|
Arborloo
An arborloo is a simple type of composting toilet in which feces are collected in a shallow pit and a fruit tree is later planted in the fertile soil of the full pit. Arborloos have: a pit like a pit latrine but less deep; a concrete, ferrocement or other strong floor; a superstructure (toilet house or outhouse) to provide privacy; and possibly a ring beam to protect the pit from collapsing. The pit should remain well above the water table in the soil, so as to not contaminate groundwater. The arborloo works by temporarily putting the slab and superstructure above a shallow pit while it fills. Feces, urine, paper, leaves, other materials for wiping, and potentially anal wash water all go into the pit. After each use, a cup of the excavated soil should be added to help to control smell and flies. When the pit is nearly full, the outhouse and slab are moved to a newly dug pit and the old pit is covered with some of the earth from the new pit and left to compost. A fruit tree or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arborloo (5567538554)
An arborloo is a simple type of composting toilet in which feces are collected in a shallow pit and a fruit tree is later planted in the Soil fertility, fertile soil of the full pit. Arborloos have: a pit like a pit latrine but less deep; a concrete, ferrocement or other strong floor; a superstructure (toilet house or outhouse) to provide privacy; and possibly a ring beam to protect the pit from collapsing. The pit should remain well above the water table in the soil, so as to not Water pollution, contaminate groundwater. The arborloo works by temporarily putting the slab and superstructure above a shallow pit while it fills. Feces, urine, paper, leaves, other materials for wiping, and potentially Anal hygiene, anal wash water all go into the pit. After each use, a cup of the excavated soil should be added to help to control smell and flies. When the pit is nearly full, the outhouse and slab are moved to a newly dug pit and the old pit is covered with some of the earth from the ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composting Toilet
A composting toilet is a type of dry toilet that treats human waste by a biological process called composting. This process leads to the decomposition of organic matter and turns human waste into compost-like material. Composting is carried out by microorganisms (mainly bacteria and fungi) under controlled aerobic conditions. Most composting toilets use no water for flushing and are therefore called "dry toilets". In many composting toilet designs, a carbon additive such as sawdust, coconut coir, or peat moss is added after each use. This practice creates air pockets in the human waste to promote aerobic decomposition. This also improves the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio and reduces potential odor. Most composting toilet systems rely on mesophilic composting. Longer retention time in the composting chamber also facilitates pathogen die-off. The end product can also be moved to a secondary system – usually another composting step – to allow more time for mesophilic composting to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Sanitation
Ecological sanitation, commonly abbreviated as ecosan (also spelled eco-san or EcoSan), is an approach to sanitation provision which aims to safely reuse excreta in agriculture. It is an approach, rather than a technology or a device which is characterized by a desire to "close the loop", mainly for the nutrients and organic matter between sanitation and agriculture in a safe manner. One of the aims is to minimise the use of non-renewable resources. When properly designed and operated, ecosan systems provide a hygienically safe system to convert human excreta into nutrients to be returned to the soil, and water to be returned to the land. Ecosan is also called resource-oriented sanitation. Definition The definition of ecosan has varied in the past. In 2012, a widely accepted definition of ecosan was formulated by Swedish experts: "Ecological sanitation systems are systems which allow for the safe recycling of nutrients to crop production in such a way that the use of non-ren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Home Composting
Home composting is the process of using household waste to make compost at home. Composting is the biological decomposition of Biodegradable waste, organic waste by recycling food and other Organic matter, organic materials into compost. Home composting can be practiced within households for various environmental advantages, such as increasing soil fertility, reduce landfill and methane contribution, and limit Food loss and waste, food waste. History While composting was cultivated during the Neolithic, Neolithic Age in Scotland, home composting experienced a much later start. Indoor composting, also known as home composting, was discovered in 1905 by Albert Howard who went on to develop the practice for the next 30 years. J. I. Rodale, J.I. Rodale, considered the pioneer of the organic method in America, continued Howard's work and further developed indoor composting from 1942 on. Since then, various methods of composting have been adapted. Indoor composting aided in Organic h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoremediation Plants
Phytoremediation technologies use living plants to clean up soil, air and water contaminated with hazardous contaminants. It is defined as "the use of green plants and the associated microorganisms, along with proper soil amendments and agronomic techniques to either contain, remove or render toxic environmental contaminants harmless". The term is an amalgam of the Greek ''phyto'' (plant) and Latin ''remedium'' (restoring balance). Although attractive for its cost, phytoremediation has not been demonstrated to redress any significant environmental challenge to the extent that contaminated space has been reclaimed. Phytoremediation is proposed as a cost-effective plant-based approach of environmental remediation that takes advantage of the ability of plants to concentrate elements and compounds from the environment and to detoxify various compounds without causing additional pollution. The concentrating effect results from the ability of certain plants called hyperaccumulators t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toilet Types
A toilet is a piece of sanitary hardware that collects human waste (urine and Human feces, feces) and sometimes toilet paper, usually for disposal. Flush toilets use water, while dry toilet, dry or non-flush toilets do not. They can be designed for a sitting position popular in Europe and North America with a toilet seat, with Accessible toilet, additional considerations for those with disabilities, or for a squatting posture more popular in Asia, known as a squat toilet. In urban areas, flush toilets are usually connected to a sewer system; in isolated areas, to a septic tank. The waste is known as ''Blackwater (waste), blackwater'' and the combined effluent, including other sources, is sewage. Dry toilets are Pit latrine, connected to a pit, Container-based sanitation, removable container, Composting toilet, composting chamber, or other storage and treatment device, including urine diversion with a Urine-diverting dry toilet, urine-diverting toilet. "Toilet (room), Toilet" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banana Growing On Arborloo Pit (5566954981)
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large treelike herbaceous flowering plants in the genus ''Musa''. In some countries, cooking bananas are called plantains, distinguishing them from dessert bananas. The fruit is variable in size, color and firmness, but is usually elongated and curved, with soft flesh rich in starch covered with a peel, which may have a variety of colors when ripe. It grows upward in clusters near the top of the plant. Almost all modern edible seedless ( parthenocarp) cultivated bananas come from two wild species – ''Musa acuminata'' and ''Musa balbisiana'', or hybrids of them. ''Musa'' species are native to tropical Indomalaya and Australia; they were probably domesticated in New Guinea. They are grown in 135 countries, primarily for their fruit, and to a lesser extent to make banana paper and textiles, while some are grown as ornamental plants. The world's largest producers of bananas in 2022 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterless Urinal
A urinal (, ) is a sanitary plumbing fixture similar to a toilet, but for urination only. Urinals are often provided in men's public restrooms in Western countries (less so in Muslim countries). They are usually used in a standing position. Urinals can be equipped with manual flushing, automatic flushing, or without flushing, as is the case for waterless urinals. They can be arranged as single sanitary fixtures (with or without privacy walls), or in a trough design without privacy walls. Urinals designed for females ("female urinals") also exist but are rare. It is possible for females to use stand-up urinals using a female urination device. The term "urinal" may also apply to a small building or other structure containing such fixtures. It can also refer to a small container in which urine can be collected for medical analysis, or for use where access to toilet facilities is not possible, such as in small aircraft, during extended stakeouts, or for the bedridden. Descript ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
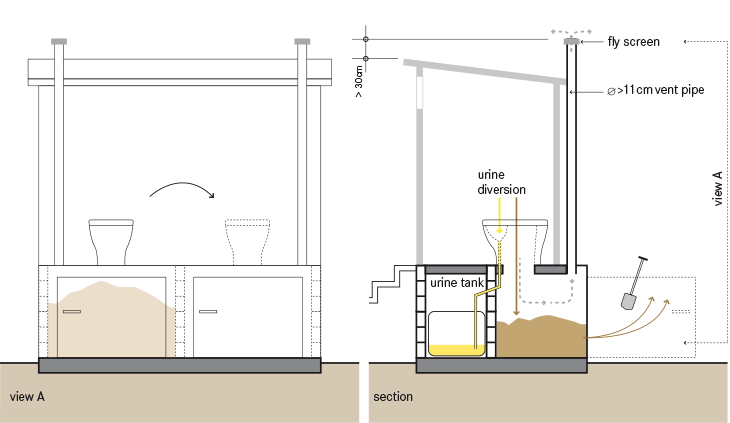
Urine-diverting Dry Toilet
A urine-diverting dry toilet (UDDT) is a type of dry toilet with urine diversion that can be used to provide safe, affordable sanitation in a variety of contexts worldwide. The separate collection of feces and urine without any flush water has many advantages, such as odor-free operation and pathogen reduction by drying. While dried feces and urine harvested from UDDTs can be and routinely are used in agriculture (respectively, as a soil amendment and nutrient-rich fertilizer—this practice being known as reuse of excreta in agriculture), many UDDT installations do not apply any sort of recovery scheme. The UDDT is an example of a technology that can be used to achieve a sustainable sanitation system. This dry excreta management system (or "dry sanitation" system) is an alternative to pit latrines and flush toilets, especially where water is scarce, a connection to a sewer system and centralized wastewater treatment plant is not feasible or desired, fertilizer and soil condit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treebog
A treebog is a type of low-tech compost toilet. It consists of a raised platform above a compost pile surrounded by densely planted willow trees or other nutrient-hungry vegetation. It can be considered an example of permaculture design, as it functions as a system for converting urine and feces to biomass, without the need to handle excreta. Defecating in nature is frowned upon in most countries, as it pollutes the environment and causes health problems. High levels of open defecation are linked to high child mortality, poor nutrition, poverty, and large disparities between the rich and the poor. Human faeces normally take about a year to biodegrade outdoors. In the UK, a system like this is potentially legal, so long as it not in a public place, i.e. on a large private estate. Etymology The term "Treebog" was coined by Jay Abrahams. ''Bog'' is a British English slang word for toilet, not to be confused with its other meaning of wetland. History The treebog is a simple me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |