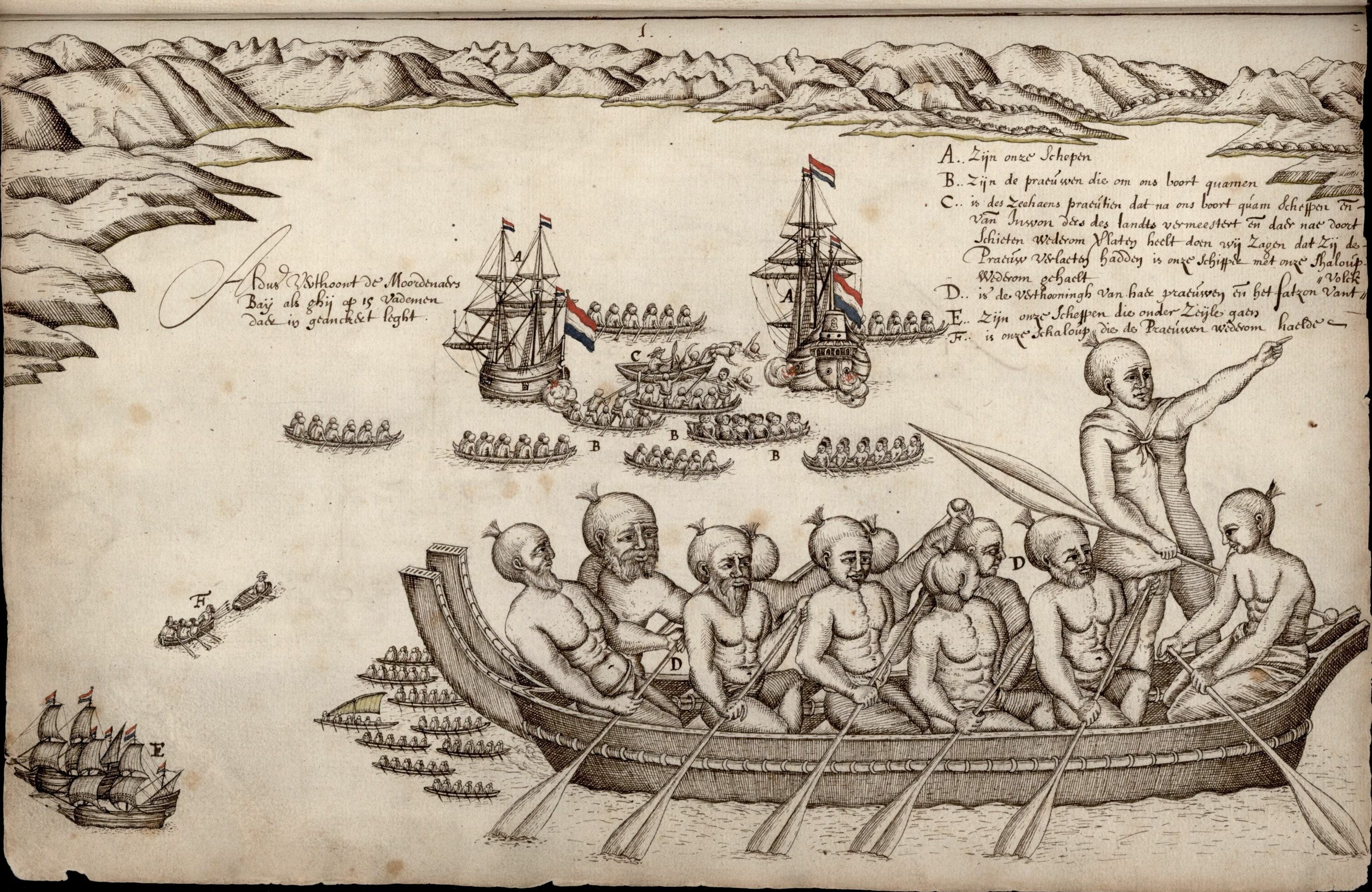
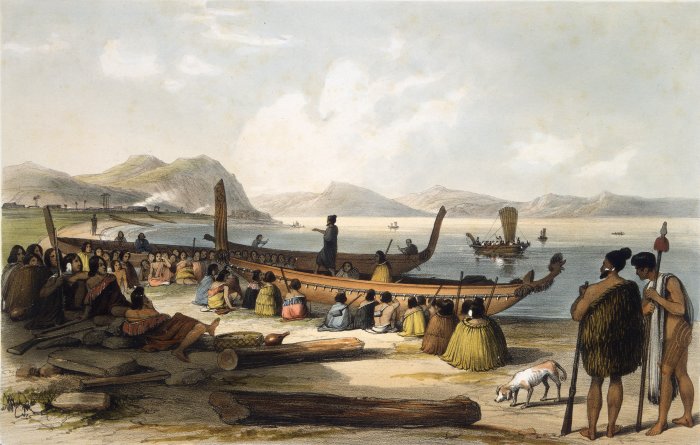|
Arahura (canoe)
was a divine canoe () made of pounamu in Ngāi Tahu's Māori mythology. The chiefs who travelled to New Zealand in her were Peki(te)tahua, Rongokahe, Rangitatau, Hineraho, Te Rangitamau, Taewhenua, Te Mikimiki (Te Mingimingi), Atua-whakanihoniho, Te Atua-whakataratara, and Whakarewa. may have also been the name of the that was brought along with the canoe. References See also * Āraiteuru * Ngahue * Tākitimu ''Tākitimu'' was a '' waka'' (canoe) with ''whakapapa'' throughout the Pacific particularly with Samoa, the Cook Islands, and New Zealand in ancient times. In several Māori traditions, the ''Tākitimu'' was one of the great Māori migration ... * Uruaokapuarangi Māori waka Māori mythology {{Māori-myth-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngāi Tahu
Ngāi Tahu, or Kāi Tahu, is the principal Māori (tribe) of the South Island. Its (tribal area) is the largest in New Zealand, and extends from the White Bluffs / Te Parinui o Whiti (southeast of Blenheim), Mount Mahanga and Kahurangi Point in the north to Stewart Island / Rakiura in the south. The comprises 18 (governance areas) corresponding to traditional settlements. Ngāi Tahu originated in the Gisborne District of the North Island, along with Ngāti Porou and Ngāti Kahungunu, who all intermarried amongst the local Ngāti Ira. Over time, all but Ngāti Porou would migrate away from the district. Several were already occupying the South Island prior to Ngāi Tahu's arrival, with Kāti Māmoe only having arrived about a century earlier from the Hastings District, and already having conquered Waitaha, who themselves were a collection of ancient groups. Other that Ngāi Tahu encountered while migrating through the South Island were Ngāi Tara, Rangitāne, Ng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Island
The South Island, also officially named , is the larger of the two major islands of New Zealand in surface area, the other being the smaller but more populous North Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasman Sea, and to the south and east by the Pacific Ocean. The South Island covers , making it the world's 12th-largest island. At low altitude, it has an oceanic climate. The South Island is shaped by the Southern Alps which run along it from north to south. They include New Zealand's highest peak, Aoraki / Mount Cook at . The high Kaikōura Ranges lie to the northeast. The east side of the island is home to the Canterbury Plains while the West Coast is famous for its rough coastlines such as Fiordland, a very high proportion of native bush and national parks, and the Fox and Franz Josef Glaciers. The main centres are Christchurch and Dunedin. The economy relies on agriculture and fishing, tourism, and general manufacturing and serv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori Migration Canoes
Various Māori traditions recount how their ancestors set out from their homeland in ''waka hourua'', large twin-hulled ocean-going canoes (''waka''). Some of these traditions name a mythical homeland called Hawaiki. Among these is the story of Kupe, who had eloped with Kuramarotini, the wife of Hoturapa, the owner of the great canoe '' Matahourua'', whom Kupe had murdered. To escape punishment for the murder, Kupe and Kura fled in Matahourua and discovered a land he called Aotearoa ('land of the long-white-cloud'). He explored its coast and killed the sea monster Te Wheke-a-Muturangi, finally returning to his home to spread the news of his newly discovered land. Other stories of various Māori tribes report migrations to escape famine, over-population, and warfare. These were made in legendary canoes, the best known of which are '' Aotea'', ''Te Arawa'', ''Kurahaupō'', '' Mātaatua'', ''Tainui'', ''Tākitimu'', and '' Tokomaru''. Various traditions name numerous other ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waka (canoe)
Waka () are Māori watercraft, usually canoes ranging in size from small, unornamented canoes (''waka tīwai'') used for fishing and river travel to large, decorated war canoes (''waka taua'') up to long. The earliest remains of a canoe in New Zealand were found near the Anaweka estuary in a remote part of the Tasman District and radiocarbon-dated to about 1400. The canoe was constructed in New Zealand, but was a sophisticated canoe, compatible with the style of other Polynesian voyaging canoes at that time. Since the 1970s about eight large double-hulled canoes of about 20 metres have been constructed for oceanic voyaging to other parts of the Pacific. They are made of a blend of modern and traditional materials, incorporating features from ancient Melanesia, as well as Polynesia. Waka taua (war canoes) ''Waka taua'' (in Māori, ''waka'' means "canoe" and '' taua'' means "army" or "war party") are large canoes manned by up to 80 paddlers and are up to in length. Large w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pounamu
Pounamu is a term for several types of hard and durable stone found in southern New Zealand. They are highly valued in New Zealand, and carvings made from pounamu play an important role in Māori culture. Name The Māori word , also used in New Zealand English, refers to two main types of green stone valued for carving: nephrite jade, classified by Māori as , , , and other names depending on colour; and translucent bowenite, a type of serpentine, known as . The collective term pounamu is preferred, as the other names in common use are misleading, such as New Zealand jade (not all pounamu is jade) and greenstone (a generic term used for unrelated stone from many countries). Pounamu is only found in New Zealand, whereas much of the carved "greenstone" sold in souvenir shops is jade sourced overseas. The Māori classification of pounamu is by colour and appearance; the shade of green is matched against a colour found in nature, and some hues contain flecks of red or bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori Mythology
Māori mythology and Māori traditions are two major categories into which the remote oral history of New Zealand's Māori may be divided. Māori myths concern fantastic tales relating to the origins of what was the observable world for the pre-European Māori, often involving gods and demigods. Māori tradition concerns more folkloric legends often involving historical or semi-historical forebears. Both categories merge in to explain the overall origin of the Māori and their connections to the world which they lived in. Māori had yet to invent a writing system before European contact, beginning in 1769, so they had no method to permanently record their histories, traditions, or mythologies. They relied on oral retellings memorised from generation to generation. The three forms of expression prominent in Māori and Polynesian oral literature are genealogical recital, poetry, and narrative prose. Experts in these subjects were broadly known as . The rituals, beliefs, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atua
Atua are the gods and spirits of the Polynesian peoples such as the Māori or the Hawaiians (see also ); the Polynesian word literally means "power" or "strength" and so the concept is similar to that of ''mana''. Today, it is also used for the monotheistic conception of God. Especially powerful atua included: * '' Rongo-mā-Tāne'' – god of agriculture and peace * ''Tāne Mahuta'' – creator of all living things such as animals, birds and trees * ''Tangaroa'' – god of the sea * ''Tūmatauenga'' – a god of war * ''Whiro'' – god of darkness and evil In Samoa, where means "god" in the Samoan language, traditional tattooing was based on the doctrine of tutelary spirits. There is also a district on the island of Upolu in Samoa called Atua. Atua or gods were also the center of Māori religion. In Māori's belief, there was no such word as "religion" because the natural and supernatural world were one. In other Austronesian cultures, cognates of ''atua'' include the Pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Āraiteuru
(also written ) was a canoe () of some of Ngāi Tahu's ancestors in Māori tradition. The canoe was conveyed to New Zealand by the north-east wind, carrying the chiefs Kirikirikatata, Aroarokaehe, Mauka Atua, Aoraki, Kakeroa, Te Horokoatu, Ritua, Ngamautaurua, Pokohiwitahi, Puketapu, Te Maro-tiri-a-te-rehu, Hikuroroa, Pahatea, Te Waioteao, and Hapekituaraki. The canoe's fishing net and the water gourd (calabash) were turned into stone at Moeraki in the South Island, where they can still be seen in the form of the Moeraki Boulders. The canoe itself remained at Shag Point. Dunedin's pan- marae, located in the suburb of Wakari, is named after the canoe. See also * Arahura (canoe) * Tākitimu ''Tākitimu'' was a '' waka'' (canoe) with ''whakapapa'' throughout the Pacific particularly with Samoa, the Cook Islands, and New Zealand in ancient times. In several Māori traditions, the ''Tākitimu'' was one of the great Māori migration ... * Uruaokapuarangi References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngahue
According to Māori mythology Ngahue (sometimes known as Ngake) was a contemporary of Kupe and one of the first Polynesian explorers to reach New Zealand. He was a native of the Hawaiki and voyaged to New Zealand in “ Tāwhirirangi”, his waka (canoe). No time has been fixed for these voyages, but according to legend he discovered pounamu (Greenstone) and Ngahue killed a Moa (large flightless bird - now extinct). Pounamu was sometimes called Te Ika-o-Ngāhue (Ngāhue's fish) and they took several boulders back to Hawaiki. Ngai Tahu tradition Ngati Kahungunu tradition According to a Ngāti Kahungunu tradition, Ngahue was a major chief on Hawaiki at the time when the first Māori travelled to New Zealand. In his old age, he remained in Hawaiki, but his sons and grandsons had gone to the new land. Worried that they might not have enough food, Ngahue ordered a large fish to swim to his children, so that they could eat it. The fish reached the Bay of Plenty, then swam round East ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tākitimu
''Tākitimu'' was a '' waka'' (canoe) with ''whakapapa'' throughout the Pacific particularly with Samoa, the Cook Islands, and New Zealand in ancient times. In several Māori traditions, the ''Tākitimu'' was one of the great Māori migration ships that brought Polynesian migrants to New Zealand from Hawaiki. The canoe was said to be captained by Tamatea. Cook Islands Māori traditions The ''Tākitumu'' (sic) was an important waka in the Cook Islands with one of the districts on the main island of Rarotonga consequently named after it. Sir Tom Davis, Pa Tuterangi Ariki, KFE, wrote in the form of a novel, an account of 300 years of voyaging of the ''Tākitumu'' (sic) by his own forebears as told in their traditions. New Zealand Māori traditions The ''Tākitimu'' appears in many traditions around New Zealand. Most accounts agree that the ''Tākitimu'' was a sacred canoe. Many also give the name of the captain as "Tamatea", although in different forms. (He is not to be conf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uruaokapuarangi
(also ; often known simply as ) was one of the great ocean-going, voyaging canoes () that was used in the migrations that settled the South Island according to Māori tradition. is linked to many southern , first landing near Nelson. The was captained by Rākaihautū, who was accompanied by his wife Waiariki-o-āio, their son Te Rakihouia, and a man named Matiti. Origins Originally, was said to belong to a chief from Te Patunuioāio named Taitewhenua. He decided to give the canoe to the renowned (astronomer) Matiti, who then gave it to Rākaihautū and encouraged him to use it to explore new lands. In the 9th century, Rākaihautū, accompanied by his wife Waiariki-o-āio, their son Te Rakihouia, Matiti, and other kin of the Te Kāhui Tipua, Te Kāhui Roko, and Te Kāhui Waitaha tribes, set sail across the Pacific Ocean in search of new land. Voyage and arrival On the journey to the South Island the heavens and the ocean blocked the canoe's path, until Rākaihautū ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori Waka
Māori or Maori can refer to: Relating to the Māori people * Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group * Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand * Māori culture * Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the Cook Islands * Cook Islands Māori, the language of the Cook Islanders Ships * SS ''Maori'', a steamship of the Shaw Savill Line, shipwrecked 1909 * , a Royal Navy Tribal-class destroyer, sunk in 1915 * , a Royal Navy Tribal-class destroyer, launched 1936 and sunk 1942 * TEV ''Maori III'', a Union Steam Ship Company inter-island ferry, 1952–74 Sports teams * New Zealand Māori cricket team * New Zealand Māori rugby league team * New Zealand Māori rugby union team Other * ''Maori'', a novel by Alan Dean Foster *Mayotte, in the Bushi language Bushi or Kibosy (''Shibushi'' or ''Kibushi'') is a dialect of Malagasy spoken in the Indian Ocean island of Mayotte. Malagasy dialects most closely related to Bushi are spoken in northwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)