups being denoted speaking Danao languages and giving name to the island of Mindanao. They are grouped with other Moro people due to their shared religion. Etymology The name "Maranao" (also spelled "Mëranaw", or "Maranaw") means "people of the lake" (''lanaw'' or ''ranaw'', Archaism, archaic ''danaw'', means "lake" in the Maranao language). This is in reference to Lake Lanao, the predominant geographic feature of the ancestral hom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palace
A palace is a large residence, often serving as a royal residence or the home for a head of state or another high-ranking dignitary, such as a bishop or archbishop. The word is derived from the Latin name palātium, for Palatine Hill in Rome which housed the Roman Empire, Imperial residences. Most European languages have a version of the term (''palats'', ''palais'', ''palazzo'', ''palacio'', etc.) and many use it to describe a broader range of buildings than English. In many parts of Europe, the equivalent term is also applied to large private houses in cities, especially of the aristocracy. It is also used for some large official buildings that have never had a residential function; for example in French-speaking countries ''Palais de Justice'' is the usual name of important courthouses. Many historic palaces such as parliaments, museums, hotels, or office buildings are now put to other uses. The word is also sometimes used to describe an elaborate building used for public ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torogan
A torogan () is a type of pre-colonial vernacular house of the Maranao people of the Philippines. A torogan was a symbol of high social status. They were very large buildings and served as the residence to a ''datu'' of a Maranao community, along with his retainers and their families. Nowadays, concrete houses are found all over Maranaw communities, but there remain torogans a hundred years old. The best-known are in Dayawan and Marawi City, and around Lake Lanao. Description Torogan are massive structures built entirely without using nails. Instead, they use fitted joints and fiber lashings. They are usually the biggest structure in a village. They are elevated from the ground on large wooden columns, not all of them load-bearing. There are usually around 25 columns, but very large torogan can have as many as 56. Each column is made out of a single huge tree trunk, often transported over long distances from forests. The raising of the columns are individually celebrated by fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribal Culture
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide use of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. The definition is contested, in part due to conflicting theoretical understandings of social and kinship structures, and also reflecting the problematic application of this concept to extremely diverse human societies. Its concept is often contrasted by anthropologists with other social and kinship groups, being hierarchically larger than a lineage or clan, but smaller than a chiefdom, ethnicity, nation or state. These terms are similarly disputed. In some cases tribes have legal recognition and some degree of political autonomy from national or federal government, but this legalistic usage of the term may conflict with anthropological definitions. In the United States (US), Native American tribes are legally considered to have "domestic dependent nation" status within the territorial U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrace (agriculture)
A terrace in agriculture is a flat surface that has been cut into hills or mountains to provide areas for the cultivation for crops, as a method of more effective farming. Terrace agriculture or cultivation is when these platforms are created successively down the terrain in a pattern that resembles the steps of a staircase. As a type of landscaping, it is called terracing. Terraced fields decrease both erosion and surface runoff, and may be used to support growing crops that require irrigation, such as rice. The Rice Terraces of the Philippine Cordilleras have been designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site because of the significance of this technique. Uses Terraced paddy fields are used widely in rice, wheat and barley farming in East Asia, east, South Asia, south, Western Asia, southwest, and southeast Asia, as well as the Mediterranean Basin, Africa, and South America. Drier-climate terrace farming is common throughout the Mediterranean Basin, where they are used for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |